Prognosis For Hepatitis A
Most people get better within 2 months. There are usually no long-term effects. After you recover, youâll be immune for the rest of your life.
Itâs rare, but for some people, the disease comes and goes for about 6 months before it goes away completely.
You are very unlikely to develop liver failure, though the chances are higher if you already had a liver condition or youâre elderly. If you have liver failure, youâll need a transplant.
Show Sources
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Some people who are infected with the hepatitis B virus have mild, flu-like symptoms and some do not become sick at all. Children who are infected are less likely to have an illness or get sick after getting hepatitis B than adults.
In more severe cases, hepatitis B can cause:
- Loss of appetite.
- Pain in the joints.
Normally, these health problems disappear in a few weeks, but even when the person feels much better, they may still be infectious.
Most adults who become infected with the hepatitis B virus recover completely and do not become infected again. A few people become very ill in the time just after infection and need to go to hospital some may even die.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Turn Into Hiv
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2018, 3,322 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 21,600 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 257 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
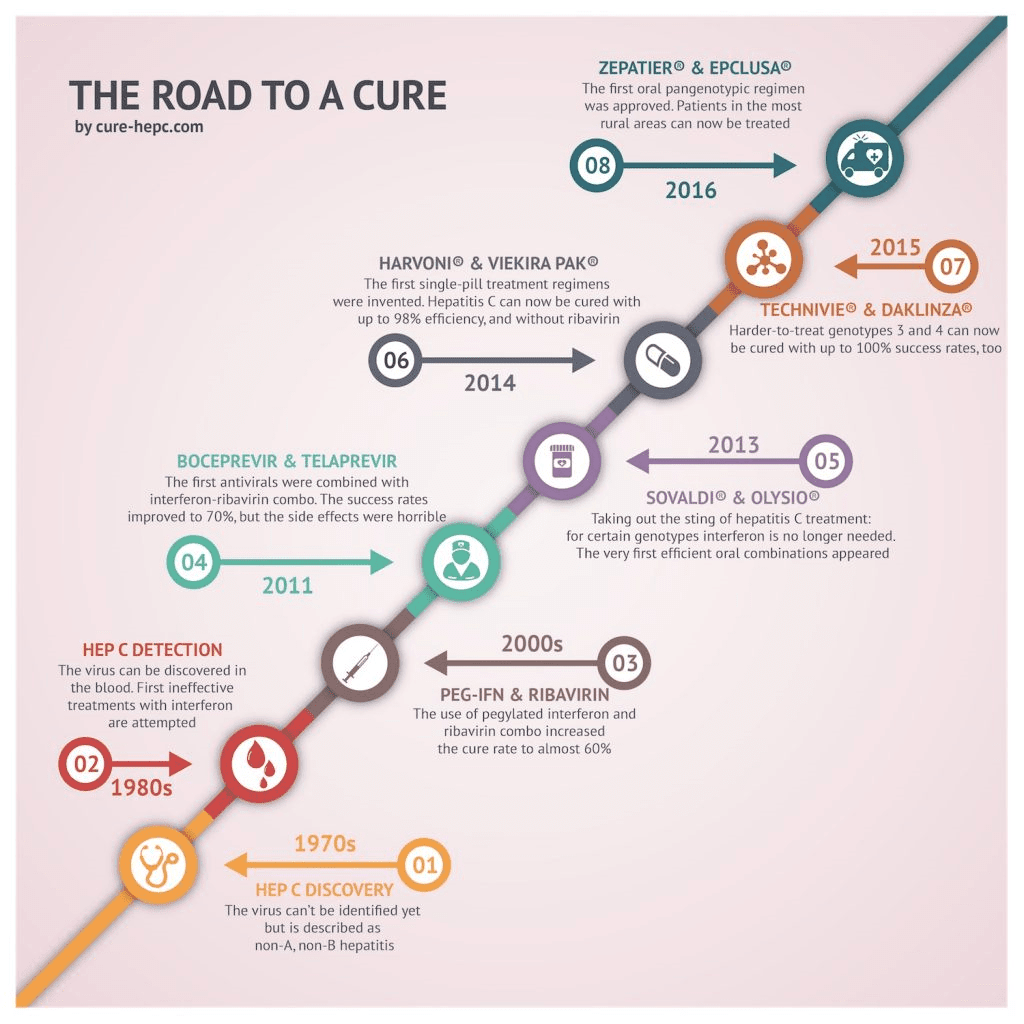
The course of chronic HBV infection is characterized by fluctuations in HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase levels, reflecting variations in the balance between HBV replication and host immune response. Traditionally, three clinical parameters are used to define the four phases of chronic HBV infection .
Phases of chronic HBV infection.3 Traditionally, phases of chronic HBV infection are defined by HBeAg status, serum HBV DNA, and ALT levels. Quantitative HBsAg levels are different in each phase and are generally highest in the immune tolerant phase and lowest in the inactive carrier phase. Although most patients progress from one phase to the next, not all patients go through each phase reversion to an earlier phase can occur. Immune tolerant: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA but normal ALT levels. Immune clearance/HBeAgpositive chronic hepatitis: HBeAgpositive, high serum HBV DNA, and elevated ALT levels HBeAg seroconversion to antiHBe occurs after varying durations. Inactive carrier: HBeAgnegative, serum HBV DNA low or undetectable. Reactivation/HBeAgnegative chronic hepatitis: HBeAgnegative, elevated levels of HBV DNA and ALT in serum, HBV precore and/or basal core promoter variant often present. Abbreviation: HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen.
You May Like: Where Do I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Read Also: How Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Work
Vaccines And Immune Globulin
Vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B are available in the United States. A vaccine for hepatitis E is currently available only in China. No vaccines against hepatitis C or D virus are available. However, vaccination against hepatitis B virus also reduces the risk of infection with hepatitis D virus. Hepatitis vaccines are given by injection into muscle.
) and for adults at high risk of getting hepatitis .
As with most vaccines, protection requires allowing a number of weeks for the vaccine to reach its full effect as the immune system gradually creates antibodies against the particular virus.
If people who have not been vaccinated are exposed to hepatitis A virus, they are given a single dose of hepatitis A vaccine or an injection of standard immune globulin, depending on their age and health. Standard immune globulin contains antibodies obtained from blood collected from a large group of people who have a normal immune system. Immune globulin prevents infection or decreases its severity. However, the amount of protection it provides varies, and the protection is only temporary.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B are given hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine.
Treatment Of Children With Acute Hbv Infection
Children with acute HBV infection are usually asymptomatic. Those with fulminant hepatitis, severe acute hepatitis and protracted acute hepatitis might benefit from NA treatment. Lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir and tenofovir are considered acceptable options. IFN is contraindicated . Although an optimal duration of NA treatment has not been established, it is recommended that NA treatment be continued until HBsAg clearance, or at least 3 months after HBsAg seroconversion, or 1 year after HBeAg seroconversion without HBsAg loss .
Read Also: How Effective Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Causes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can happen through exposure to infected blood and other bodily fluids in the following situations:
- sharing needles and other injecting drug equipment
- sharing razors, toothbrushes or nail clippers
- tattooing with unsterilised needles and equipment
- close family contact with someone who has hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- accidental exposure such as a needle stick injury or being splashed with infected blood or body fluid
- blood transfusion this is now very rare as blood in Australia is screened for hepatitis B
You cannot catch hepatitis B through being coughed or sneezed on by infected people or by consuming contaminated food and drink. You cannot catch the virus from saliva, breast milk or tears.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
You May Like: Disease Caused By Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis Treated
Someone who has hepatitis will need to drink lots of fluids, eat healthy foods, and get rest. The person’s family members may need to get hepatitis vaccines, if they haven’t already.
Later on, the person will get follow-up blood tests. Often the blood tests will show that the person no longer has hepatitis. Sometimes, the blood tests may show that someone is now a carrier of hepatitis they won’t have hepatitis symptoms, but could pass the infection to other people.
Sometimes, blood tests will continue to show that some people still have hep B or C, which means they may have chronic hepatitis. If so, they will need to eat healthy foods and take very good care of themselves by getting rest and visiting the doctor regularly. In some cases, someone with chronic hepatitis may get special medicine for the condition.
Relation Between Hepatitis C And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma accounts for 85 to 90% of the cases of primary liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis constitute the major preneoplastic conditions in the majority of HCC. The risk of developing HCC for a patient with HCV-related cirrhosis is approximately 2-6% per year. HCC risk increases to 17-fold in HCV-infected patients compared to HCV-negative subjects. In general, HCC develops only after two or more decades of HCV infection and the increased risk is restricted largely to patients with cirrhosis or advanced fibrosis.
Multiple steps are required in the induction of all cancers it would be mandatory for hepatocarcinogenesis that genetic mutations accumulate in the hepatocytes. In HCV infection, however, some of these steps might be skipped in the development of HCC, in presence of the core protein. The overall effects achieved by the expression of the core protein would be the induction of HCC, even in the absence of a complete set of genetic aberrations, required for carcinogenesis. By considering such a non-Vogelstein type process for the induction of HCC, a plausible explanation might be given for many unusual events happening in HCV carriers.
Recommended Reading: Why Do You Need Hepatitis B Vaccine
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
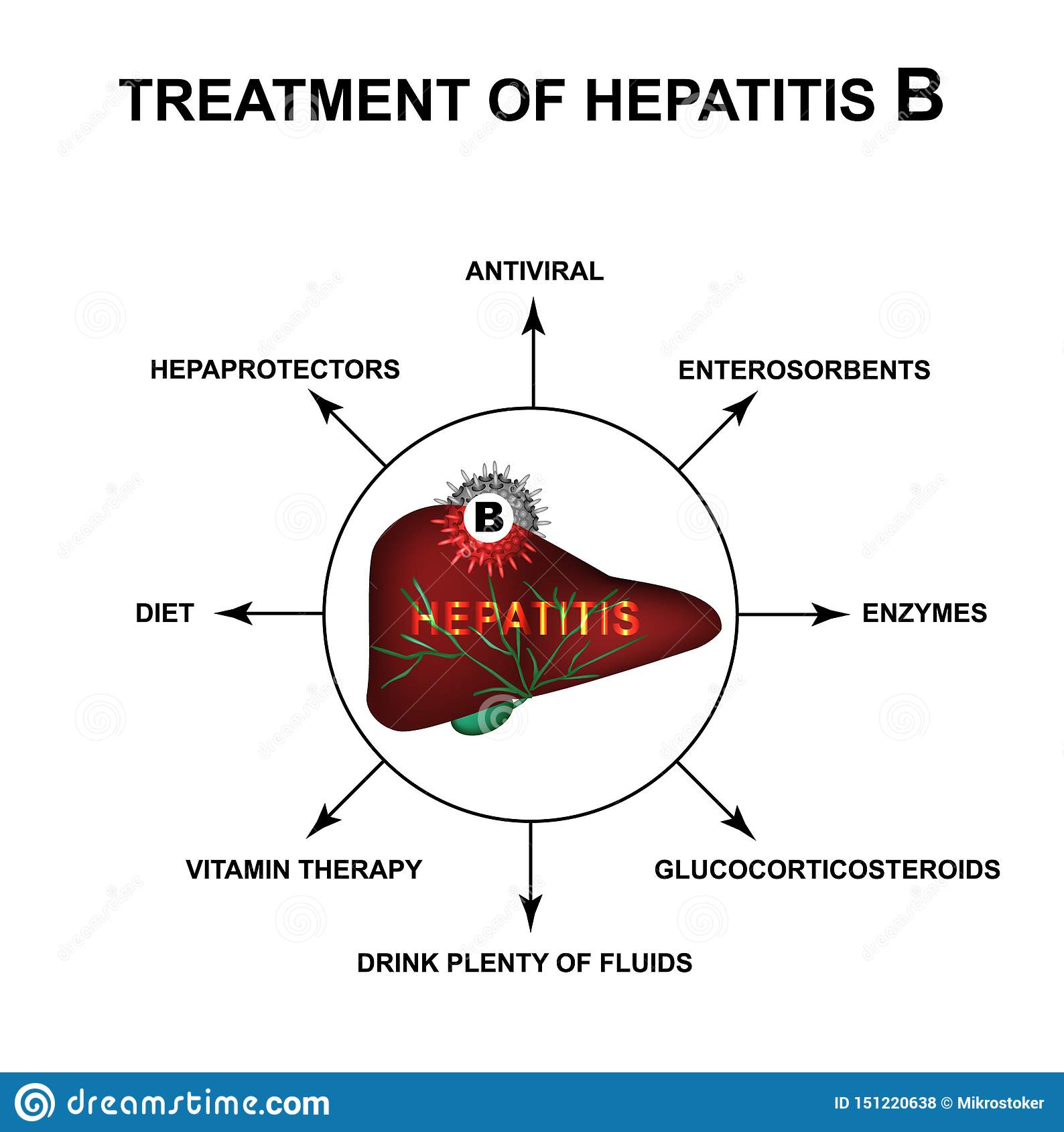
People living with chronic hepatitis B infection should expect to live a long and healthy life. There are decisions people can make to protect their livers such as seeing a liver specialist or health care provider regularly, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and eating healthy foods. There are also approved drugs for both adults and children that control the hepatitis B virus, which helps reduce the risk of developing more serious liver disease, but there is still no complete cure.
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories:
- Immune modulator Drugs These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot over 6 months to 1 year.
- Antiviral Drugs These are drugs that stop or slow down the hepatitis B virus from reproducing, which reduces the inflammation and damage of your liver. These are taken as a pill once a day for at least 1 year and usually longer.
It is important to know that not everyone with chronic hepatitis B infection needs to be treated. This can be difficult to accept when first diagnosed because taking a drug to get rid of the virus seems like the first step to getting better. Current treatments, however, are generally found to be most effective in those who show signs of active liver disease .
Hepatitis B Drug Watch
Visit the HBF Drug Watch for a complete list of the approved treatments for hepatitis B and promising new drugs in development.
Read Also: How Soon Can You Detect Hepatitis C
How Is Chronic Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are several blood tests available that can identify whether you are currently infected or have developed immunity to hepatitis B. Your sexual partners and people living in your household should also get tested. If you are diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B infection, you will require life-long blood and liver tests at least every 6 months to assess the condition of your liver. Learning that you have chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting. Because most people do not have symptoms and can be diagnosed decades after their initial exposure to the hepatitis B virus, it can be a shock and a surprise to be diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B. The good news is that most people with this condition can expect to live a long and healthy life because there are medicines that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging your liver. If you have been diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, contact The Hepatitis Foundation of New Zealand freephone 0800 332 010. They provide a free hepatitis B follow-up programme with information, support and regular blood tests.
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Also Check: Is A Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
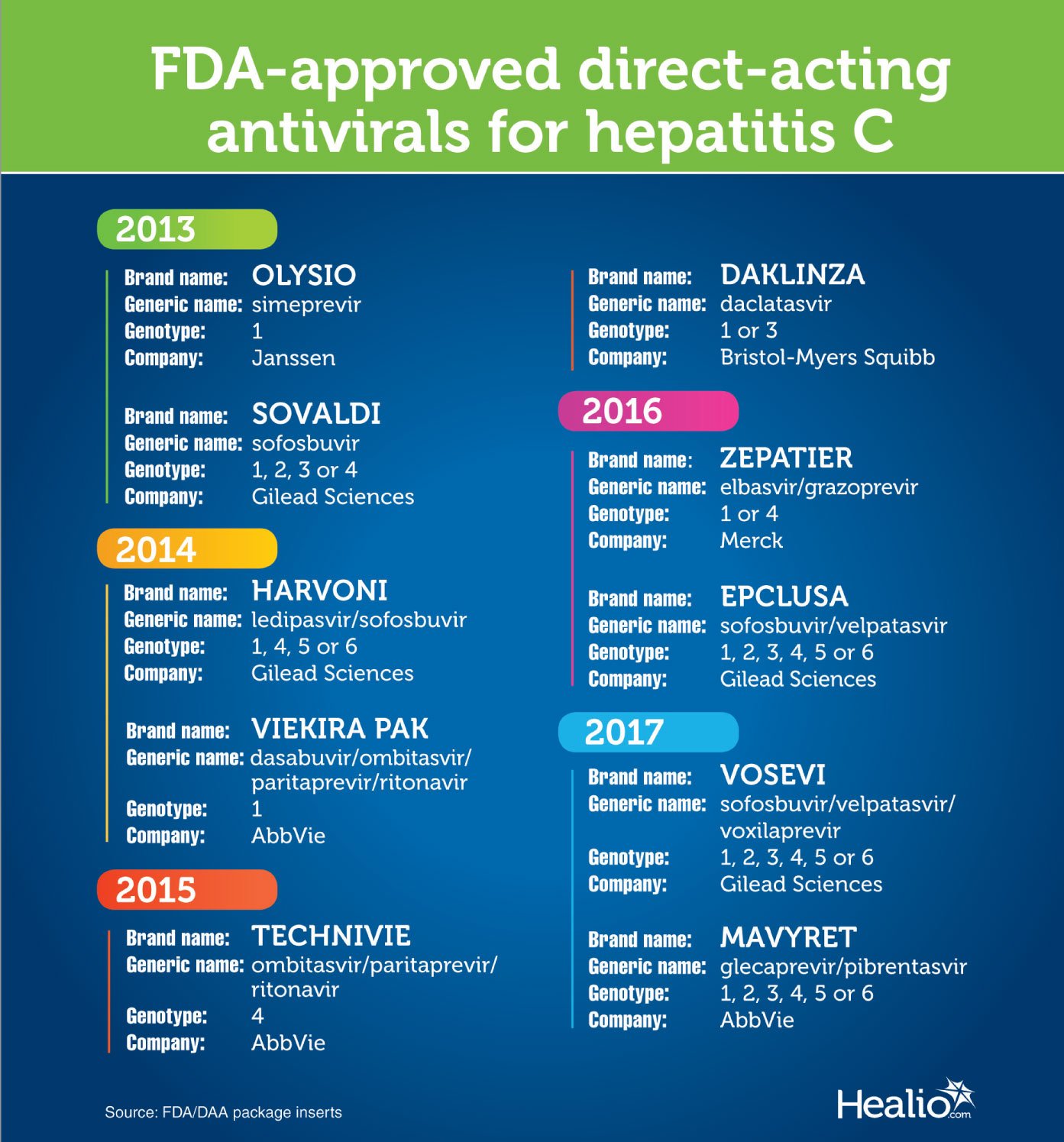
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
Unlocking The Immune System To Control Hepatitis B
One sequence of the viral RNA code can contribute to several different hepatitis B virus proteins and also to viral replication. By targeting that sequence for clean out there is a potential broad impact on viral protein production, with the goal of eliminating the proteins effects on the immune system. This could set the stage for the immune system to take over and keep the virus suppressed for the long term without the need for ongoing medication.
Whilst the ultimate aspiration is to find a cure for hepatitis B, this approach could lead to what is called a functional cure, where the virus is undetectable in blood and at a low enough level in the liver that it can be controlled by the immune system without medication, meaning liver damage is less likely to progress and the burden of the disease on people will be reduced. Scientists hope this new approach will control the hepatitis B virus and lead to longer-lasting solutions for the 296 million people currently living with this disease.
Hepatitis B has been causing death and disability on a global scale for many years. We are committed to following the science to explore new approaches to address unmet needs and provide longer-lasting solutions for patients with this potentially life-threatening liver infection.
Don’t Miss: Common Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Why Should People Take Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis C
The purpose of taking antiviral medications for hepatitis C is to:
- remove all the hepatitis C virus from your body permanently
- stop or slow down the damage to your liver
- reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis
- reduce the risk of developing liver cancer
- reduce the risk of liver failure and the need for a liver transplant
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often doesnt have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged. This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition. Symptoms can include:
- flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches and a high temperature
- feeling tired all the time
- loss of appetite
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
Hepatitis B: Should I Have The Vaccine
In most adults, an acute hepatitis B infection will usually clear up on its own, without treatment. If it becomes chronic, though, it can have serious consequences. There is a vaccine to prevent hepatitis B. It is recommended for all babies and toddlers, as well as for adults who have a high risk of becoming infected.
The hepatitis B virus is mainly spread through blood, but also through other body fluids. This usually happens during unprotected sex most commonly between men who have sex with other men. Having several sexual partners and recurring sexual STIs can increase the risk of getting hepatitis B too. Other routes of infection include using non-sterile syringes when injecting drugs or having a tattoo done with non-sterile needles.
If a pregnant woman has hepatitis B, she might pass it on to her baby while giving birth. In Germany and other countries, pregnant women are offered a hepatitis B test to see whether they are infected.
The likelihood of becoming infected is generally quite low in countries like Germany, where less than 1 out of 100 people have hepatitis B.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis Contagious Through Saliva