Chronic Hepatitis B Symptoms
Most patients with chronic hepatitis B are asymptomatic unless their disease progresses. Others might have nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue.
Some patients experience worsening of the infection and develop signs and symptoms similar to acute hepatitis.
If patients with chronic hepatitis B progress to cirrhosis they will develop signs and symptoms of liver failure, including:
- Peripheral edema
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Approaches By Virus Life Cycle Stage
consist of a and sometimes a few stored in a capsule made of , and sometimes covered with a layer . Viruses cannot reproduce on their own and instead propagate by subjugating a host cell to produce copies of themselves, thus producing the next generation.
Researchers working on such ââ strategies for developing antivirals have tried to attack viruses at every stage of their life cycles. Some species of mushrooms have been found to contain multiple antiviral chemicals with similar synergistic effects.Compounds isolated from fruiting bodies and filtrates of various mushrooms have broad-spectrum antiviral activities, but successful production and availability of such compounds as frontline antiviral is a long way away. Viral life cycles vary in their precise details depending on the type of virus, but they all share a general pattern:
Before cell entry
This stage of viral replication can be inhibited in two ways:
Uncoating inhibitor
Inhibitors of uncoating have also been investigated.
During viral synthesis
Transcription
Read Also: Hepatitis A And B Symptoms
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
You May Like: Where To Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis B
People are more likely to get hepatitis B if they are born to a mother who has hepatitis B. The virus can spread from mother to child during birth. For this reason, people are more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- were born in a part of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection
- were born in the United States, didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant, and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection
People are also more likely to have hepatitis B if they
- are infected with HIV, because hepatitis B and HIV spread in similar ways
- have lived with or had sex with someone who has hepatitis B
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have sex with men
- are injection drug users
- work in a profession, such as health care, in which they have contact with blood, needles, or body fluids at work
- live or work in a care facility for people with developmental disabilities
- have been on kidney dialysis
- live or work in a prison
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before the mid-1980s
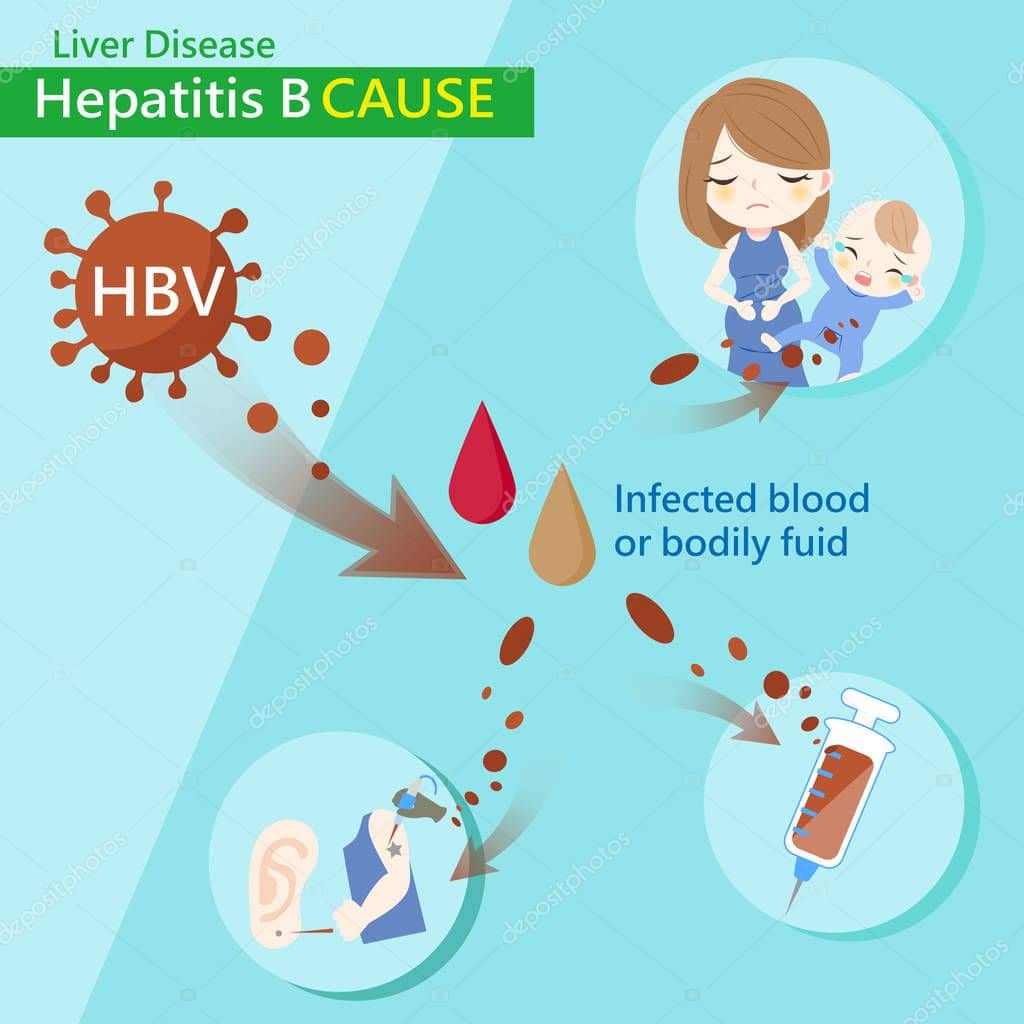
In the United States, hepatitis B spreads among adults mainly through contact with infected blood through the skin, such as during injection drug use, and through sexual contact.12
How Is Hepatitis B Virus Transmitted
The hepatitis B virus transmits through the following:
Also Check: Can Alcohol Cause Hepatitis C
Key Facts About Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is a liver infection capable of causing both short-term and long-term disease.
- The virus is contracted through blood or body fluids of someone who is infected.
- The virus is up to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
- Two thirds of people who have caught Hepatitis B virus remain unaware of their infection.
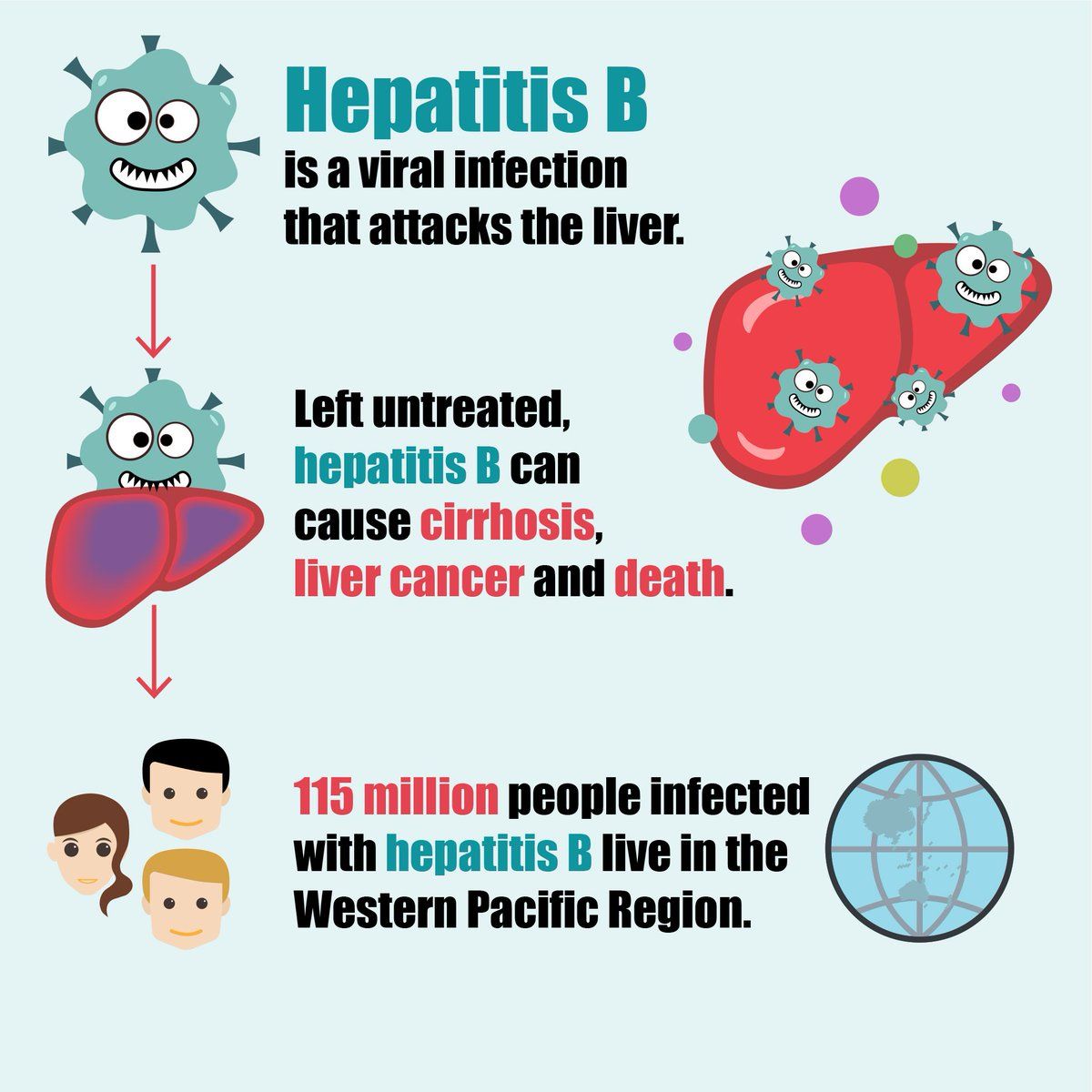
- Every year more than 780,000 fatalities are registered due to complications caused by hepatitis B such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Hepatitis B is a major occupational hazard for health care professionals.
- It is possible to prevent the disease by taking a safe and effective vaccine.
Hepatitis B Prevention And Vaccination
Hepatitis B infection is vaccine-preventable. An effective and safe vaccine is used to protect children and adults from the disease. In addition, the implementation of safe injection procedures, blood safety strategies and safer sex practices can protect against HBV transmission. There are simple and effective ways to prevent the spread of Hepatitis B:
- Practice safe sex using protective measures
- Avoid direct contact with bodily fluids and blood
- Wash your hands carefully after any potential exposure
- Clean up blood spills with a disinfecting solution
- Avoid sharing sharp personal items such as nail clippers, razors or toothbrushes
- Cover all wounds and cuts carefully
- Avoid street drugs
- Make sure sterile needles are used for tattoos, piercing, and acupuncture
- Moreover, all blood and blood components used for blood transfusions should undergo quality-assured screening to reduce the chance of getting HBV.
Hepatitis B virus vaccine
Read Also: What Does Non Reactive Hepatitis B Mean
Where Can I Get More Detailed Information On How To Live With Hepatitis B
More detailed information can be found in the Canadian Liver Foundations Healthy Living with Viral Hepatitis booklet, including:
- What to expect if you have hepatitis B
- The different types of blood tests and what they measure
- How to prepare for an appointment with your doctor
- What choices to make to prevent additional damage to your liver
- Who needs to know if you have hepatitis B and how to tell them
- How to recognize and deal with symptoms
- How to find financial assistance
- What questions to ask when considering alternative therapies.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
You May Like: What Is Drug Induced Hepatitis
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down – if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate – or create – itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis C Come From
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
Hepatitis A infection is usually spread through contaminated food and water. However, there are many other ways through which HAV spreads. The following are major ways:
Read Also: When Was Hepatitis C Discovered
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C And Liver Transplantation
Treatment For Hepatitis B Disease
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis
Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
About The Hepatitis B Virus
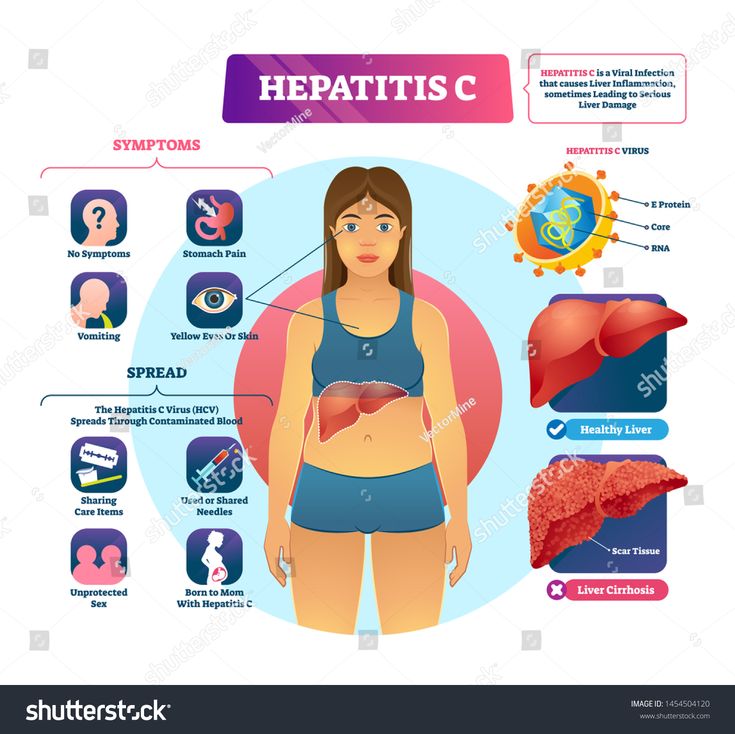
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or âHBsAgâ. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or âHBcAg,â which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive
Hepatitis B Is A Leading Cause Of Death Disease And Economic Burden Globally
Globally, chronic hepatitis B affects approximately 296 million people and contributes to an estimated 820,000 deaths every year. In 2019, over 6 million children under 5 years old were living with hepatitis B. This is because not all countries have a hepatitis B birth dose vaccination program, and some have low vaccination rates for all 3 required doses.
Hepatitis B causes significant economic burden on patients and their families both from direct healthcare costs and indirect costs . The complications of chronic hepatitis B occur later in adult years when the individual is making the most economic contribution, so the indirect costs of income earning affects the economy of their entire community.
How Is It Transmitted
Hepatitis B is highly infectious, and is spread from one person to another through exposure to infected blood and body fluids . It can be spread through:
- blood transfusions or organ transplantation in countries where blood or blood products have not been properly screened for hepatitis B and other viruses transmitted through blood
- unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing needles or equipment for injecting drugs
- unsterilized medical/dental equipment and shared/contaminated materials or equipment used for tattooing, body piercing or acupuncture
- sharing toothbrushes or razors
- household contact between family members
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B