Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A And C Symptoms
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
The Correlation Between The Anti
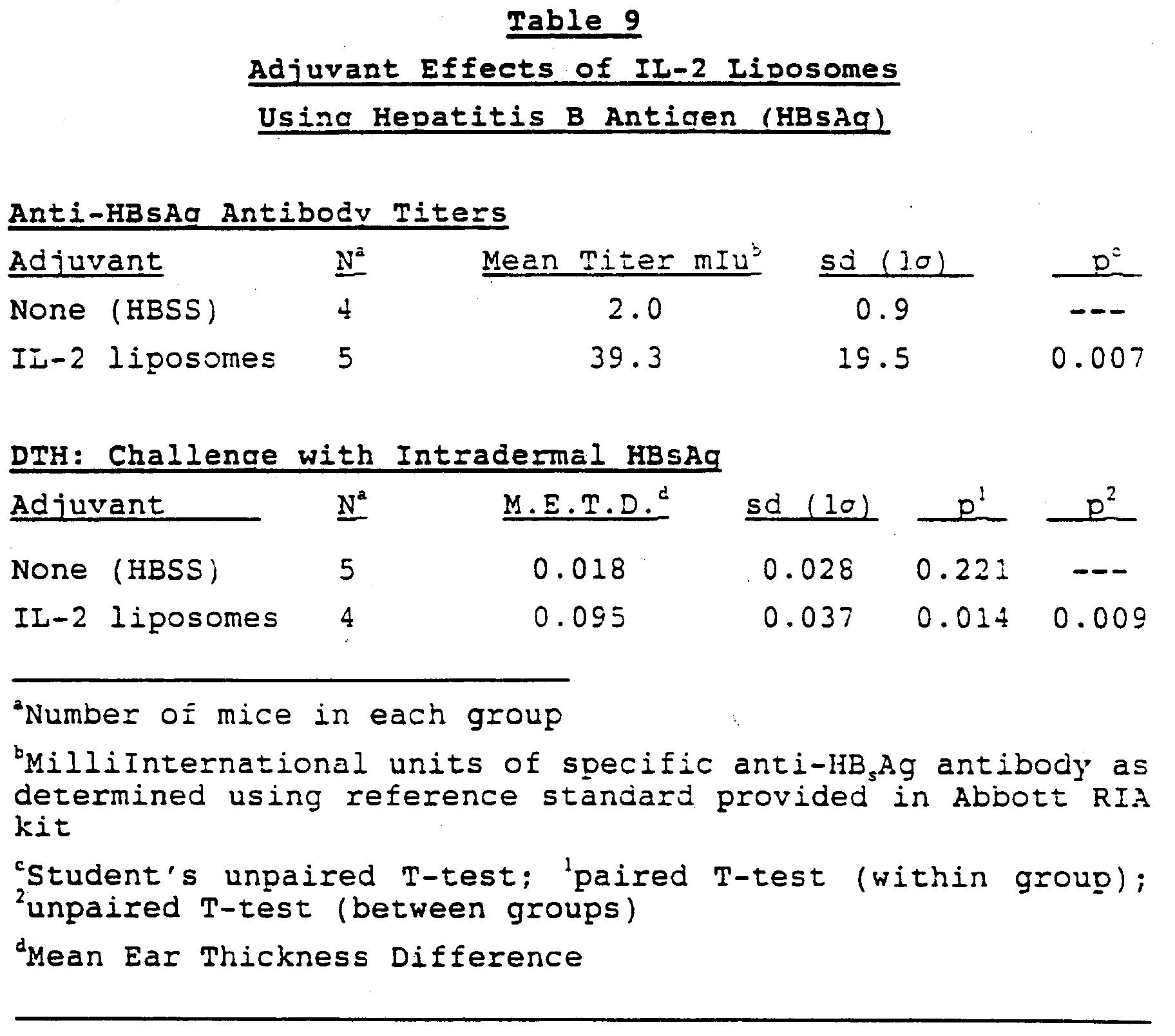
We evaluated correlations between the anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination and the anti-HBs titer at the primary response . The anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination were significantly correlated with the anti-HBs titer at the primary response . Age, sex, and primary response were included in a multivariate linear regression analysis to identify factors associated with anti-HBs titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination the primary response was the only significant factor .
Read Also: How Does One Contract Hepatitis C
What To Do If Your Titer Is Negative
If you have received 3 doses of hepatitis B, and your titer is negative, you need to proceed to additional doses to determine whether you are able to develop immunity. Consistent with CDC recommendations, there are two options to proceed:
OPTION 1:
- Hepatitis B, shot #4 is given as a booster dose. A test for immunity is drawn one to two months after shot #4.
- If the titer is positive, no other steps are required.
- If the titer is negative, you will complete a full second series of 3 shots meaning you will complete 2 more doses of hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis B, shot #5 is administered four to eight weeks following shot #4.
- Hepatitis B, shot #6 is administered 8 weeks after shot #5 and 16 weeks after shot #4.
- The final hepatitis B surface antibody titer is drawn 1 month after completing the hepatitis B, shot #6.
- If titer is positive, you have documented immunity.
- If titer is negative, you are considered a non-responder and should remember this for processing any future blood-borne exposures.
OPTION 2:
Spontaneous Decrease In Anti
To confirm the spontaneous decreases in anti-HB titers, we re-measured anti-HB titers in 247 and 91 subjects who did not receive a booster HBV vaccination at 1 and 2 years after completing the initial vaccination schedule, respectively . Overall, the mean anti-HB titers at 1 and 2 years after vaccination were lower than the mean primary response titers . During the observation period, 18 of the 247 and 17 of the 91 subjects showed anti-HB titers of < 10 mIU/mL at 1 and 2 years after vaccination, respectively.
Correlation between the primary response and the anti-HB titer at 1 and 2 years after vaccination. The vertical axis shows the anti-HB titers at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. The horizontal axis shows the primary response to vaccination. Spearmans correlation coefficient was used to assess the correlation between the anti-HB titer and the primary response at both time periods both values were statistically significant: r=0.893, p< 0.0001 r=0.902, p< 0.001.
Recommended Reading: How Can One Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
Persistence Of Seroprotective Anti
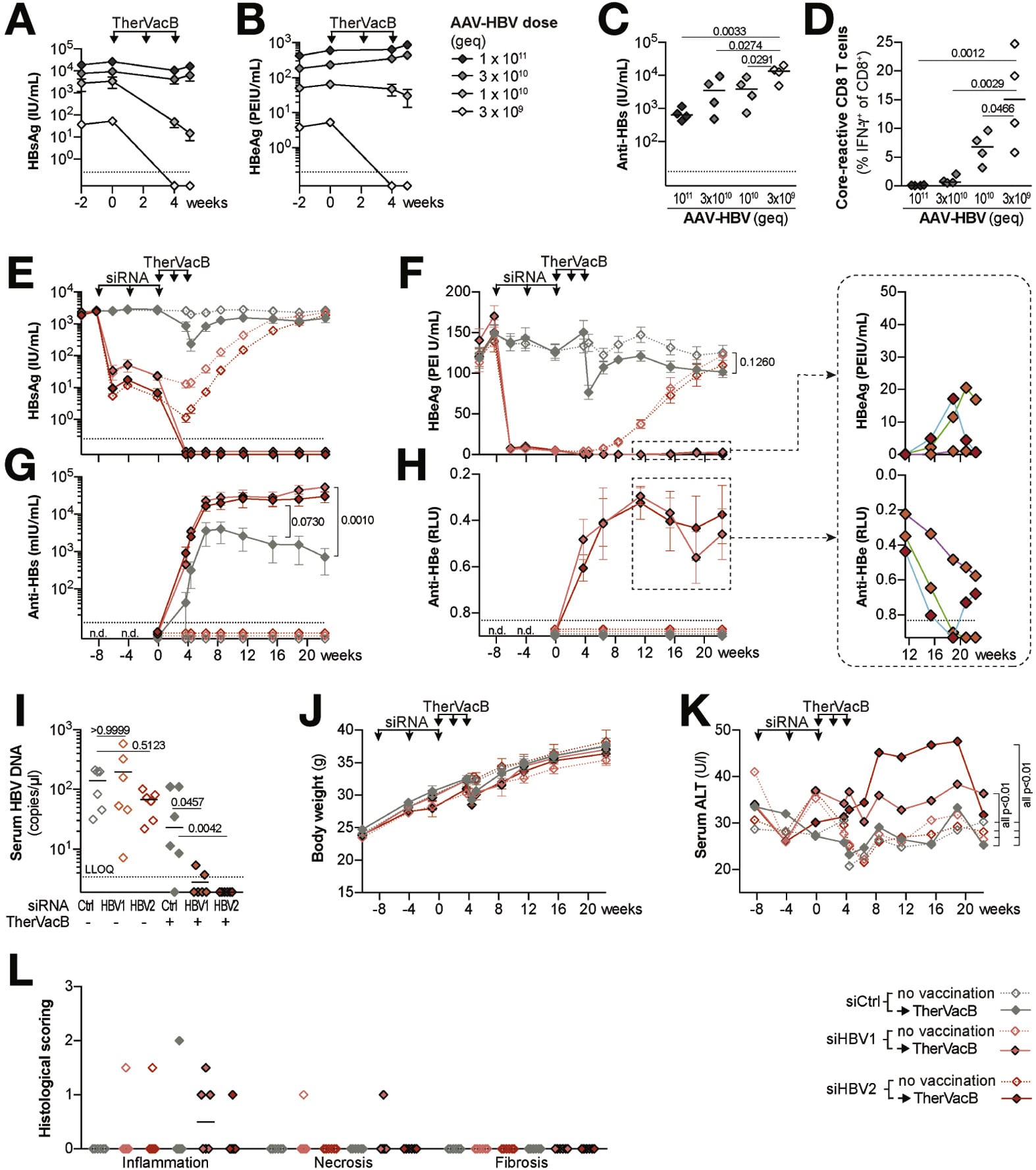
A total of N=5805 patients were presented across the twelve studies,,,,,,,,,,,. Only six studies have reported the anti HBS titer after booster dose of hepatitis-B vaccine, with a follow up of two years,,,,,. A single booster dose of vaccine was administered only to those participants who had antibody titer10mIU/ml at the time of follow up, antibody titer was again determined one month after challenge dose. However Su et al. administered two subsequent booster doses of Hepatitis-B vaccine. Second booster dose was administered six months after the first dose, if the participant had ant-HBV titer10mIU/ml after the first challenge dose. Anti-HBV antibody titer was again determined one month after the second challenge dose. An increase in anti HBS titer10mIU/ml after booster dose ranging from 23.4% to 68.0% of participants than the anti HBS titer before booster dose. Details are given in Table . Among the eligible studies one was randomized placebo controlled study, one study was Phase-4 Open follow up and Challenge Study, three were Cohort Studies,,. Three were follow up studies,, four were cross sectional studies,,,.
Also Check: Antiviral Treatment For Hepatitis C
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Get Hepatitis C
Why Choose Us For Your Hepatitis B Titer
- Since 2002, we have a proven track record of offering excellent customer service, affordable pricing with no hidden fees, and our enduring commitment to protect your personal information.
- No doctor’s order? Our national physician network provides the required doctor’s order for the lab. Insurance is not needed to order lab testing nor will your insurance company be billed.
- We are partnered with two of the largest CLIA certified labs in the US, to offer you the latest lab testing technology with prompt and accurate results.
- With over 3,600 lab locations to choose from and same day collection, we make lab testing quick and convenient. No appointment is needed. Find your local lab with our location finder.
- We offer an extensive and detailed test menu. Ordering can be done online or over the phone. Not finding a test? Simply give us a call.
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
Also Check: Where I Can Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
You May Like: Early Warning Signs Of Hepatitis C
What Is A Surface Antibody Titer
This is the blood test that checks for immunity to Hepatitis B. A positive or reactive anti-HBs test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus. This protection can be the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine or successfully recovering from a past hepatitis B infection. This test is not routinely included in blood bank screenings and is not a routine blood test, so it is not likely that you have done it in the past, unless needed for another academic health related program or job.
A positive anti-HBs test result means you are immune and protected against the hepatitis B virus and cannot be infected. You are not infected and cannot spread hepatitis B to others.
Source: Hepatitis B Foundation: Hepatitis B Blood Tests
Where Can I Find A Hepatitis Titer Test Near Me
Check our lab finder to locate a collection site in your area.
Note: Result turn around times are an estimate and are not guaranteed. Our reference lab may need additional time due to weather, holidays, confirmation/repeat testing, or equipment maintenance.
Requirements:
It may take 6-8 weeks after vaccination for titer tests to be accurate.
It is recommended that someone taking Biotin stop consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection of a sample.
Categories:
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The Hep B Surface Antibody provides numerical results for the antibody level. A positive Surface Antibody typically means that a person has immunity to Hep B. The Hep B Core Antibody will typically be detectable if a person has ever had a Hep B infection. A positive Core Ab with a Positive Surface Ab may mean that a person has a natural immunity due to a previous infection and recovery. The Hepatitis B Surface Antigen is typically used to detect if a person has a current Hep B infection. A positive Hep B Surface Antigen test should be followed up with a doctor.
The Hepatitis Titer Test can be ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hep A and B or just want to check their immune status.
For additional testing, please see our Titer Category.
Turnaround is typically 1-3 business days.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Normal Range
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
21 December 2021
Manal H. El-Sayed & Jordan J. Feld
10 December 2021
Gayatri Amirthalingam, Jamie Lopez Bernal, Mary E. Ramsay
volume 8, Article number: 12550
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a liver infection that is spread through contact with blood or other bodily fluids. It is most commonly spread through sexual contact, shared drug needles, from an infected mother to her child in the womb, or direct contact with the blood of an infected person. Some cases of hepatitis B are acute and do not require medical treatment. However, some people may develop chronic hepatitis B which may require lifelong treatment. According to the CDC, there were 3,218 reported cases of acute hepatitis B in the United States in 2016. However, given that symptoms are not always present, the CDC estimates that total number of acute hepatitis B cases in that year to be closer to 20,900. The number of people in the United States with chronic hepatitis is estimated to be 850,000, but the CDC believes this number may actually be as high as 2.2 million.
You May Like: What Does Non Reactive Mean For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
Question 5 What Is The Natural History Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody During Acute Hepatitis B Infection And Convalescence
HBsAg can be detected in the blood 4 to 10 weeks after exposure. This corresponds to onset of symptoms and viremia detectable by nucleic acid amplification methods. Most hepatitis B infections are self-limited and are associated with disappearance of HBsAg within 4 weeks of onset of symptoms. The anti-HBs then appears and increases to a plateau level that persists indefinitely.2
Recommended Reading: Medical Treatment For Hepatitis C