How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called “fulminant” hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Mortality And Survival Plots
General population mortality data were provided for age groups in 5-year intervals. Liver cancer mortality was adjusted for the proportion with an HCC diagnosis, the percentage of HCC associated with hepatitis B, and the population prevalence of HbsAg. The same process was performed for CLD death. Mortality was also analyzed with respect to HbeAg status and adjusted by relative risk and age-specific HbeAg prevalence. The overall carrier mortality rate was obtained by summing the rates of non-liver, HCC, CLD, and non-HCC liver cancer. The values for noncarriers were calculated using the same methods. Survival plots and life expectancies were obtained by using an abridged life table, whereby a hypothetical cohort was subjected to age-specific mortality rates, with survivors proceeding to the subsequent age interval.29 Relative mortality risks were calculated and standardized to the 2006 Taiwan population distribution.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if you have an active infection. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can transmit the virus to others. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B.
This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the state of a hepatitis B infection.
You May Like: Why Is My Doctor Testing Me For Hepatitis C
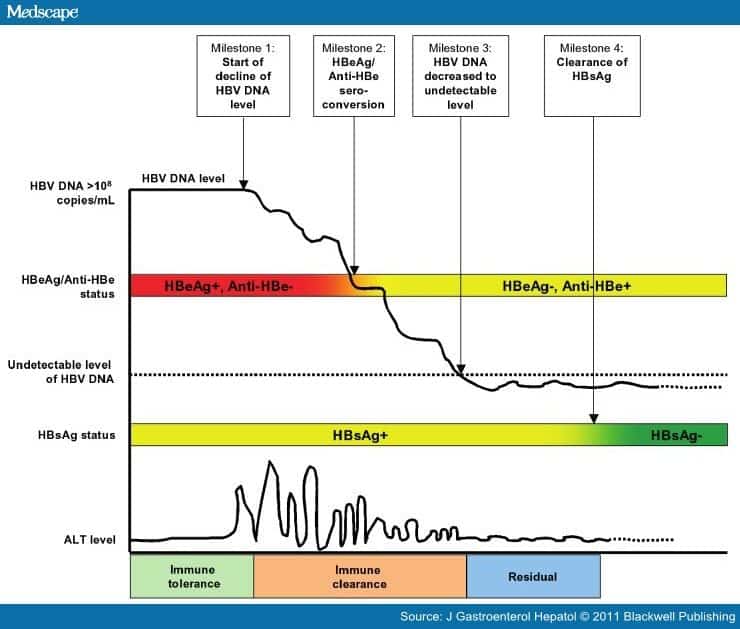
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection can lead to the development of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and HCC. As well as in HCV, chronic HBV infection is associated with age, cell cycle arrest, and CS. In one study the authors assessed the HBV antigen production in relation to cell cycle arrest and CS in vitro using hepG2 and hepG2.2.15 cell lines . HepG2.15 cells were transfected with sub-genomic HBV thus HBV production is a result of transcription of the transgene. The authors found that in vitroinduced cell cycle arrest by the addition of hydrogen peroxide caused increased levels of supernatant HBsAg and HBV DNA also an increased expression of HBcAg expression was noted. In contrast no effect on HBsAg or HBV DNA production was observed in senescent cells, with only a minor increase in cytoplasmic HBcAg staining. The authors also found that fewer telomeres were detected in patients with chronic HBV infection compared with controls of healthy livers however, when telomeres were detected they were shorter than controls . Widespread telomere shortening is consistent with accelerated aging in chronic HBV .
Jules L. Dienstag, Andrew S. Delemos, in, 2015
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Read Also: What Are The Signs Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Is Transmitted Sexually
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Chronic Inactive Hepatitis B: What It Means
The condition of asymptomatic hepatitis B virus infection is now more correctly defined as inactive carrier status.
Although these individuals are chronic carriers of the B virus infection, they do not show signs of active disease.
This means that these people have the viral infection, but their blood test values are consistently normal and do not show the typical signs of hepatitis.
This condition is thought to be the result of constant monitoring of viral activity by the infected persons immune system and carries a very low risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B How Is It Spread
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. This means their immune system was not able to get rid of the hepatitis B virus and it still remains in their blood and liver.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is also directly related to the age at which one first becomes exposed to the hepatitis B virus:
- 90% of infected newborns and babies will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of infected children will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of infected adults will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
Learning that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting. Because most people do not have symptoms and can be diagnosed decades after their initial exposure to the hepatitis B virus, it can be a shock and a surprise to be diagnosed with a chronic hepatitis B infection. The good news is that most people with chronic hepatitis B should expect to live a long and healthy life.
There are effective drug therapies that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging a liver. There are also promising new drugs in the research pipeline that could provide a cure in the very near future. Although the risk of developing a serious liver disease or liver cancer is higher for those living with chronic hepatitis B than those who are not infected, there are still many simple things a person can do to help reduce their risks.
Can Hepatitis B Be Prevented
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the best ways to control the disease. It is safe, effective and widely available. More than one billion doses of the vaccine have been administered globally since 1982. The World Health Organization says the vaccine is 98-100% effective in guarding against the virus. Newborns should be vaccinated.
The disease has also been more widely prevented thanks to:
- Widespread global adoption of safe blood-handling practices. WHO says 97% of the blood donated around the world is now screened for HBV and other diseases.
- Safer blood injection practices, using clean needles.
- Safe-sex practices.
You can help prevent hepatitis B infections by:
- Practicing safe sex .
- Never sharing personal care items like toothbrushes or razors.
- Getting tattoos or piercings only at shops that employ safe hygiene practices.
- Not sharing needles to use drugs.
- Asking your healthcare provider for blood tests to determine if you have HBV or if you are immune.
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Also Check: Effects Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
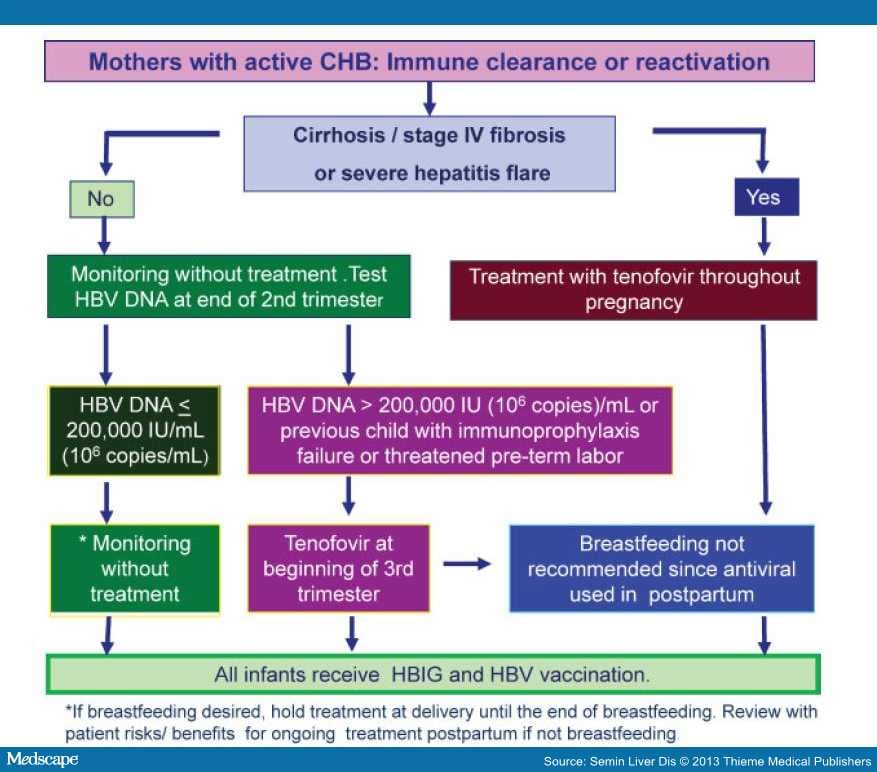
What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Fatty Liver And Hepatitis
Distinctions Based On Epidemiologic Considerations
Chronic hepatitis B follows acute HBV infection in more than 90% of neonates born to mothers with chronic hepatitis B but in only approximately 1% of immunocompetent adults with clinically apparent acute hepatitis B.57-59 In Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, the prevalence of HBV infection is high, exceeding 10% of the population, and in many western countries, such as the United States, prevalence rates of less than 1% are the rule. These differences in frequency translate into marked distinctions in clinical expression of HBV infection.
In high-prevalence areas, women of childbearing age have the high likelihood of infection characteristic of the population at large consequently, the risk of perinatal transmission of HBV infection from infected mother to her baby is high and represents the most common mode of HBV transmission in the population. Acquired in the perinatal period, HBV infection is unlikely to be accompanied by clinically apparent acute hepatitis but almost universally results in chronic infection, a reflection of tolerance of the virus by the host-immune system.57 Although most such infected persons can have mild asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B during childhood and early to middle adulthood, the lifetime risk of succumbing to chronic hepatitis B in such high-prevalence HBV populations can reach 40%, the result of cirrhosis and HCC.50
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
You May Like: How To Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Whats The Outlook For People With Chronic Hep B
The majority of people who have hep B as adults fully recover within 1 to 3 months. Children under the age of 5 are at the highest risk of developing chronic hep B infection.
Medications can help manage chronic hep B, but about 15 to 25 percent of people die prematurely from liver cancer, cirrhosis, or liver failure.
More than half of liver cancers are caused by chronic hep B infection. Taking your medications as prescribed and following your healthcare professionals recommendations can help you minimize your chances of complications.