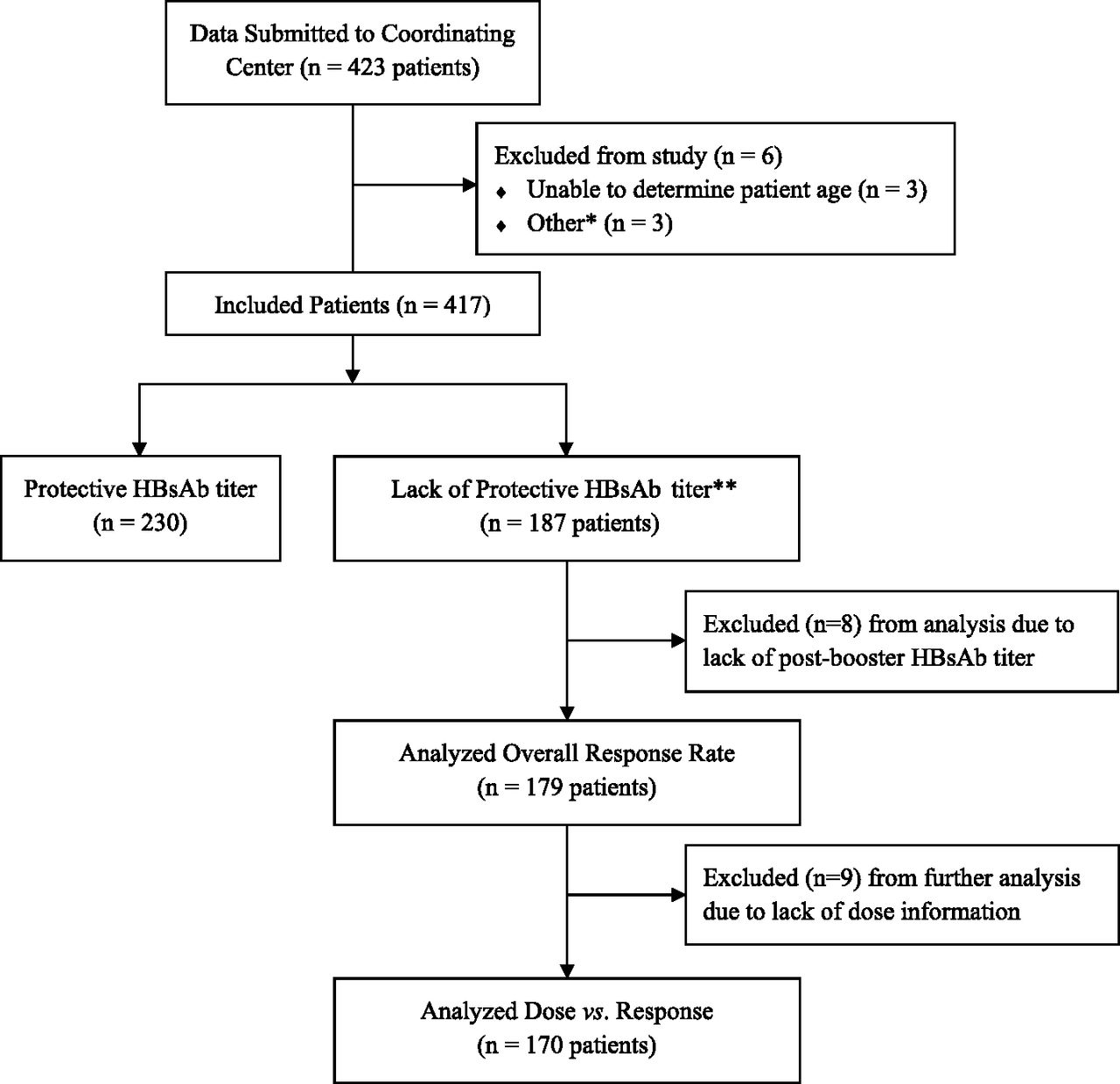
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Cautions Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Positive screen results without need for confirmation testing should be interpreted in conjunction with test results of other hepatitis B virus serologic markers .
Positive hepatitis B surface antigen test results should be reported by the health care provider to the State Department of Health, as required by law in some states.
Individuals, especially neonates and children, who recently received hepatitis B vaccination may have transient positive HBsAg test results because of the large dose of HBsAg used in the vaccine relative to the individual’s body mass.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly lipemic
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Containing particulate matter
Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A positive result indicates recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection or acquired immunity from HBV vaccination. This assay does not differentiate between a vaccine-induced immune response and an immune response induced by infection with HBV. A positive total antihepatitis B core result would indicate that the hepatitis B surface antibody response is due to past HBV infection.
Per assay manufacturer’s instructions for use, positive results, defined as anti-HBs levels of 12.0 mIU/mL or greater, indicate adequate immunity to hepatitis B from past hepatitis B or HBV vaccination. However, per current CDC guidance, individuals with anti-HBs levels greater than 10 mIU/mL after completing an HBV vaccination series are considered protected from hepatitis B.
Negative results, defined as anti-HBs levels of less than 5.0 mIU/mL, indicate a lack of recovery from acute or chronic hepatitis B or inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. The US Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices does not recommend more than 2 HBV vaccine series in nonresponders.
Indeterminate results, defined as anti-HBs levels in the range from 5 to 11.9 mIU/mL, indicate inability to determine if anti-HBs is present at levels consistent with recovery or immunity. Repeat testing is recommended in 1 to 3 months.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Flare Up
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A What Is It
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Serum
Diagnosis of acute, recent, or chronic hepatitis B infection
Determination of chronic hepatitis B infection status
This test is not offered as a screening or confirmatory test for blood donor specimens.
This test, by itself , is not useful during the “window period” of acute hepatitis B virus infection . Testing for acute HBV infection should also include hepatitis B core IgM antibody .
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Food
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health-care and public-safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Hemodialysis patients
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
- fever,
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
High Titers Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk Of Hepatitis B Virus
Sung-Nan Pei, Ming-Chung Wang, Ming-Chung Ma, Ching-Yuan Kuo, Chien-Hung Chen, Po-Nan Wang High Titers of Hepatitis B Surface Antibodies Indicating Low Risk of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatitis in Lymphoma Patients Treated with Rituximab-Based Chemotherapy. Blood 2015 126 : 3869. doi:
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Interpretation Provides Information To Assist In Interpretation Of The Test Results
A reactive screen result confirmed as positive by hepatitis B surface antigen confirmatory test or a positive screen result is indicative of acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection, or chronic HBV carrier state.
Specimens with initially reactive screen results, but negative by HBsAg confirmatory test results, are likely to contain cross-reactive antibodies from other infectious or immunologic disorders. These unconfirmed HBsAg-reactive screening test results should be interpreted in conjunction with test results of other HBV serologic markers . Repeat testing is recommended at a later date if clinically indicated.
Confirmed presence of HBsAg is frequently associated with HBV replication and infectivity, especially when accompanied by presence of hepatitis B e antigen and/or detectable HBV DNA.
–Viral Hepatitis Serologic Profiles
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Comprehensive Hepatitis B Profile Test
This panel includes 6 tests that can aid in diagnosing infection with Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection that is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Hep B is spread through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. The most common means of transmission are through sexual contact or sharing needles used for intravenous drug use. Infected mothers can also pass the virus to their infants during childbirth. Hepatitis B infections often show no symptoms but when symptoms do occur they can include abdominal pain, fever, loss of appetite, nausea, joint pain, fatigue, jaundice, and dark-colored urine. Chronic Hep B infections can cause serious health complications like Cirrhosis and Liver Cancer. Vaccination against Hep B is available which can provide immunity to the virus. People who are successfully treated for Hep B typically develop a natural immunity that can protect against future infections.
This panel combines 6 tests that can provide more information when used together than any single test. Used in combination, these tests can help to determine if a person has been exposed to Hep B and whether they have an active infection. These tests can also be useful for determining if a person has immunity to the Hep B Virus. Results for these tests may have more than one interpretation and should be reviewed by a person’s doctor.
This panel includes:
Detection Period:
Requirements:
You May Like: Hepatitis C Test Results Non Reactive
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
What Is A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Test
Hepatitis B surface antibody test is part of a panel of blood tests to diagnose HBV infection. Hepatitis B surface antibody test determines the presence and quantity of anti-HBs in the blood serum, which can indicate protection from HBV infection.
Hepatitis B disease affects the liver and commonly spreads through body fluids such as blood, semen, and vaginal secretions.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Hepatitis C
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to hepatitis B, your body mounts an immune reaction against it as an invader. This happens whether you are exposed due to blood or sexual contact or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The hepatitis B virus has proteins on its surface that cause your immune system to produce antibodies. With the vaccine, the sample contains the protein only and not the virus itself.
The first response your body will make when exposed to hepatitis B is to manufacture hepatitis B IgM antibodies. These early antibodies are produced to fight against several parts of the virus including its core. These antibodies are seen in the initial response, but they eventually fade away.
Your immune system then begins to produce IgG antibodies. It continues to produce these antibodies for the rest of your life. In this way, your immune system is always ready to attack hepatitis B virus when it is exposed to it.
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
-Grossly lipemic
-Grossly hemolyzed
-Containing particulate matter
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Is It Curable
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.