Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
What Is The Risk
Because universal vaccination of newborns has been recommended since 1991, rates of Hepatitis B in the United States have been going down. But certain groups are still at higher risk, including:
- Infants born to mothers with hepatitis B
- People born outside the United States, or those who travel to areas like Asia or sub-Saharan Africa, where hepatitis B is more common
- Sexual partners of people with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs and share needles or syringes
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting
Hepatitis B Treatment: Medication
There are five FDA-approved oral medications and one injection available to treat hepatitis B. The newer oral medications are stronger and less likely to develop viral resistance and have very few side effects.
The medication cannot cure the disease, but can help reduce the number of viruses in the body and the risk of complications. You may undergo periodic blood tests to monitor drug resistance and determine whether the medication is having an effect.
Read Also: Can Drinking Cause Hepatitis C
How Is Hepatitis B Prevented
Testing & Vaccination
- The hepatitis B vaccine offers excellent protection against HBV. The vaccine is safe and highly effective. Vaccination consists of 3 doses of vaccine over the course of 6 months. Protection lasts for 20 years to life.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all children should receive hepatitis B vaccine starting at birth. .
- The CDC recommends hepatitis B vaccine for persons traveling to countries where HBV is common .
- If you have one or more risk factors for hepatitis B infection, you should get a simple HBV blood test. The blood test will determine whether you are:
- immune to hepatitis B or
- susceptible to hepatitis B and need vaccination or
- infected with hepatitis B and need further evaluation by a physician
Perinatal Hepatitis
- California law requires testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B infection
- If the mother is HBV-infected, she will pass the infection to the baby during the birth process, unless the baby gets immunized within hours of birth
- Giving the infant HBIG and HBV vaccine right away will reliably prevent infection of the infant
- Other family members should best tested for hepatitis B too, and given vaccine if they are not already infected or immune
Healthy Habits
After Exposure to Hepatitis B
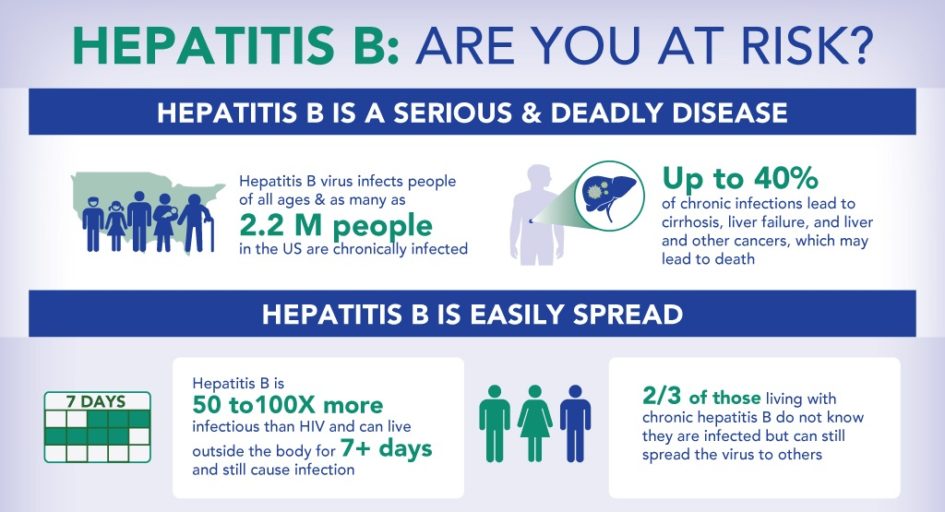
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Also Check: What Is True About Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Because their immune systems arent fully developed, infants and young children are more likely to develop chronic hepatitis B, so its important to limit their exposure to the virus. All expecting women should be screened for hepatitis B. If a high viral load is detected through testing, your doctor will initiate treatment during your third trimester to reduce the likelihood that your baby will contract the disease during delivery.
Additionally, the infants of mothers with hepatitis B should receive the hepatitis B vaccination series and immune globulins at birth so they do not develop hepatitis B.
Eating Diet And Nutrition For Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis B, you should eat a balanced, healthy diet. Obesity can increase the chance of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease , and NAFLD can increase liver damage in people who have hepatitis B. Talk with your doctor about healthy eating and maintaining a healthy weight.
You should also avoid alcohol because it can cause more liver damage.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Injection For
Accessibility And Hbsag Clearance Rate
HBsAg clearance occurs spontaneously or via antiviral treatment in CHB patients. The most commonly used drugs are nucleoside analogue and pegylated interferon . NA drugs include entecavir , tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate . The 2018 AASLD guidelines recommend Peg-IFN, ETV, or TDF as the preferred initial therapy for adults with immune-active CHB. It also suggests that alanine transaminase levels be tested at least every 6 months for adults with immune-tolerant CHB to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or immune-inactive CHB . The 2017 EASL guideline recommends ETV, TDF and TAF as the preferred monotherapy regimens, and the extension of the duration of Peg-IFN therapy beyond week 48 may be beneficial in selected HBeAg-negative CHB patients . The potential side effects of NAs include lactic acidosis for ETV and nephropathy, osteomalacia, lactic acidosis for TDF. CHB patients should be clinically monitored. The most frequently reported side effects for Peg-IFN are flu-like syndrome, myalgia, fatigue, mood disturbances, weight loss, hair loss and local reactions at the site of injection, and these side effects may be partially managed with dose reduction . Currently, the clearance of HBsAg is based primarily on sequential or combined treatment with NA and Peg-IFN.
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Core Ab Total
Preparing For An Appointment
You’re likely to start by seeing your family health care provider. However, in some cases, you may be referred immediately to a specialist. Doctors who specialize in treating hepatitis B include:
- Doctors who treat digestive diseases
- Doctors who treat liver diseases
- Doctors who treat infectious diseases
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
Recommended Reading: Treatment For Hepatitis C Genotype 3
What Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
Chronic hepatitis B is a serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, which can cause severe illness and even death.
If a pregnant woman has hepatitis B, even with no symptoms, her baby has a very high chance of catching it at birth or just after, unless the baby gets a special immune injection and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine shortly after birth.
Sometimes, HBV doesn’t cause symptoms until a person has had the infection for a while. At that stage, they already might have more serious problems, such as liver damage.
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B infection may be short-lived, also called acute. Or it might last a long time, also known as chronic.
- Acute hepatitis B infection lasts less than six months. Your immune system likely can clear acute hepatitis B from your body, and you should recover completely within a few months. Most people who get hepatitis B as adults have an acute infection, but it can lead to chronic infection.
- Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can’t fight off the infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. Some people with chronic hepatitis B may have no symptoms at all. Some may have ongoing fatigue and mild symptoms of acute hepatitis.
The younger you are when you get hepatitis B particularly newborns or children younger than 5 the higher your risk of the infection becoming chronic. Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Home Remedies In Urdu
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated
Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. Most of the time, a doctor or healthcare professional will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever to help with any abdominal pain you have. Speak with a doctor about which medications can help your symptoms.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. For some people, monitoring their symptoms and getting regular liver tests is an appropriate care regimen.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce your symptoms and prevent liver damage, but they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is for you to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
You can lower your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
Read Also: How Many Different Types Of Hepatitis Are There
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Where To Get
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B
Durability And Related Factors After Hbsag Clearance
When patients with HBeAg-positive CHB achieve a satisfactory antiviral treatment endpoint , the clinical recurrence is 2040%, and the virological recurrence can be as high as 8090% after drug withdrawal . Because the safety of drug withdrawal is uncertain, HBsAg clearance is recommended as the ideal treatment endpoint for CHB patients. The accessibility and rate of HBsAg clearance was mentioned above, but the durability of HBsAg clearance after treatment cessation remains controversial.
HBeAg status should also receive attention in the pursuit of HBsAg clearance. The clearance of HBsAg in most patients is based on HBV DNA suppression and HBeAg seroconversion, but a few patients exhibit different HBsAg response patterns, such as HBsAg clearance without HBeAg seroconversion. Only HBsAg clearance based on HBV DNA suppression and HBeAg seroconversion is safe for drug withdrawal .
How Common Is It

In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Caused From
What Happens After A Hepatitis B Infection
Some people carry the virus in their bodies and are contagious for the rest of their lives. They should not drink alcohol, and should check with their doctor before taking any medicines to make sure these won’t cause more liver damage.
Anyone who has ever tested positive for hepatitis B cannot be a blood donor.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Don’t Miss: Can You Heal From Hepatitis C
Closing In On A Cure For Hepatitis B
For Thomas Tu, eliminating hepatitis B is a deeply personal goal.
Tu, a molecular virologist at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research in Sydney, Australia, learnt he had chronic hepatitis B as a teenager. A blood test revealed telltale signs of the infectious liver disease, which Tu had probably acquired at birth.
In his late 20s, Tu started taking a medication to limit the viruss replication and prevent collateral damage to his liver cells. Now 36, he has been on that daily treatment a pill known as a nucleoside analogue ever since.
Yet, even with a therapy that keeps his infection well under control, Tu remains at heightened risk for liver disease. He must juggle visits to specialist doctors and bear prescription-drug costs. And he knows that many others racked by the financial instability, emotional toil and stigma that the lifelong infection can bring have it much worse.
Part of Nature Outlook: Hepatitis B
Im in this quite privileged space to be able to be on therapy and not have any side effects or feel any burden from taking daily medicines, Tu says. Thats not the same for the majority of people living with hepatitis B.
We are using all our weapons to tackle every single step of the virus, says Man Fung Yuen, a hepatologist at the University of Hong Kong.