What Abnormal Results Mean
There are different tests for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. A positive test is considered abnormal.
A positive test may mean:
- You currently have a hepatitis infection. This may be a new infection , or it may be an infection that you have had for a long time .
- You had a hepatitis infection in the past, but you no longer have the infection and cant spread it to others.
Hepatitis A test results:
- IgM anti-hepatitis A virus antibodies, you have had a recent infection with hepatitis A
- Total antibodies to hepatitis A, you have a previous or past infection, or immunity to hepatitis A
Hepatitis B test results:
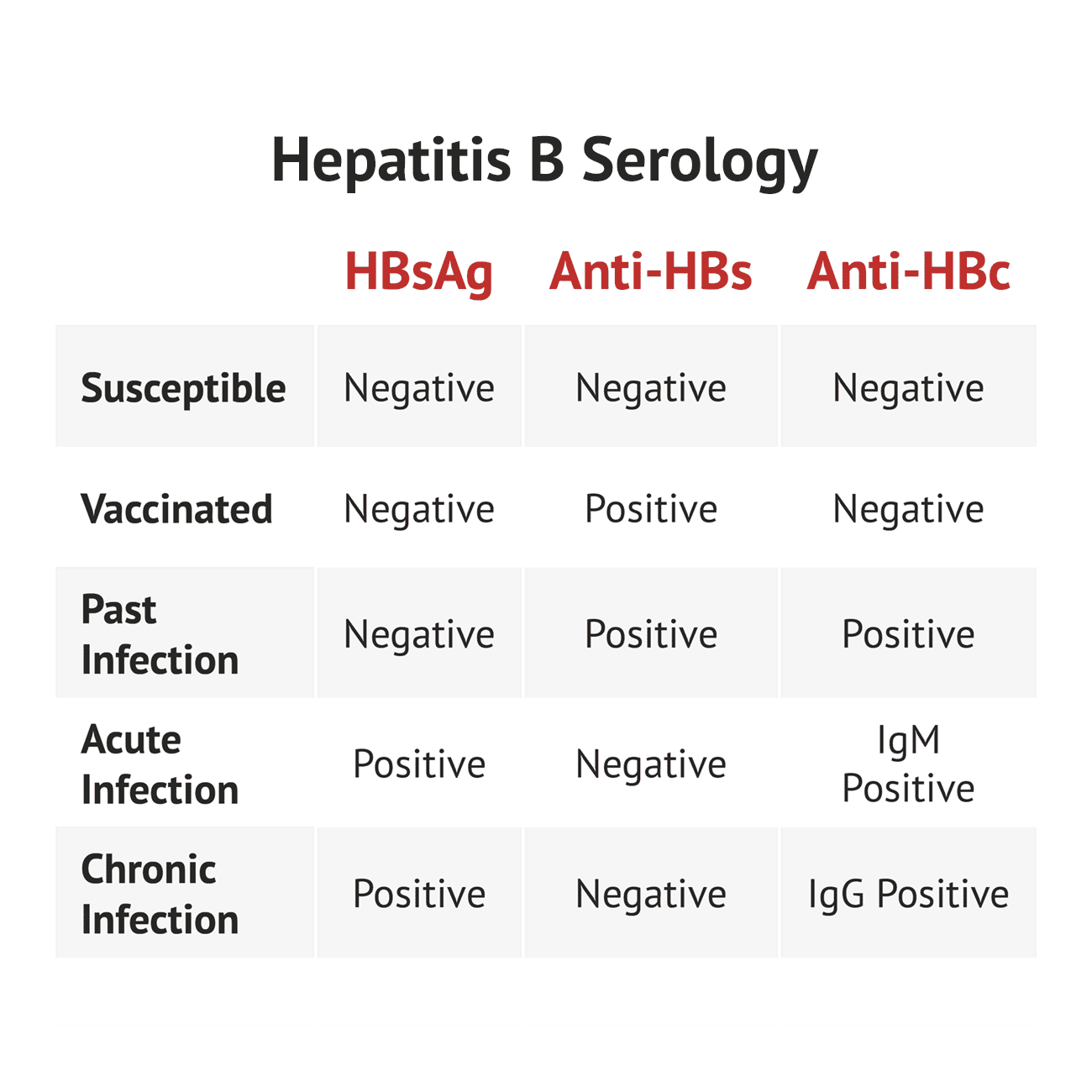
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : you have an active hepatitis B infection, either recent or chronic
- Antibody to hepatitis B core antigen , you have a recent or past hepatitis B infection
- Antibody to HBsAg : you have a past hepatitis B infection or you have received the hepatitis B vaccine and are unlikely to become infected
- Hepatitis B type e antigen : you have a chronic hepatitis B infection and you are more likely to spread the infection to others through sexual contact or by sharing needles
Antibodies to hepatitis C can most often be detected 4 to 10 weeks after you get the infection. Other types of tests may be done to decide on treatment and monitor the hepatitis C infection.
Also Check: Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster For Healthcare Workers
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Can Hbsag And Hbsab Be Positive
Both in vitro simulation and in vivo animal models demonstrated that HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of the same serotypes could not coexist, but HBsAg antigen and HBsAb of different serotype could coexist. HBsAg/HBsAb double positive hepatitis B virus infection could be due to infection of viruses of different serotypes.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Read Also: How Deadly Is Hepatitis C
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
From an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Do
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
â Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
â It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
â People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
â Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
Also Check: Where Does Hepatitis Come From
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: How Long Is Hepatitis C Treatment
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Dont Miss: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
Also Check: Hepatitis C Blood Test Results
Why Do I Need This Test
You may need this test if your healthcare provider suspects you have a liver infection caused by HBV. You may also need this test if you have symptoms of hepatitis B. Symptoms usually start slowly. Many people have no symptoms or only feel like they have a mild case of the flu. You may not have symptoms until the infection is chronic or severe.
The most common symptom is extreme tiredness. Other symptoms may include:
-
Swelling and confusion. This is in extreme cases.
You may also have this test if you have a history that puts you at risk for being in contact with the virus. Risk factors for hepatitis B infection include:
-
Having sex with someone infected with the virus
-
Living in close contact with someone who has the virus
-
Being a man who has sex with men
-
Being a child born to a mother who has the virus
-
Sharing needles for intravenous, or IV, drug use
-
Working in a healthcare center where you are exposed to blood
-
Getting a blood transfusion or organ transplant. This is less common with active screening.
Hepatitis B Risk Factors Include:
- Being born to mothers infected with hep B
- Being born or traveling in countries where hep B is common
- Exposure to blood on the job, such as health care workers
- Having sexual partners with hep B
- Coming into contact with infected bodily fluids
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
- Being born in the US, not vaccinated as an infant, and having parents born in high-risk countries
- Living or lived with a partner who has chronic hep B
- Having had a tattoo or body piercing with unsterilized tools
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Chronic Vs Acute
Additional Specimen Collection Information
Collect blood in a lithium heparin, green-top, EDTA purple-topor red-top tube. PST and SST are acceptable. Serum orplasma should be separated from contact with the cells within 2hours of collection. Specimens not centrifuged within 4 hours ofcollection may be rejected. Refrigerate the specimen if unable toassay within 8 hours of collection. Samples with > 1+ lipemiamust be cleared prior to analysis.
What Type Of Disease Is Cystic Fibrosis
It means that the test result was positive for the antibody thatwas being tested.
If it is the Hepatitis B surface antibody then it means you havebeen exposed to either the infection of gotten the immunizations.
If it is other antibodies, such as the core or envelope, then itmeans you have been exposed to the infection at some point.
About 90% of adults who catch Hepatitis B get better on theirown so if you are antibody positive in order to know if you stillhave the infection you need to check a surface antigen or do a DNAtest.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Infected By Hepatitis C
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patientâs body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a personâs ability to spread HBV to others.
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check:
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Transmission
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Non Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
What Does Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive Mean
If this test is positive or reactive, then your immune system has successfully developed a protective antibody against the hepatitis B virus. This will provide long-term protection against future hepatitis B infection. Someone who is HBsAb+ is not infected and cannot pass the virus to others.
Can reactive hepatitis B be cured?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic hepatitis B infection. A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but theres no cure if you have the condition.
What is the normal level for Hep B surface AB?
For hepatitis B surface antibody , a level less than 5 mIU is considered negative, while a level more than 12 mIU is considered protective. Any value between 5 and 12 mIU is indeterminate and should be repeated.
You May Like: Best Medicine For Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Test Kit Walgreens
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Can You Get It
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive Mean Clfeax
Reactive results from the hepatitis B surface antibody test means that people are now immune to the virus because they have been infected in the past and their immune systems produced antibodies to fight the infection, This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B â¦
Recommended Reading: How Does One Contract Hepatitis C
You May Like: How Do You Catch Hepatitis C
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Dont Miss: What Is Hepatitis C From
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Recommended Reading: Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Read Also: What Is The Prognosis For Hepatitis C