What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
About 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments almost always work if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Joint And Muscle Pain
A condition called arthralgia causes joint pain and is common in people with hepatitis C. Itâs different from arthritis, which causes pain and swelling in joints. But infected people can also get hepatitis C-related arthritis.
Fibromyalgia, which causes body aches and muscle pain, is also common in people with hepatitis C.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Flare Up
What Is Acute Hepatitis B
If someone has hepatitis B for less than 6 months it is called an acute infection. Most people who get hepatitis B as adults will only have an acute infection and recover from it. If you have acute hepatitis B, you might not experience any symptoms.
The older a person is when they become infected with hepatitis B, the better their chances of successfully fighting it off . Around 95% of adults who contract hepatitis B will go on to have an acute infection and are then clear it naturally. On the other hand, up to 90% of babies and 30% of children who become infected will go on to have chronic hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: Cost For Hepatitis B Test
Vaccination Is The Best Way To Prevent Hepatitis A And B Infection
Narrator: ÂYou are a traveller .
Narrator: Âand you are already dreaming of your next getaway. .
Disclaimer on-screen reads: TWINRIX is a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine used in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over the age of 1 year to prevent hepatitis A and hepatitis B diseases
Narrator: ÂWhile your travel plans probably donÂt include hepatitis A or hepatitis BÂ .
Disclaimer reads: 100% protection cannot be guaranteed and booster doses may be required.
Narrator: Âyou know that many common travel activities can put you at risk of acquiring these two serious liver diseases .
Disclaimer reads: TWINRIX does not protect against hepatitis C or E, and is not indicated to treat or reduce the severity of hepatitis A or B infections. .
Narrator: Âwhich is why you plan on talking to your doctor about TWINRIX, right? Of course, right Âbecause you are a traveller.Â
Video concludes with TWINRIX logo, GSK logo, You are a traveller slogan, and safety information: Very commonly reported adverse events in adults were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur. Full product information can be found on Twinrix.ca. If you need to report an adverse event, please call 1-800-387-7374.
Twinrix.ca
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get A Tdap Vaccine
Can You Get A Vaccine To Prevent Hepatitis C
Vaccines are a way to expose your body to a virus before you encounter the live virus naturally. A vaccine contains traces of a dead virus, so your body can form a memory of the virus. Your body then remembers how to attack and destroy the virus if you ever come into contact with it.
There isnt a vaccine for hepatitis C at this time. Hepatitis C has many different subtypes and strains, so creating a vaccine that protects against all the different types is complicated. Vaccines are available for both hepatitis A and B, but one for hepatitis C hasnt been approved.
If you have hepatitis C, your doctor may suggest you get the vaccine for both hepatitis A and B. These two types of viruses cause liver damage, so the added protection is a smart idea.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Hepatitis A Virus
I Received My Vaccine Years Ago
If it has been years since you have been vaccinated, you may need or may request a hepatitis B surface antibody titer blood test to confirm that you are still protected. A person is considered protected if they have a positive anti-HBs or HBsAb test result greater than 10 mIU/mL. Sometimes these test results are under 10 and there is concern whether these low levels will still provide protection against hepatitis B. Anti-HBs or HBsAb test results can decrease over time, but an individual can still be protected even if the test results are less than 10 mIU/mL.
If your test results are low, your doctor may recommend a booster shot or a repeat of the series. If you confirm you completed the vaccine series, you can get a booster dose of the vaccine. Your surface antibody level will be tested again 1 or 2 months after the booster. If the blood test result is greater than 10 mIU/mL, then you are protected and will not require an additional booster shot in the future. If a booster shot does not result in a level greater than 10, then complete the remaining two-doses of the vaccine series and recheck the levels again after 1-2 months. Retain a copy of the anti-HBs titer test as proof of protection.
Blood And Vessel Problems
People with hepatitis C often get a condition called cryoglobulinemia. This happens when certain proteins in your blood stick together in cold weather. They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints.
Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
The infection can also make you bruise easily or get red or purple spots under your skin. Those are signs of a bleeding disorder called immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
Read Also: What Do You Get Hepatitis From
Also Check: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Through Saliva
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
If blood tests show that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor may recommend medication to reduce the risk of complications of hepatitis B and regular tests to assess the health of your liver.
Treatment is usually offered if:
- your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B by itself
- there’s evidence of ongoing liver damage
Hepatitis B medications can help keep the virus under control and stop it damaging your liver, although they won’t necessarily cure the infection and some people need lifelong treatment.
The main medicines for chronic hepatitis B are outlined below.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
A diagnosis of hepatitis B infection is made using blood tests.
Because many people do not have symptoms when they get hepatitis B, they may never be diagnosed. Thats why screening for hepatitis B is recommended in a number of people including:
- people at higher risk
If you think you have been exposed to infected blood or body fluids, see a doctor as soon as possible. There are treatments that can reduce your risk of developing the infection, if given shortly after exposure.
Don’t Miss: Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
What Tests Are There For Hepatitis B
All of the tests used to diagnose hepatitis B are blood tests. Some indicate different stages of the illness or immunity. The following list shows the different tests available, and what a positive result indicates for each of them.
- Hepatitis B surface antigen – Shows the person has hepatitis B. It can be detected during acute and chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody – Shows the person has developed immunity to hepatitis B. It can be detected in people who have recovered from acute hepatitis B or been vaccinated against it.
- Hepatitis B e antigen – Shows the hepatitis B virus is multiplying, and that it can be more easily passed on.
- Hepatitis B e antibody – Shows the persons immune system has responded to hepatitis B and in some circumstances, the virus is not actively replicating.
- Hepatitis B core antibody – Shows a person has had hepatitis B, either past or present infection. If someone has immunity through vaccination he or she will not test positive.
- Hepatitis B virus DNA – Measures the amount of hepatitis B virus in the bloodstream and indicates how actively the virus is multiplying.
You May Like: What Should I Do If I Have Hepatitis B
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
What Is Hepatitis B
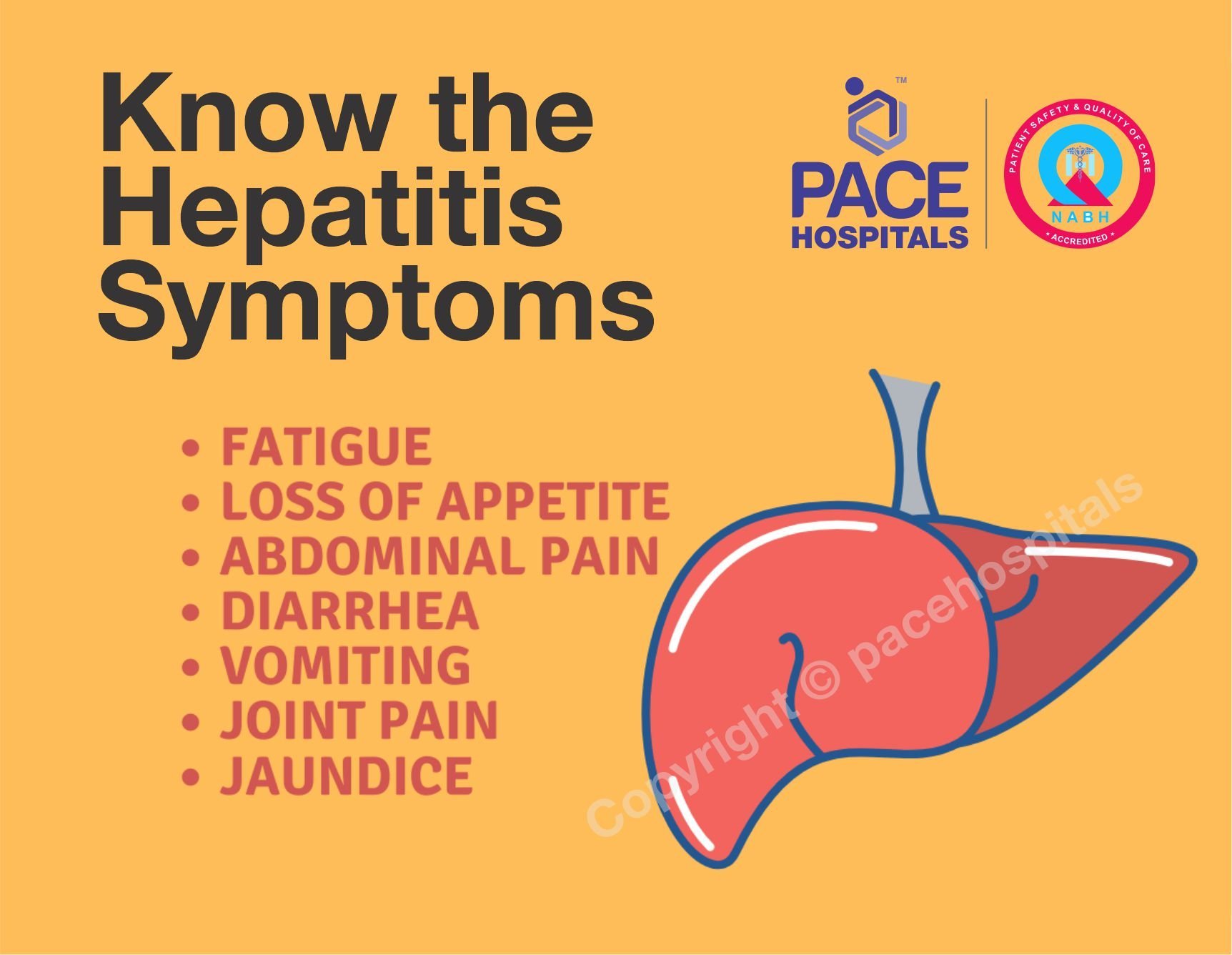
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It can cause long lasting liver damage.
Hepatitis B can be acute or chronic. If a person has acute hepatitis B, the virus makes them sick for a short time , then their body clears the virus and they recover.
If the infection last for more than 6 months, it is called chronic hepatitis. Chronic hepatitis is a lifelong illness.
Vaccination can prevent hepatitis B.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
Can The Liver Repair Itself From Hepatitis B
With a chronic hepatitis B infection, however, the liver is constantly under attack by the virus and eventually it can become hardened over time. Some of the changes and liver damage that can occur are described below: Fibrosis: After becoming inflamed, the liver tries to repair itself by forming tiny scars.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Itchy Skin
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
You May Like: What Is Genotype 3 Hepatitis C
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
You May Like: Can Alcohol Cause Hepatitis C
How Does One Administer Twinrix
Twinrix is given by injecting the liquid into the muscles. How many Twinrix shots do I need? It is provided as a sequence of three dosages. With the second dose given at least one month after the first. The final and third dose given at least six months after the first dosage.
A 4-dose rapid schedule is also accessible for individuals 19 years of age and over. It is safe to receive the hepatitis A and B vaccination in conjunction with other vaccines.
What Do I Do If I Am Exposed To Hepatitis B
Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible after the exposure. If you have not been vaccinated or are incompletely vaccinated, it may make sense for you to get a shot of hepatitis B immune globulin as soon as possible . HBIG provides short-term protection against the hepatitis B virus. When given shortly after an exposure , HBIG is 70-75% effective in preventing hepatitis B infection. Hepatitis B vaccination can be given at the same time, for long-term protection.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Test Non Reactive
Benefits Of The Hepatitis C Test
Did you know that annually around three to four million new hepatitis C infection are reported? This virus is transmitted primarily through blood but also through unprotected sexual intercourse. There is also a risk of becoming infected when getting a tattoo or piercing in an unhygienic and unsanitized environment.
For the cerascreen® Hepatitis C Test, you do not need to go to the doctor or wait for an appointment. You simply receive a straightforward instruction booklet with pictures and then collect the sample yourself in the comfort of your home. Afterward, you will get an overview of the consequences of an unknown STI.
Profit from our expertise: cerascreen® is the in Europe, with eight years of experience in test development and analysis. In Europe we have developed more than 50 certified send-in sample collection kits , analyzed over 250,000 samples, and offer our products to 19 different countries.
Hepatitis B In The United States

In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Can Drinking Cause Hepatitis C