Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
What Is Hep Be Ag
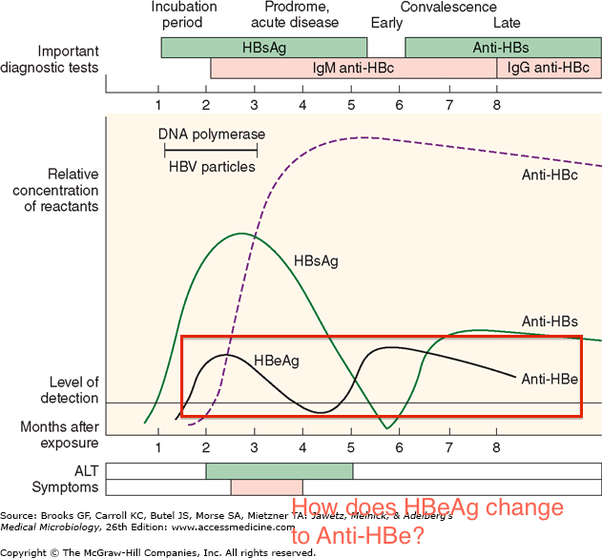
The hepatitis e antigen, or HBeAg, is a marker of an actively replicating HBV virus infection. Those with a positive HBeAg have active replication in their liver cells, more of the virus circulating in their blood, and as a result, they are more infectious, with a higher likelihood of transmitting HBV to others.
What Do The Hepatitis B Immunity Results Mean
If an individual is positive for both surface and core antibodies, it can indicate that they had a natural HBV infection and recovered. If only surface antibodies are positive, it can indicate that the individual was vaccinated. In both of these cases, immunity is confirmed, meaning that further vaccination is not generally required.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Recommended Reading: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis B
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Curable Disease
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
At-home testing kits are available for hepatitis B and C. Usually the test kit will include a sharp device, to prick your finger so you can collect a drop of blood to send to a lab for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your provider.
Check If You Have Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B infection include:
- a high temperature
- pain in your upper tummy
- feeling sick or being sick
- patches of raised skin that may be itchy
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
The infection usually lasts for 1 to 3 months and most people either have no symptoms or mild symptoms. If the infection lasts longer than 6 months it is called chronic hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Baby
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis Turn Into Hiv
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
When Should I Get This Test
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups at an increased risk of infection. You may benefit from hepatitis B screening if you:
- Were born in parts of the world where the disease is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- Didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- Are HIV-positive
- Use injectable drugs
- Are at risk of HBV infection due to sexual exposure
A doctor may order hepatitis testing based on your symptoms, medical and family history, and a physical exam. If you develop symptoms without recent exposure to HBV, doctors may recommend an acute viral hepatitis panel that looks for hepatitis A, B, and C in one sample of blood.
Hepatitis tests may also be performed as follow-up tests when other tests of liver health are abnormal.
Testing is common in those that show symptoms that could be caused by hepatitis B. Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may take place before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that you have previously been infected with HBV or have already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Fast Track Hepatitis B Vaccine In Houston Tx
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
Read Also: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
What Does Hepatitis B Envelope Antigen Mean
Hepatitis refers to liver inflammation caused by a viral infection. This is one of the most widespread and contagious diseases in the world with more than 400 million people being a carrier of the hepatitis B virus. When the hepatitis B virus is actively circulating and replicating in the blood, it produces the hepatitis B antigen protein. The presence of this antigen protein means that the person is infected with the virus and can spread the infection to other people.
Read Also: Can You Give Yourself Hepatitis B
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Chronic Inactive Hepatitis B: What It Means
The condition of asymptomatic hepatitis B virus infection is now more correctly defined as inactive carrier status.
Although these individuals are chronic carriers of the B virus infection, they do not show signs of active disease.
This means that these people have the viral infection, but their blood test values are consistently normal and do not show the typical signs of hepatitis.
This condition is thought to be the result of constant monitoring of viral activity by the infected persons immune system and carries a very low risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Read Also: Which Statement Is True About The Hepatitis C Virus
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Test Kit Walgreens
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If I Have Hepatitis
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Module 3 Interpretation Of Hbv Diagnostic Test Results
This table describes 6 possible interpretations of diagnostic test results and subsequent recommended actions for clinicians.
In the first scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are negative total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done.
Itâs noted that approximately 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to vaccine or else do not produce protective levels of antibody post-vaccination .
The recommended action when a patient is considered to be susceptible to hepatitis B is to vaccinate.
In the second scenario of this table, a patient should be considered to be immune to hepatitis B due to vaccination when: hepatitis B surface antigen results are negative hepatitis B surface antibody results are positive total hepatitis B core antibody results are negative and the IgM marker of the hepatitis B core antibody is not available/or not done. Regarding the hepatitis B surface antibody, clinicians are reminded that about 5 percent to 10 percent of people will not respond to the vaccine or else do not produce a protective level of antibody post-vaccination . Note that in immune individuals, levels of hepatitis B surface antibody may decline over time and become undetectable.
Also Check: Can You Cure Hepatitis C
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Epidemiology Of Acute And Chronic Hbv In Canada
Acute HBV: Canada is a region of low endemicity however, certain vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected. These include Aboriginal peoples, MSM, street-involved youth, and people who are or have been incarcerated.Endnote 2 Peak incidence is among those aged 3039 years. The most commonly identified risk factors are high-risk sexual activities and injection drug use.
Canada has had universal HBV immunization programs in place since the mid-1990s. All provinces and territories have programs that target children aged 913 years, and some have also implemented a neonatal immunization program.Endnote 3 In addition, some provinces/territories provide coverage for high-risk individuals, but eligibility varies across jurisdictions . Despite the success of these programs, there may be many who remain at risk of acquiring HBV.
Immunization contributes to disease control by interrupting disease transmission and decreasing the pool of susceptible people. It is essential to identify those at risk who would benefit from receiving the HBV vaccine.
There is an urgent need to screen, diagnose, and treat chronic HBV infection so as to reduce associated morbidity and mortality and to prevent further transmission.
You May Like: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Don’t Miss: What Age Do You Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B usually clears up on its own without treatment. You may be offered medicine to help with the symptoms, such as painkillers or medicines to stop you feeling sick.
Your GP will refer you to see a liver specialist who will check how well your liver is working.
If hepatitis B lasts for over 6 months it is called long-term hepatitis B.
It is usually treated with antivirals and medicine to help relieve symptoms such as itchiness, pain, and sickness. You will also need to see a liver specialist for regular check-ups.
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Results And Next Steps
The results of a hepatitis B titer panel can help a doctor determine a persons hepatitis B status. The results can be confusing if a person has never been through this type of testing before, but the doctor can explain the findings.
The results for the titer come back as either negative or positive on each subtest of the panel. Positive means that the virus or antibodies showed up on the test, while negative means that they did not.
The following table outlines what positive and negative results mean on different parts of the test and the possible next steps.
The information comes from the Immunization Action Coalition:
| Test |
|---|