Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Last In The Body
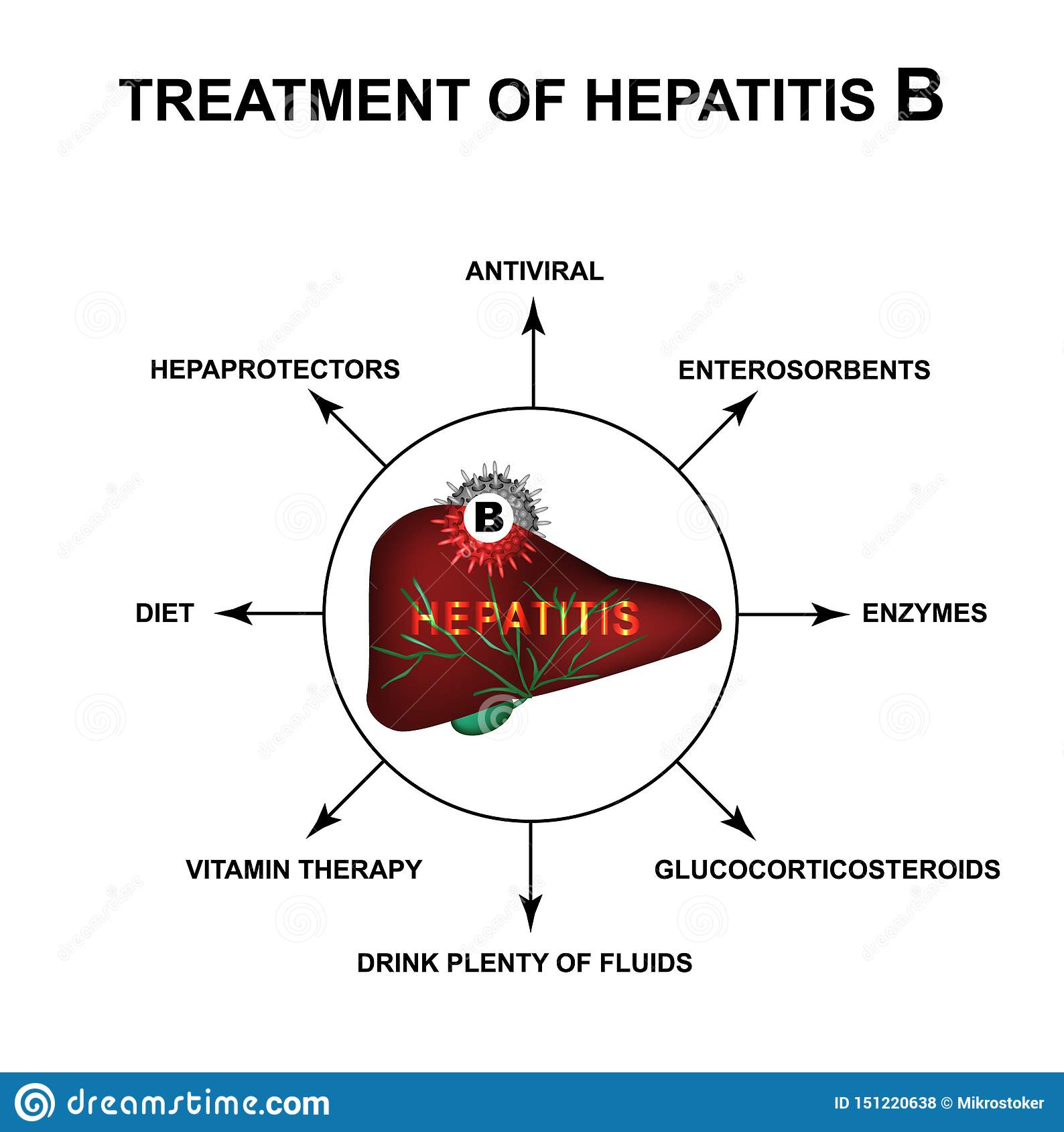
Treatment For Acute Hepatitis B Infection
If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection. In severe cases, antiviral drugs or a hospital stay is needed to prevent complications.
Interpreting Hepatitis B Laboratory Results
Many jurisdictions have regulations requiring laboratories to report all positive HBsAg, HBV DNA, and anti-HBc IgM laboratory results to the HD while a subset might also routinely receive positive total anti-HBc and anti-HBs results.
Additionally, some HDs might receive negative hepatitis B laboratory results, which are useful for determining false-positive results and monitoring patients through their infection and recovery. Table 3-1 shows how to interpret the combinations of laboratory results frequently available in hepatitis B test panels, following the biomarker changes over the course of disease as shown in Figure 3-1.
Table 3-1. Interpretation of hepatitis B laboratory results
| HBsAg |
|---|
- Concurrent ALT and total bilirubin result
- Other hepatitis serological results
- Negative HBsAg and/or negative/undetectable HBV DNA results
Total anti-HBc is detectable, on average, approximately 5 weeks post-HBV exposure, remains detectable indefinitely following exposure, and indicates past or current infection. In the presence of total anti-HBc, a positive HBsAg, HBeAg, or anti-HBc IgM result is a more reliable indication of recent or current infection. Jurisdictions that receive total anti-HBc laboratory results can use these results to clarify a persons HBV infection status.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Recommendations For Frequency Of Repeat Testing In An Asymptomatic Patient
The frequency of testing depends on the history of sexual exposure and number of sexual partners. However, in the case of hepatitis A and B, once the patient has completed a course of vaccination no further repeat testing is required.
For those at continuing risk and who have not received a course of vaccination, the following is recommended.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Kissing
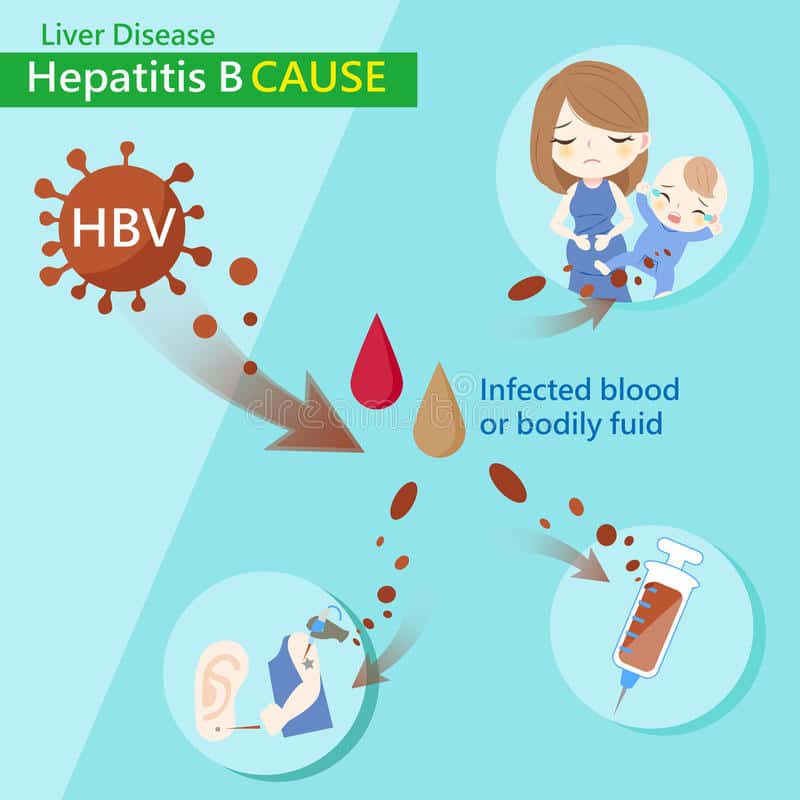
What Causes Hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person and werent properly sterilized, or cleaned in a way that destroys all viruses and other microbes
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You cant get hepatitis B from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking unclean water or untreated water that has not been boiled
- eating food that is unclean or has not been properly cooked
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Mothers who have hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies. If a baby receives hepatitis B immune globulin and starts receiving the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection shortly after birth, hepatitis B is unlikely to spread from mother to child through breastfeeding.15
Who Is At A Greater Risk Of Hepatitis B Viral Infection
Hepatitis B viral infection can occur in any individual. However, a certain group of people are at a higher risk of developing hepatitis B viral infection. Doctors generally recommend the blood test to screen patients with hepatitis B viral infection. The screening test is generally done for people who are prone to hepatitis B. Screening is important to isolate or alert the people infected with the virus so that the transmission of the virus can be controlled. The people at a greater risk of developing hepatitis B viral infection include:
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
What Are The Symptoms Of Having Hepatitis B
A majority of adults develop symptoms from acute hepatitis B virus infection however, young children often do not. Symptoms, when they occur, may include:
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Abdominal pain near the liver
On average, symptoms appear three months after exposure to the virus, but they can appear anywhere between six weeks and six months. Symptoms usually last for a few weeks, but can last up to six months. Most adults infected with hepatitis B virus recover fully even if their signs and symptoms are severe.
Some of the people who go on to develop chronic hepatitis B virus have ongoing symptoms similar to acute hepatitis B virus, but most people with chronic Hepatitis B remain symptom free for 20 or 30 years.
If you think you have signs of symptoms of Hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
You May Like: How To Tell If Someone Has Hepatitis
Hepatitis B During Pregnancy
If a woman with HBV becomes pregnant, they may transmit the virus to their baby. Women should inform the doctor who delivers their baby that they have HBV.
The infant should receive an HBV vaccine and HBIG with 1224 hours of birth. This significantly reduces the risk that they will develop HBV.
The HBV vaccine is safe to receive while pregnant.
People with a high risk of HBV include:
- the infants of mothers with HBV
- the sexual partners of people with HBV
- people who engage in sexual intercourse without contraception and those who have multiple sexual partners
- men who have sex with men
- people who inject illicit drugs
- those who share a household with a person who has a chronic HBV infection
- healthcare and public safety workers who are at risk of occupational exposure to blood or contaminated bodily fluids
- people receiving hemodialysis, which is a type of kidney treatment
- people taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as chemotherapy for cancer
People can prevent HBV infection by:
- wearing appropriate protective equipment when working in healthcare settings or dealing with medical emergencies
- not sharing needles
- following safe sexual practices
- cleaning any blood spills or dried blood with gloved hands using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts water
A vaccine against HBV has been available since 1982.
People who should receive this vaccine include:
Advocating For Hepatitis Awareness
Looking back on his experience, Vhal is happy that he was able to survive and that he himself is helping raise awareness about hepatitis with his life story.
Since my hepatitis medical history is public knowledge, there are people who approach me even on Facebook to share their situation or ask for advice, shared Vhal. There are many people with hepatitis who have not told their lovedones that they have it for various reasons, but a common reason is that they dont want to be shunned.
Aside from financial challenges to combat their infection, Vhal said that people living with hepatitis have also experienced discrimination due to lack of awareness. People have shared with him online how loved ones have left them because they had hepatitisB.
Vhal is lucky that his immediate family members, friends and officemates supported him throughout his ordeal. But he still experienced some stigma from other relatives, sharing: When our relatives learned we had hepatitis, even during my brothersburial, they distanced themselves from us. Perhaps they were not aware on how hepatitis is transmitted, they didnt know if its through airborne infection or saliva. I understand where they were coming from but it still hurt.
Vhal added that increased awareness will help end the stigma to people living with hepatitis B.
For me, even if you have limited amount of money, prevention is still cheaper than cure, he added.
Fact sheets
Read Also: Which Oil Is Good For Hepatitis B Patient
Lifestyle And Home Remedies
If you’ve been infected with hepatitis B, take steps to protect others from the virus.
- Make sex safer. If you’re sexually active, tell your partner you have HBV and talk about the risk of transmitting it to him or her. Use a new latex condom every time you have sex, but remember that condoms reduce but don’t eliminate the risk.
- Tell your sexual partner to get tested. Anyone with whom you’ve had sex needs to be tested for the virus. Your partners also need to know their HBV status so that they don’t infect others.
- Don’t share personal care items. If you use IV drugs, never share needles and syringes. And don’t share razor blades or toothbrushes, which may carry traces of infected blood.
Causes Of Hepatitis B And C
Common reasons for transmission of hepatitis B and C include having unprotected sex with an infected person, sharing needles with an infected person , getting a piercing or tattoo with an unsterilized tools, and sharing certain items that involve blood such as razors and toothbrushes . Both conditions usually cant be contracted through normal, everyday contact such as hugging, coughing, or sharing food and drinks.
You May Like: Treatment For Hepatitis C Medications
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take Hepatitis B To Show Up
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
Our Areas Of Innovation For Hepatitis B
Liver biopsies provide a great deal of information about the extent of damage in a childs liver, but the procedure is invasive and can be both painful and risky. Researchers at Boston Childrens are investigating an ultrasound-based imaging technology called FibroScan that may be able to help doctors assess liver scarring without the need for a biopsy.
Don’t Miss: Cure For Hepatitis A And B
Treatment Options For Antiviral Resistant Pathogens
If a virus is not fully wiped out during a regimen of antivirals, treatment creates a bottleneck in the viral population that selects for resistance, and there is a chance that a resistant strain may repopulate the host. Viral treatment mechanisms must therefore account for the selection of resistant viruses.
The most commonly used method for treating resistant viruses is combination therapy, which uses multiple antivirals in one treatment regimen. This is thought to decrease the likelihood that one mutation could cause antiviral resistance, as the antivirals in the cocktail target different stages of the viral life cycle. This is frequently used in retroviruses like HIV, but a number of studies have demonstrated its effectiveness against influenza A, as well. Viruses can also be screened for resistance to drugs before treatment is started. This minimizes exposure to unnecessary antivirals and ensures that an effective medication is being used. This may improve patient outcomes and could help detect new resistance mutations during routine scanning for known mutants. However, this has not been consistently implemented in treatment facilities at this time.
Hepatitis B Virus Infection In Newborns
, MD, University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Newborns may become infected at birth or rarely after birth.
-
Newborns who develop symptoms have jaundice, lethargy, and failure to thrive.
-
The diagnosis is typically based on blood tests.
-
Children are at risk of liver problems later in life.
-
The hepatitis B vaccine and sometimes hepatitis B immune globulin are given to newborns to protect them against the infection.
The infection occurs during delivery if the mother is infected. However, newborns may become infected after birth from other sources, such as the mothers saliva, stool, urine, or breast milk.
You May Like: How Do You Say Hepatitis C In Spanish