Primary Biliary Cholangitis/primary Sclerosing Cholangitis And Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap Syndrome
Disease definition
A rare hepatic disease characterized by the overlap of primary biliary cholangitis and/or primary sclerosing cholangitis with autoimmune hepatitis, defined by the presence of at least two of the three recognized biochemical, serological, and histological criteria of each disease. The onset of the overlapping diseases can be simultaneous or sequential, with a variable interval of up to several years. Age of onset, gender predisposition, and clinical phenotype vary between each of the diseases, and the clinical presentation ranges from asymptomatic disease or unspecific symptoms such as fatigue, arthralgia, and pruritus, to established cirrhosis and decompensation, or also acute, fulminant hepatitis and liver failure. Association with extrahepatic autoimmune diseases is common.
Cell Purification And Stimulation
CD4+ or CD8+ cells were prepared by magnetic separation using a MiniMACS system . In brief, splenocytes were incubated with anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 magnetic microbeads for 15 min, washed, and collected on a magnetic flow-through column. Purified cells were stimulated as described previously . In brief, cells were suspended in complete medium consisting of RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS, 1 mM l-alanyl-glutamine , 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin , 1 mM sodium pyruvate , and 50 μM 2-ME. Cells were then transferred to 24-well plates precoated with anti-CD3 antibody, and 1 μg/ml anti-CD28 antibody was added to each well. The cells were cultured for 72 h at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. The supernatants were collected at the end of culture and stored at â80°C.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Positive
What Are The Symptoms And Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Often, the symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis are minor. When symptoms do occur, the most common are fatigue, abdominal discomfort, aching joints, itching, jaundice , enlarged liver, nausea and spider angiomas on the skin. Other symptoms may include dark urine, loss of appetite, pale stools and absence of menstruation. More severe complications can include ascites and mental confusion. In 10%-20% of cases, autoimmune hepatitis may present with symptoms like an acute hepatitis.
Read Also: Hepatitis B How Do You Get It
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost For Adults
Epidemiology And Demographic Features
The worldwide prevalence of AIH is unknown most reported cases are in patients of European Caucasian or Japanese extraction. In North American populations, the prevalence is estimated as 1 per 100000 population. In Western Europe and North America, where viral hepatitis prevalence rates are relatively low, AIH accounts for roughly 20% of chronic hepatitis in the white populations.
In patients of European descent, AIH is associated with the HLA A1-B8-DR3 haplotype and particularly with DR3. In Japan, it appears to be primarily associated with the DR4 haplotype this form of the disease occurs in elderly patients who exhibit mild necroinflammatory activity and a good response to immunosuppressive therapy.
Complementary And Alternative Medicines
Many complementary and alternative medicines are available that may ease the symptoms of liver disease. But certain medications used in non-liver related disease can damage the liver. At present, healthcare professionals are not clear on the role and place of some therapies in managing liver disease. More research needs to be done on the use of these therapies. You may wish to discuss the use of these therapies with your doctor.
Read Also: New Medicine For Hepatitis B
Read Also: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
Role Of Autoimmunity In Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
Correspondence to: Feng-Chun Zhang, MD, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Science, No. 41 Da Mu Cang, Western District, Beijing 100032, China.
Telephone: +86-10-88068795 Fax: +86-10-88068794
Recommended Reading: How Does A Person Get Hepatitis B
Autoimmune Hepatitis And Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Dependent Or Independent Association
ABSTRACT
Background and objective:Methods:Results:
REFERENCES
Beuers U. Hepatic overlap syndromes. J Hepatol 2005 42: S93-S99.
Jonson PG, McFarlene IG. Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology 1993 18: 998-1005.
Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FP, Bianchi L, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group report: review criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol 1999 31: 928-37.
Czaja AJ. Current concepts in autoimmune hepatitis. Ann Hepatol 2005 4: 6-24.
Woodward J, Neuberger J. Autoimmune overlap syndromes. Hepatology 2001 33: 994-1002.
Czaja AJ. The variant forms of autoimmune hepatitis. Ann Intern Med 1996 125: 588-98.
Poupon R. Autoimmune overlapping syndromes. Clin Liver Dis 2003 7: 865-78.
Durazzo M, Premoli A, Fagoonee S, et al. Overlap syndromes of autoimmune hepatitis. Dig Dis Sci 2003 48: 423-30.
Michieletti P, Wanless IR, Katz, et al. Antimitochondrial antibody negative primary biliary cirrhosis: a distinct syndrome of autoimmune cholangitis. Gut 1994: 35: 260-5.
Chazouilleres O, Wendum D, Serfaty L, et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis-autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome: clinical features and response to therapy. Hepatology 1998 28: 296-301.
Gregorio GV, Portmann B, Karani J, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis/sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome in childhood: a 16 year prospective study. Hepatology 2001 33: 544-53.
Also Check: How Do You Cure Hepatitis
Antibodies Found In Patients With Pbc And Additional Signs Of Aih
Features of AIH may be present in 1020% of patients who present with PBC. There are no generally accepted criteria to define these variant syndromes. In most patients, both diseases manifest simultaneously and in these patients, the Paris criteria have been established and endorsed by EASL to indicate additional AIH in a PBC patient . AIH can be diagnosed if two of three criteria are present: elevation of ALT levels > 5 times upper limit the normal , elevation of serum IgG levels > 2 times ULN or positive anti-SMA, and moderate to severe interface hepatitis on histology. In addition, the presence of anti-SLA/LP and anti-dsDNA may raise the suspicion of AIH in patients with PBC .
B Cells And Plasma Cells
Plasma cells that originate from B cells are sources of antibodies. As antigen presentation cells, B cells can secrete many kinds of cytokines and present costimulatory signals to active antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Migita et al found that serum B-cell-activating factor levels were significantly higher in PBC patients than in healthy controls and HCV-infected patients, and were positively correlated with aspartate amino-transferase and total bilirubin levels. In liver, CD5+ and CD20+ cells were associated with BEC damage, suggesting that B cells have a role in regulating the portal destruction in PBC. Therefore, B cell depletion therapy might be an alternative to UDCA. In murine experiments, IgNOD.c3c4 mice demonstrated a decreased number of activated NK cells in the liver. The degree of granuloma formation, bile duct destruction, and salivary gland histology were also shown to be significantly attenuated. Moreover, anti-CD20 therapy every 2 wk in transforming growth factor-beta receptor II dominant negative mice at age of 4-6 wk could reduce the number of B cells and CD8+ T cells in liver. In clinical therapy, two doses of 1000 mg rituximab separated by 2 wk were safe and effective in patients with an incomplete UDCA response. After treatment, not only did serum levels of total IgG, IgM, and IgA decrease significantly, but T regulatory cells also increased, which was associated with increased mRNA levels of forkhead box 3 and TGF- in CD4+ T cells.
Recommended Reading: Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
Can Primary Biliary Cholangitis Be Prevented
Because doctors do not know the cause of PBC, it cannot be prevented. However, you can take steps to lessen liver damage, including:
- Quit smoking, stop drinking alcohol and stop using illegal drugs
- Take all medicines as directed by your doctor.
- Eat a healthy, well balanced diet.
- Get regular exercise, such as walking.
Healthy food choices could include eating foods rich in vitamins A, D, E and K and/or supplements of these vitamins. Also, foods high in vitamin D and calcium could help prevent osteoporosis. Ask your doctor for specific foods high in these vitamins and minerals.
Foods to avoid include raw shellfish plus food high in salt, fat, and carbohydrates especially added sugars.
Symptoms And Signs Of Pbc
About half of patients present without symptoms. Symptoms or signs may develop during any stage of the disease and may include fatigue or reflect cholestasis , hepatocellular dysfunction, or cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic fibrosis that has resulted in widespread distortion of normal hepatic architecture. Cirrhosis is characterized by regenerative nodules surrounded by dense… read more .
Symptoms usually develop insidiously. Pruritus, fatigue, and dry mouth and eyes are the initial symptoms in > 50% of patients and can precede other symptoms by months or years. Other initial manifestations include right upper quadrant discomfort an enlarged, firm, nontender liver splenomegaly hyperpigmentation xanthelasmas and jaundice . Eventually, all the features and complications of cirrhosis occur. Peripheral neuropathy and other autoimmune disorders associated with primary biliary cholangitis may also develop.
You May Like: How To Get Hepatitis B
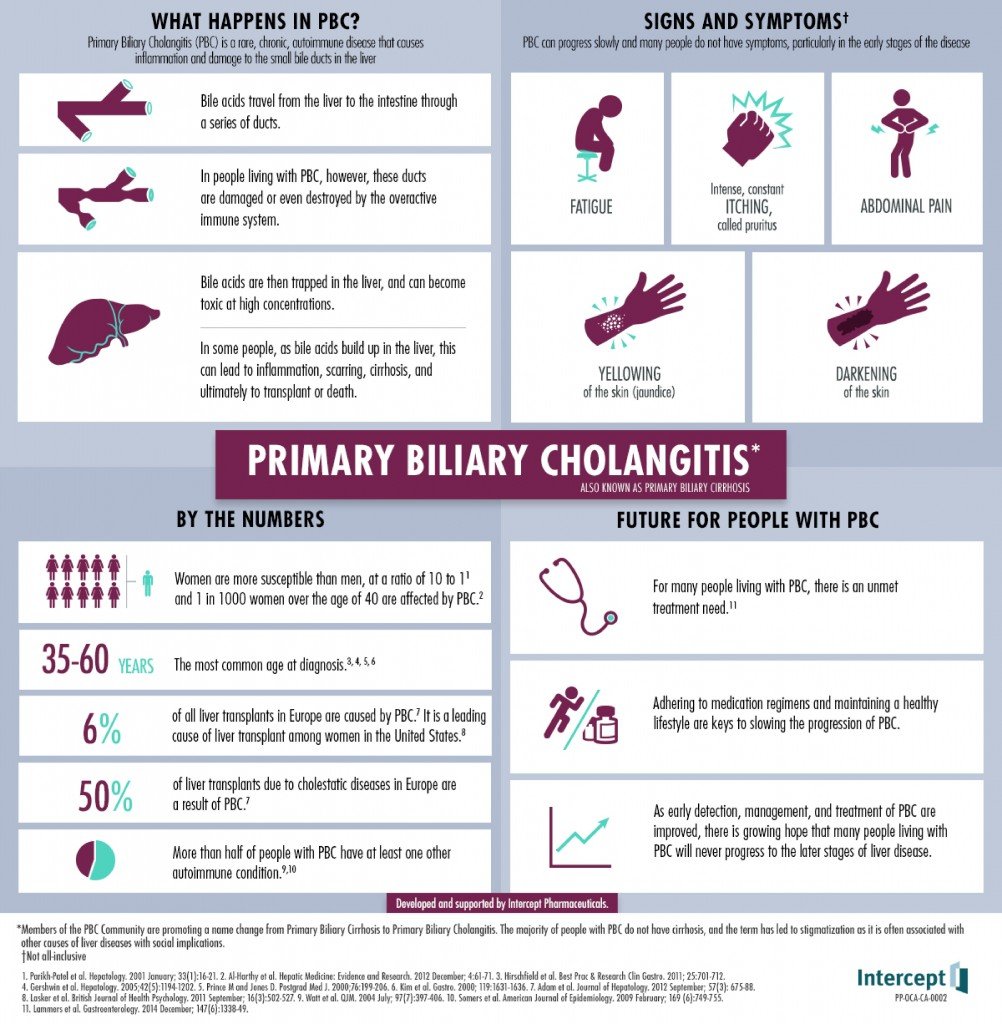
What Is Primary Biliary Cholangitis
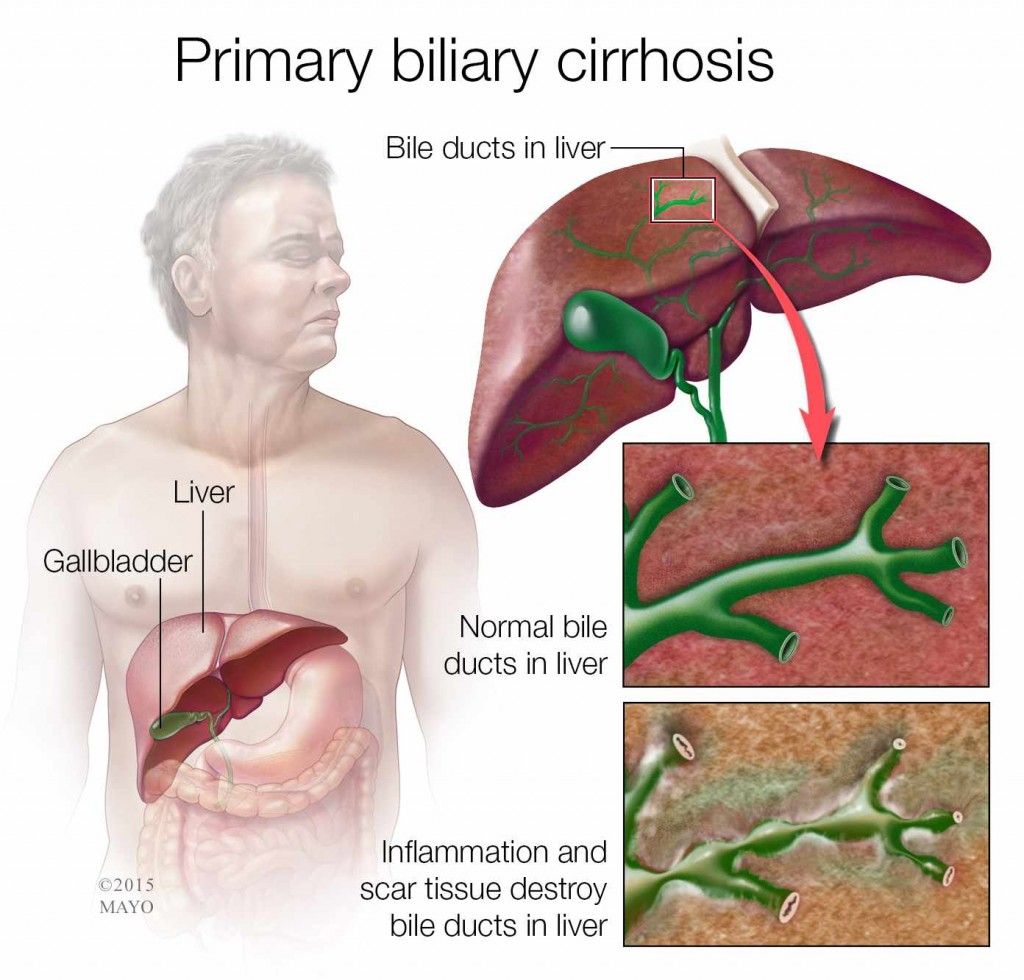
Primary biliary cholangitis is a chronic autoimmune disease of the liver that slowly destroys its small to medium-sized bile ducts. This causes bile to remain in the liver, which can damage cells and cause scarring that can lead to cirrhosis if unrecognized and untreated.
Bile is a liquid that is made in the liver and travels down the bile ducts to enter the duodenum, the portion of the small bowel next to the stomach. Bile contains acids, which are needed to digest fats and absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. These acids also act as hormones with important effects in maintaining health.
PBC advances slowly, providing doctors an opportunity for early treatment. Many patients lead active and productive lives for more than 10 to 15 years after diagnosis. In fact, patients who show no symptoms at the time of diagnosis often remain symptom-free for years. And the good news is that patients whose liver tests return to normal on treatment can expect a normal life expectancy.
If cirrhosis develops, PBC may lead to life-threatening complications. Cirrhosis occurs when scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and impairs its ability to function normally.
If the liver cannot filter waste from the intestine, confusion and altered levels of consciousness can result.
The goals of therapy are to prevent development of cirrhosis in patients with earlier stages of disease and slow progression and prevent deterioration in patients who already have cirrhosis.
Role Of Liver Biopsy In Autoimmune Liver Disease
The liver biopsy is an essential element in diagnosis and management of AIH. As individual histologic, serologic, and clinical features are not specific for the diagnosis of AIH, evaluation of the liver biopsy serves to help exclude other potential causes of liver disease and identify variant syndromes. Assessment of necroinflammatory activity is also important, particularly if withdrawal of immunosuppressive therapy is contemplated. For PBC, examination of the liver biopsy, in addition to providing confirmatory evidence for diagnosis, serves to determine stage of disease. Although it is recognized that disease severity is variable within the liver, evaluation of extent of fibrosis often provides helpful information regarding prognosis and may serve to guide therapy. In PSC, whereas the biopsy may not be diagnostic and may show only nonspecific changes, staging information may be clinically useful.
Don’t Miss: Current Treatment For Hepatitis B
Quick Answers For Clinicians
Antimitochondrial M2 antibodies are present in the serum of > 90% of patients with primary biliary cholangitis , and antinuclear antibodies are often present. Serum antibodies are detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays or other immunoassays. The diagnostic performance characteristics of these assays and results may not be commutable. Positive results for ANAs using solid-phase immunoassays are generally meaningless, as PBC-relevant ANA patterns can only be observed via immunofluorescence antibody assays. Immunoassays for detecting specific ANAs are important for confirmation.
Although liver biopsy is no longer recommended for the majority of patients with primary biliary cholangitis , specificity issues may arise with antimitochondrial M2 antibodies and antinuclear antibodies . Thus, histology may be needed if liver biochemistry tests, autoantibody tests, and imaging fail to establish a diagnosis of PBC or are equivocal. Histology is also useful to establish diagnosis in overlap syndromes, such as PBC/autoimmune hepatitis .
Although earlier detection and intervention have reduced the need for liver transplantation in patients with primary biliary cholangitis , the British Society of Gastroenterology recommends consideration of liver transplantation in all patients with bilirubin > 50 µmol/L or with pruritus that is refractory to all medical therapy.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- How severe is the liver damage?
- What treatment do you recommend? Will this slow down the progression of the disease?
- Will any medication be prescribed? What are the side effects?
- Should I change my diet?
- Are there any supplements you would suggest that I take?
- What can be done to relieve my symptoms?
- If cirrhosis develops, is transplantation my only option?
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Rite Aid
Overlap And Outlier Syndromes
A sizeable percentage of cases of autoimmune liver disease that generally fit into one diagnostic category will show clinical, serologic, or histologic features more characteristic of another type of autoimmune liver disease. When overlap in all three areas is present, the diagnosis of an overlap syndrome should be considered. However, it should be noted that it is controversial whether these overlap syndromes are distinct entities or variants of the major autoimmune hepatopathies, and standardization of diagnostic criteria and terminology is lacking.
The term overlap syndrome is used primarily to describe variant forms of autoimmune liver disease that present with both cholestatic and hepatitic features that do not fit readily into the usual diagnostic categories,, and which generally have overlapping characteristics of AIH+PBC or AIH+PSC .
Table 6 Variants of autoimmune liver disease
Evidence for a PSC-PBC overlap syndrome is limited and based upon case reports.
Journal Of Medical Cases
|
QUICK LINKS |
| Article copyright, the authors Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Volume 12, Number 4, April 2021, pages 131-133
Primary Biliary Cholangitis Overlap With Autoimmune Hepatitis? A Case Report
Vitor Costaa, c, Marta Moreirab, Raquel Costaa, Joana Fontesa
aDepartment of Medicine, Unidade Local de Saude do Alto Minho, Largo Conde de Bertiandos, Ponte de Lima 4990-041, PortugalbDepartment of Gastroenterology, Unidade Local de Saude do Alto Minho, Largo Conde de Bertiandos, Ponte de Lima 4990-041, PortugalcCorresponding Author: Vitor Costa, Department of Medicine, Unidade Local de Saude do, Alto Minho, Largo Conde de Bertiandos, Ponte de Lima 4990-041, Portugal
Manuscript submitted November 22, 2020, accepted December 1, 2020, published online February 8, 2021Short title: Cholangitis Overlap With Autoimmune Hepatitisdoi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc3623
| Top |
Keywords: Primary biliary cholangitis Ursodeoxycholic acid Anti-mitochondrial antibodies Cirrhosis Autoimmune hepatitis Overlap syndrome
| Introduction | Top |
The major autoimmune disorders of the liver are the autoimmune hepatitis , primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis .
| Case Report | Top |
On physical examination, he was anicteric, without adenopathies, hepatomegaly/splenomegaly, without stigmas of chronic liver disease.
| Discussion | Top |
Don’t Miss: Getting Paid For Hepatitis B Plasma
Antibodies To Biliary Epithelial Cells
Few studies found antibodies of different subtypes in sera of patients with PSC directed against BEC . Levels of IgA antibodies directed against BEC were correlated with adverse patient outcomes . Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that antibodies against BEC and bacterial lipopolysaccharides co-activate cytokine release by BEC and therefore induce biliary immune responses . This provides further evidence for the involvement of microbiota in the pathogenesis of PSC. Testing for anti-BEC antibodies has not been introduced into clinical practice.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Test
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Primary Biliary Cholangitis
PBC may progress slowly and many people do not have symptoms, particularly in the early stages of the disease. The most common initial symptoms are fatigue and itching of the skin . Other symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the legs and feet
- Enlarged abdomen from fluid accumulation
- Internal bleeding in the upper stomach and esophagus from enlarged veins
Thinning of the bones leading to fractures is another complication of PBC. While this is more common in late stages of the disease, it can occur earlier as well. In addition, people with cirrhosis are at increased risk for liver cancer .
Dont Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis C Antibodies
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
What Lifestyle Changes May Be Helpful
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help people with PBC feel better, as well as relieve or prevent some symptoms associated with the disease. Upon diagnosis, your doctor may suggest the following:
- Start a reduced sodium diet if you have fluid overload
- Reduce fat intake if you are overweight or have fatty liver
- Drink plenty of water
- Avoid or lower intake of alcohol
- Avoid undue stress when possible
- Start exercising, particularly walking
- Maintain good skin care
- Get regular dental examinations
Keep in mind that PBC usually advances slowly over a period of years. Many people lead normal lives for years without symptoms, depending on how early the diagnosis is made. And while there is no cure, people are having good results slowing disease progression and living longer without complications by adhering to their medication regimen and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Autoantibodies In Autoimmune Liver Diseaseclinical And Diagnostic Relevance
- 11st Department of Medicine, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
- 2Martin Zeitz Centre for Rare Diseases, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Testing for liver-related autoantibodies should be included in the workup of patients with hepatitis or cholestasis of unknown origin. Although most of these autoantibodies are not disease specific, their determination is a prerequisite to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cholangitis , and they are components of the diagnostic scoring system in these diseases. In primary sclerosing cholangitis , on the other hand, autoantibodies are frequently present but play a minor role in establishing the diagnosis. In PSC, however, data on antibodies suggest a link between disease pathogenesis and the intestinal microbiota. This review will focus on practical aspects of antibody testing in the three major autoimmune liver diseases AIH, PBC, and PSC.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Schedule For Adults