What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Return To School Or Child Care
- Your child may return to normal daily activity when the childs doctor or the doctor who discharges him or her from the hospital says it is OK. This will be when your child is no longer jaundiced or vomiting.
- A child who scratches, bites or gets into fights, has an overall skin condition, or a bleeding problem should probably not attend child care while he or she has hepatitis. Your childs doctor can help you make this decision.
If you have any questions, be sure to ask your childs doctor or nurse.
HH-I-43 10/76, Revised 10/15 Copyright 1976, Nationwide Childrens Hospital
Also Check: Hiv Hepatitis B And C Test
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Read Also: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis A
Immunization Of Newborns And Follow
4 ml of blood from the femoral vein was taken immediately after birth for detection of serum HBV markers and HBV DNA. Newborns who were HBV positive were immunized with 20 µg of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine prepared by yeast gene engineering technology , and 200 IU HBIG . Newborns were immunized again at the age of 1 month and 6 months with 20 µg HBVac, while HBIG treatment was repeated once at the same dose 15 days later. HBVM and HBV DNA were measured once again at age of 1 month and 7 months.
Hbsag Detection By Histochemical Methods
The ovarian and placental tissue samples were processed by routine histological procedures and paraffin sections were prepared by the standard series of operations of fixation, dehydration and paraffin embedding. The slides were then stained with hematoxylin-eosin and observed using light microscopy to evaluate the histology.
Read Also: What Is Severe Hepatic Steatosis
Clinical Presentation And Natural History
Hepatitis D is transmitted parenterally, sharing the same routes of transmission as HBV, HCV, and HIV, especially injection drug use. Only a small inoculum appears to be sufficient for infection, but perinatal transmission appears to be uncommon.45 Intrafamilial spread, as well as sexual transmission, is thought to be an underappreciated mode of transmission, especially in endemic regions. As HDV can be transmitted only in the presence of HBV, the percentage of individuals in a population who are infected with HBV, and the physical proximity of this HBV-infected network, are thought to have a direct influence on the risk and rapidity of HDV transmission.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Hepatitis D only occurs in patients with hepatitis B. Thus, healthcare workers, including the nurse practitioner should consider serological testing for HDV in patients with hepatitis B. This can be obtained by detection of total anti-HDV antibody followed by confirmatory staining for HDAg in liver tissues and/or measurement of serum HDV RNA. As HBV replication is suppressed in chronic HDV infection, hepatitis B e-antibodies are typically present.
As HDV depends on HBV, prevention can be achieved with hepatitis B vaccination. If the host is immune to HBV, they are subsequently protected against HDV. Patients who are at risk of contracting HDV infection should be encouraged to receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
At the moment there is no specific treatment for hepatitis D but unlike hepatitis B, the former is a benign infection.
Don’t Miss: I Think I Have Hepatitis
Open Questions And Future Directions
-
Can hepatitis D virus establish transcriptionally silenced but reactivatable episomes in hepatocytes as an additional mechanism of persistence?
-
To what extent do the eight HDV genotypes differ in replication efficacy and sensitivity against the upcoming novel treatments?
-
Do HDV-targeted therapies lead to a restoration of HDV-specific immunity?
-
Are these restored immune responses required for treatment response? Are they required for prevention of viral relapse? Of note, there may be differences in treatment regimens that are associated with alanine aminotransferase flares combination therapy) compared with treatment regimens without ALT flares .
-
How can a synergistic potential of antiviral drugs and immune-modulators be translated into curative regimens?
-
Are there baseline or on-treatment predictors to sustained HDV virological response for the different treatment strategies?
-
Is a sustained HDV virological response without hepatitis B surface antigen loss a realistic and achievable aim for treatment regimens without IFNs?
-
Are drugs aiming at HBsAg loss effective and safe in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus/HDV coinfection?
-
Last but not least, since HDV is prevalent in low-income countries and migrant populations, it will be important to establish new concepts to foster diagnosis and access to care.
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the bodys reaction to the viral infection or the bodys reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Read Also: Combined Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
Also Check: Early Signs Of Hepatitis C Itchy
Prognosis Of Hepatitis D
Your health outlook depends on whether you were coinfected or superinfected with hepatitis D the prognosis is better for people who were coinfected.
The vast majority of coinfected people experience only the acute phase of the disease most of these people will get better over two to three weeks. Liver enzyme levels typically return to normal within four months.
About 10 percent of people infected with hepatitis D develop a chronic liver infection.
Chronic hepatitis D leads to cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, in about 70 to 80 percent of cases. Once a person has cirrhosis, the disease may remain stable for as long as 10 years, although a high percentage of people with chronic hepatitis D and cirrhosis eventually die of acute liver failure or liver cancer unless they get a liver transplant.
The overall mortality rate of hepatitis D is unclear, with estimates placing it between 2 and 20 percent. As with most forms of hepatitis, prevention is the best strategy.
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
Also Check: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
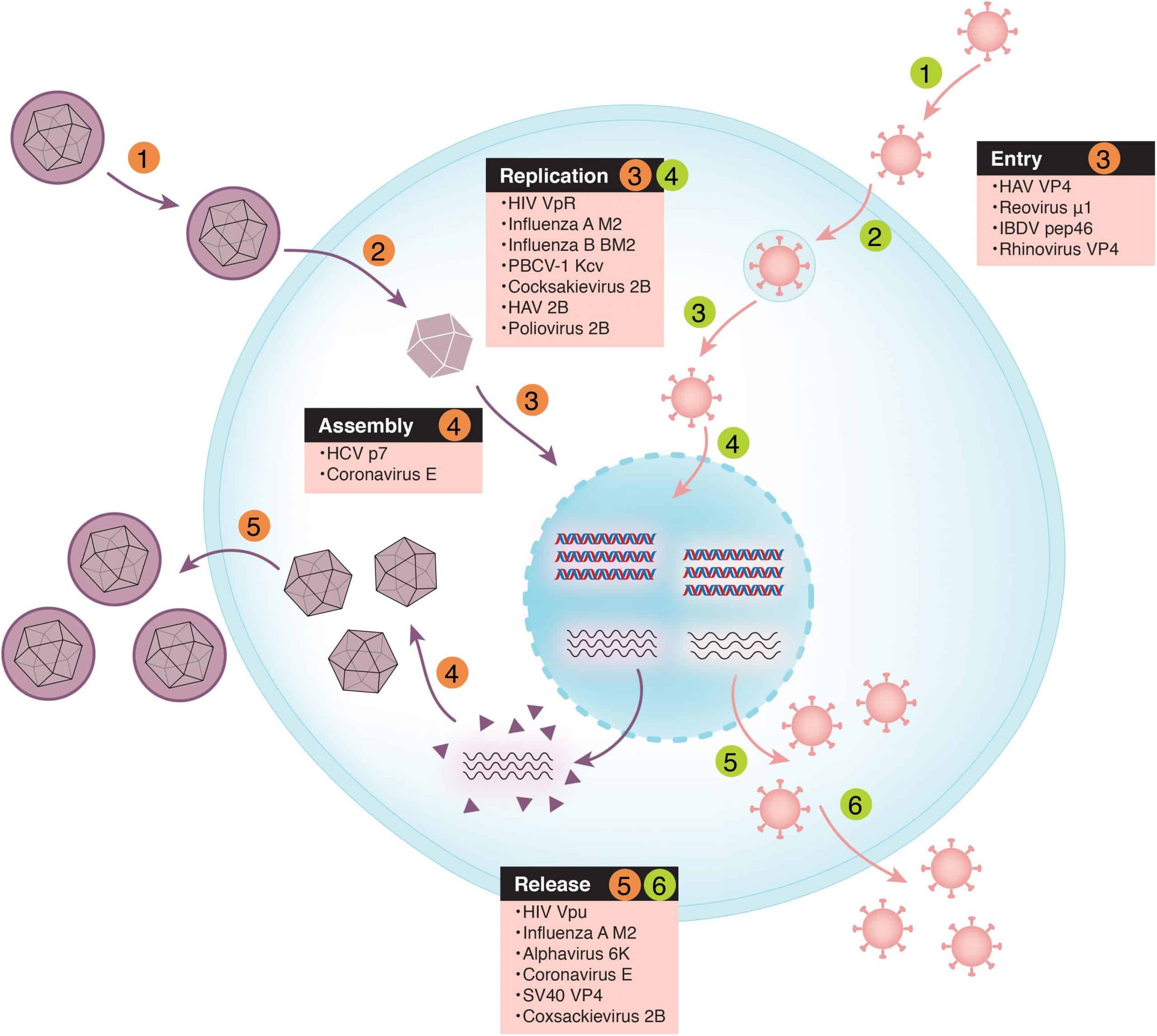
Viral Structure And Life Cycle
Hepatitis D virus viral life cycle and sites of drug target. 1. Hepatitis D virus virion attaches to the hepatocyte via interaction between hepatitis B surface antigen proteins and the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide , a multiple transmembrane transporter. 2. HDV ribonucleoprotein is translocated to nucleus mediated by the hepatitis D antigen . 3. HDV genome replication occurs via a rolling-circle mechanism. 4. HDV antigenome is transported out of the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum . 5. HDV antigenome is translated in the ER into small HDAg and large HDAg . 6. L-HDAg undergoes prenylation prior to assembly. 7. S-HDAg is transported back to the nucleus where it supports HDV replication. 8. New HDAg molecules are associated with new transcripts of genomic RNA to form new RNPs that are exported to the cytoplasm. 9. New HDV RNP associates with hepatitis B virus envelop proteins and assembled into HDV virions. 10. Completed HDV virions are released from the hepatocyte via the trans-Golgi network.
Finally, once the RNP interacts with the envelop protein of HBV and the HDV is assembled, the HDV virion is now ready for release. The HDV virion is released via the trans-Golgi network, where it can go on to infect other hepatocytes. However, the exact mechanism of HDV-virion release remains unknown .
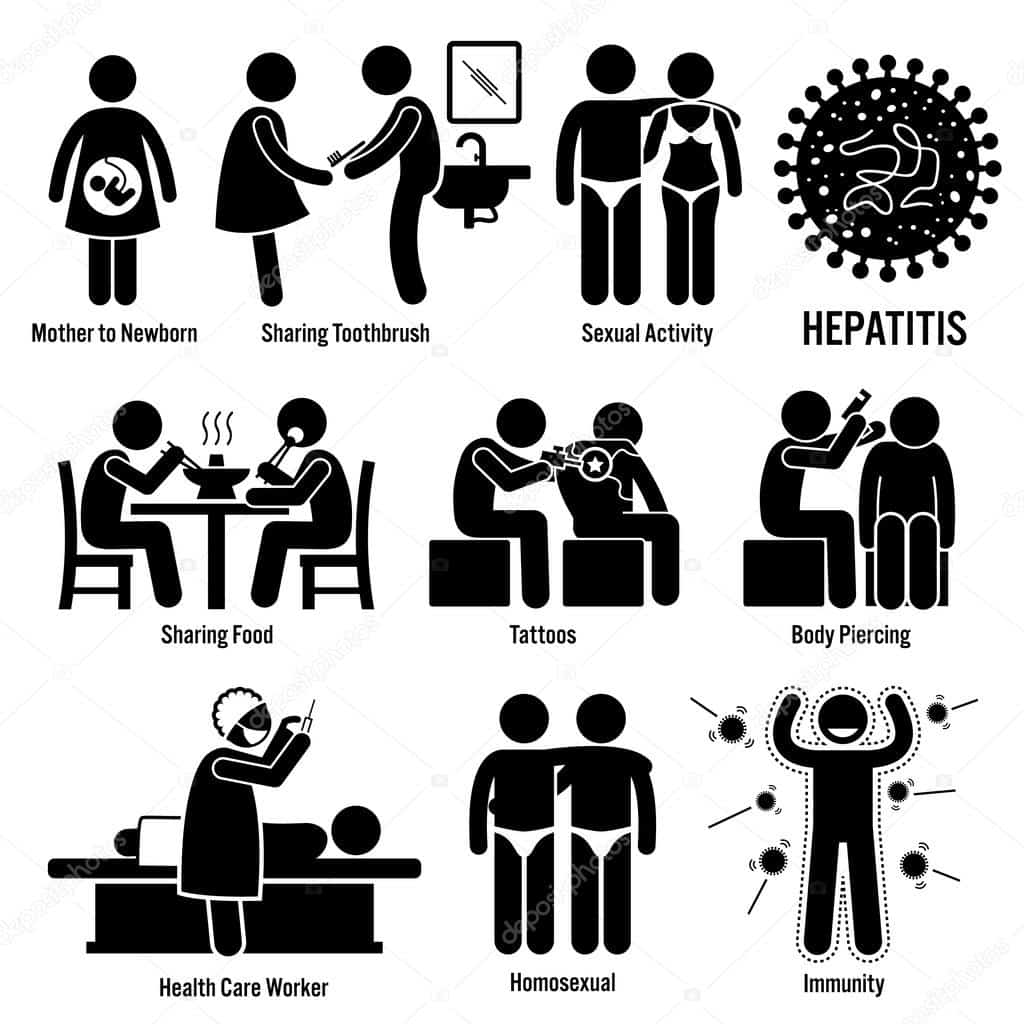
What Are The Modes Of Transmission Of Viral Hepatitis
Asked by: Nuno Costa de Torres | Last update: 23. März 2022
Score: 4.8/5
What are the forms of transmission??
- Contact with contaminated blood, by sharing needles, syringes and other objects for drug use
- Reuse or failure to sterilize medical or dental equipment
- Sterilization failure of manicure equipment
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
People who have acute hepatitis D usually have symptoms, which can include the following:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Jaundice, which causes a yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes and skin
- Discolored stools and urine
- Pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
In contrast, the majority of people with chronic hepatitis D will have few symptoms until complications develop. This could be several years after the initial infection. These symptoms can include the following:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Swelling of the ankles and abdomen
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Schedule
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D was first identified as a distinct form of hepatitis in 1977. A systematic review and meta-analysis published on April 23, 2020, in the Journal of Hepatology estimated its worldwide prevalence at 12 million people. 30220-8/fulltextâ rel=ânofollowâ> 14)
Hepatitis D is rare in the United States, and most cases occur among people who migrate or travel to the United States from countries that have a higher rate of HDV.
Hepatitis D is not a nationally notifiable condition, so the actual number of people who have it is unknown.
Study results published in Clinical Infectious Diseases found that approximately 0.11 percent of the more than 21,000 subjects had antibodies, which would indicate they had hepatitis D infection. That would correspond to approximately 357,000 people in the United States with a past or ongoing HDV infection.
The researchers found that the prevalence of hepatitis D is highest in Asian Americans and people born outside the United States.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis Be Cured Permanently
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Read Also: How Contagious Is Hepatitis C
Public Health Significance And Occurrence Of Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D occurs worldwide. It is most prevalent in countries and communities that have a high risk of hepatitis B, including Africa, South America, Romania and parts of Russia among haemophiliacs, people who inject drugs and others who come in frequent contact with blood in institutions for the developmentally disabled and, to a lesser extent, among men who have sex with men.
Outbreaks have been reported in tropical South America , in the Central African Republic, and among people who inject drugs in the United States.
In recent years, as the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers has decreased, there has been a decline in both acute and chronic HDV in the Mediterranean area and in many other parts of the world. Better sanitation and social standards may have also contributed to the decline.
New areas of high HDV prevalence continue to appear and include Albania, areas of China, northern India and Japan .
Despite high rates of hepatitis B in Asian countries, the incidence of hepatitis D is lower. Hepatitis D is uncommon in Australia. An average of 13 cases has been reported per year in Victoria since 2010.
Epidemiology And Risk Factors
The seroprevalence of HDV among HBsAg-positive carriers has substantial variations worldwide. These are depicted in . Interestingly, more recent data have shown that 8% of the general Mongolian population is estimated to be positive for HDV . Notably, in the USA, the prevalence of HDV among HBV carriers has been reported to range from 2% to 50%, depending on the patient population . A large study of the US Veterans Affairs medical system more recently reported an HDV seroprevalence of 3.4% among patients with chronic HBV who are tested for HDV . A study using the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey reported a HDV seroprevalence of 42% among HBV carriers . Finally, the highest estimation of HDV seroprevalence came from a study of HBV-positive intravenous drug users , which showed that the seroprevalence of HDV increased from 29% in 19881989 to 50% in 20052006 . However, a general lack of HDV RNA validation in these studies prevents estimation of true HDV prevalence.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Non Reactive Mean
Mother To Child Transmission
The transmission of infections from mother to offspring is traditionally known as perinatal infection. By definition, perinatal period begins from 28 weeks of gestation and ends at 28 days after delivery. Therefore, the term perinatal transmission does not actually include infections that occur before or after this time period and thus can be replaced by the term mother to child transmission which takes account of all HBV infections contracted before birth, during birth and in early childhood the importance of which as a group is their remarkably greater risk of chronicity compared to infections acquired later in life.12
Theoretically, there are three possible routes for transmission of HBV from an infected mother to her infant:13
For a newborn infant whose mother is positive for both HBsAg and HBeAg, in the absence of post-exposure immunoprophylaxis, the risk for chronic HBV infection is 70%90% by age 6 months.9 HBV vaccination can prevent 70%-95% of HBV infections in infants born to HBeAg and HBsAg-positive mothers.14 In most post-exposure prophylaxis studies, HBV vaccine has been administered to infants within 12-24 hours of their birth. The efficacy of vaccine in preventing MTCT declines by time after birth.15 Therefore it has been postulated and widely accepted that most MTCT occur at or near the time of birth .
How Can Hepatitis D Be Prevented
The only known way to prevent hepatitis D is to avoid infection with hepatitis B. You can take the following preventive measures to reduce your risk for hepatitis B:
- Get vaccinated. Theres a vaccine for hepatitis B that all children should receive. Adults who are at high risk for infection, such as those who use intravenous drugs, should also be vaccinated. The vaccination is usually given in a series of three injections over a period of six months.
- Use protection. Always practice safe sex by using a condom with all of your sexual partners. You should never engage in unprotected sex unless youre certain your partner isnt infected with hepatitis or any other sexually transmitted infection.
- Avoid or stop using recreational drugs that can be injected, such as heroin or cocaine. If youre unable to stop using drugs, make sure to use a sterile needle each time you inject them. Never share needles with other people.
- Be cautious about tattoos and piercings. Go to a trustworthy shop whenever you get a piercing or tattoo. Ask how the equipment is cleaned and make sure the employees use sterile needles.
Last medically reviewed on May 17, 2018
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Be Cured Permanently