Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccine Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis B Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Usual Adult Dose for Hepatitis A Prophylaxis:
Primary immunization: 1 mL IM in the deltoid area at 0, 1 and 6 months.Alternatively, a 4 dose schedule given on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed by a booster at month 12 may be used.
Also Check: Where To Test For Hepatitis B
What Is In The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Vaccines are given by a course of three injections, usually as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine scheme.
Although there are different types of vaccines, they usually contain one of the proteins from the surface of the hepatitis B virus thats then inserted in to the genetic code into yeast cells which stops the risk of viral DNA getting into the final product.
They also contain small amounts of sodium chloride and aluminium, and can contain yeast and formaldehyde.
Read Also: Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis C
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Why Do You Need A Hepatitis B Shot
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that cant be transferred person-to-person unless you have contact with an infected persons bodily fluids. Annual infection rates of HBV are going down in the United States thanks to vaccines. So you might be wondering if you or your child needs a shot to protect against hepatitis B.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Contagious Through Urine
For Adults At High Risk Of Exposure
Adults who have not received the hepatitis B vaccine series should be immunized when they have an increased risk of exposure. Job, travel, health condition, or lifestyle all may increase a persons risk of contracting hepatitis B.
People who live or work where there is risk of exposure include:
- Health care and public safety workers who are likely to be exposed to blood or blood products.
- Clients and staff of institutions or residential settings with known or potential HBV carriers.
- People planning extended travel to China, Southeast Asia, Africa, and other areas where hepatitis B infection is high.
People who have health conditions that put them at high risk for exposure or a severe infection include:
- People who have a severe kidney disease that requires them to have their blood filtered through a machine .
- People who have chronic liver disease.
- People who have hemophilia and other conditions in which they need to have blood products on an ongoing basis.
- People who had a stem cell transplant.
People whose lifestyle puts them at high risk for exposure include:
- People who inject illegal drugs.
- Men who have sex with men.
- People who have had more than one sex partner in the past 6 months or who have a history of sexually transmitted infection.
- Household contacts and sex partners of hepatitis B carriers.
- Prison inmates.
Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
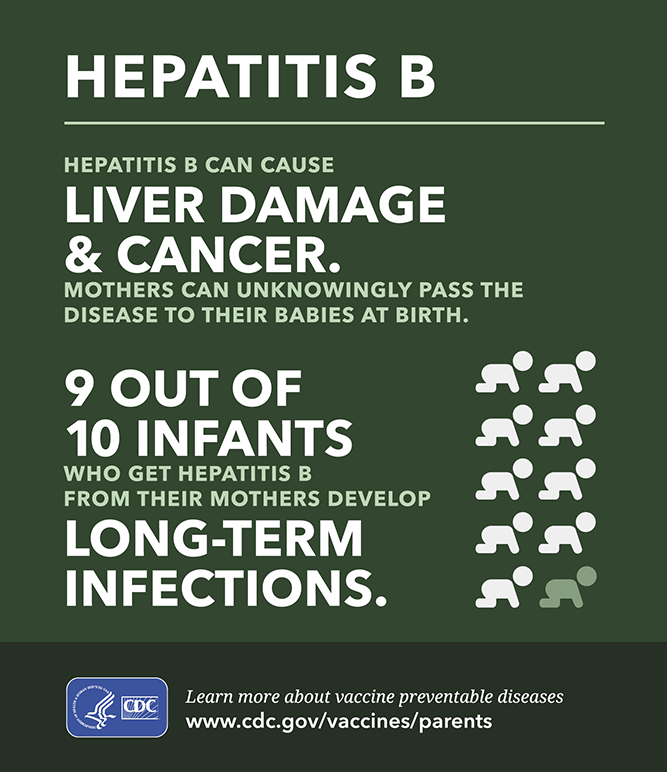
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm as a three-dose series on a 0, 1, and 6-month schedule. Alternative schedules may be considered, noting that a third dose at 6 months, meeting minimum intervals between doses, is needed for maximum, long-term protection. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection.
There are four, 3-dose vaccine brands approved in the U.S.
- PreHevbrio PreHevbrio is only approved for adults age 18 and over.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
Read Also: Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B Guidelines
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis From Seafood
How Can I Contract Hepatitis A
You can contract the hepatitis A virus by eating food or drinking beverages that have been contaminated by human fecal waste.
Resort activities that may put you at risk for hepatitis A include:
Eating food handled by an infected worker who did not wash his/her hands properly after using the washroom
Eating raw or undercooked seafood and shellfish that lived in sewage-polluted water
Eating salads or produce rinsed in contaminated water
Drinking contaminated water or drinks with contaminated ice
Bathing, showering, or swimming in contaminated water
Do The Benefits Of The Hepatitis B Vaccine Outweigh Its Risks
Every year in the United States about 2,000 people die following an overwhelming hepatitis B virus infection. In addition, every year about 22,000 people are infected with hepatitis B. Some of them will remain chronically infected, putting them at high risk of the long-term consequences of hepatitis B virus infection: cirrhosis and liver cancer. In fact, with the exception of influenza and COVID-19 viruses, hepatitis B virus causes more severe disease and death in the United States than any other vaccine-preventable disease. On the other hand, the hepatitis B vaccine is an extremely rare cause of a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. To date, no one has died from this reaction, but it is theoretically possible that this could occur.
Because hepatitis B virus is a common cause of severe disease and death in the United States, and because the hepatitis B vaccine does not cause permanent damage or death, the benefits of the hepatitis B vaccine clearly outweigh its risks.
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B
The current Australian immunisation program provides free hepatitis B vaccine to protect all children against the hepatitis B virus.
A full course of hepatitis B injections must be given for a child to be protected. It is recommended that this course begins within 24 hours of birth with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone. Further doses are routinely given at 2 months , 4 months and 6 months of age, as a combination vaccine.
Vaccination is the best protection against hepatitis B infection. In Victoria a free hepatitis B vaccine is available for a number of groups at high risk, including but not limited to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, men who have sex with men, and people living with HIV.
The adult course involves 3 doses of the vaccine over 6 months and gives protection to about 95 per cent of people. Once you have had the 3 doses, you can have a blood test to see if you are protected.
Also Check: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis Feel Like
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Don’t Miss: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Get The Shot And Stay Informed
The hepatitis A & B virus is silent but violent. The virus is 50 to 100 times more contagious than HIV and can survive outside the body for at least seven days, making it much more infectious then most infectious diseases.
Nobody is immune to the first infection, and once contracted, it can lead to chronic illness and, in extreme cases, even death.
We hope this article answered the question, “How long does Twinrix last?” Also, that it has given you further insight into hepatitis A and B.
You may have landed here because you are travelling or maybe even moving to another country. Along with your vaccinations, your travel insurance is the smartest accessory you can pack. As a leading financial comparison platform, we at Insurdinary will provide you with the best possible quote on the market for all of your insurance needs. Reach out to us today! We look forward to working with you.
Green Shield Health & Dental Plan
Online Life Insurance Quoter
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Hepatitis C
Where Can I Get More Information
- Your vaccination provider, pharmacist, or doctor can provide more information about this vaccine. Additional information is available from your local health department or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indication prescribed.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Read Also: Which Hepatitis Is Transmitted Sexually
Vaccine Side Effects And Risks
The vaccine is safe, effective and generally well tolerated. The most frequent reactions are pain and redness where the vaccine was given. Common side effects include headache, fever, dizziness, nausea or feeling faint shortly after receiving the vaccine. Reactions are usually mild and lasts only a few days.
In rare cases, serious allergic reactions such as trouble breathing, rash, swelling in the throat and face may occur. Allergic reactions can be treated and are usually temporary. Please stay at the clinic for 15 minutes after vaccination for staff to monitor for any reactions. There are no long-term side effects associated with this vaccine.
Accelerated Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
In some instances, it may be necessary to vaccinate within a short period of time to ensure protection before travel. There are accelerated schedules to provide the highest level of protection over a short period of time. Individuals who need an accelerated schedule must have a booster dose at 1 year to ensure long-term protection. Note that the 2-dose Heplisav-B vaccine will also ensure maximum protection over a 1-month period without the need for a booster dose at 1 year.
4-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
Engerix-B is a 3-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated, four-dose schedule, with 3 shots administered within 2 months, and a booster dose at 1 year to provide maximum long-term protection.
4-Dose Combination Hepatitis A and B Vaccine Series
Twinrix is a 4-dose vaccine that can be given on an accelerated schedule to provide protection against hepatitis A and B. Three doses are administered within 1 month, followed by a booster shot at 1 year. This is a common choice of vaccine for those travelling on short-notice outside the U.S. It is important to complete the booster dose at 1 year, to ensure long-term protection.
2-Dose Vaccine Series
Additional Resource Links:
You May Like: Is There A Pill That Cures Hepatitis C
Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with a partner who has HBV infection
- injection drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to a person who has HBV infection
- contact with blood from or open sores on a person who has HBV infection
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with a person who has HBV infection that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 9 parts water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to people with HBV infection
- Sex partners of people with HBV infection
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
- Household contacts or sexual partners of known people with chronic HBV infection
- Health care and public safety workers at risk for occupational exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Patients on hemodialysis
Who should be screened for HBV?