Antibody Titers And Gap Time
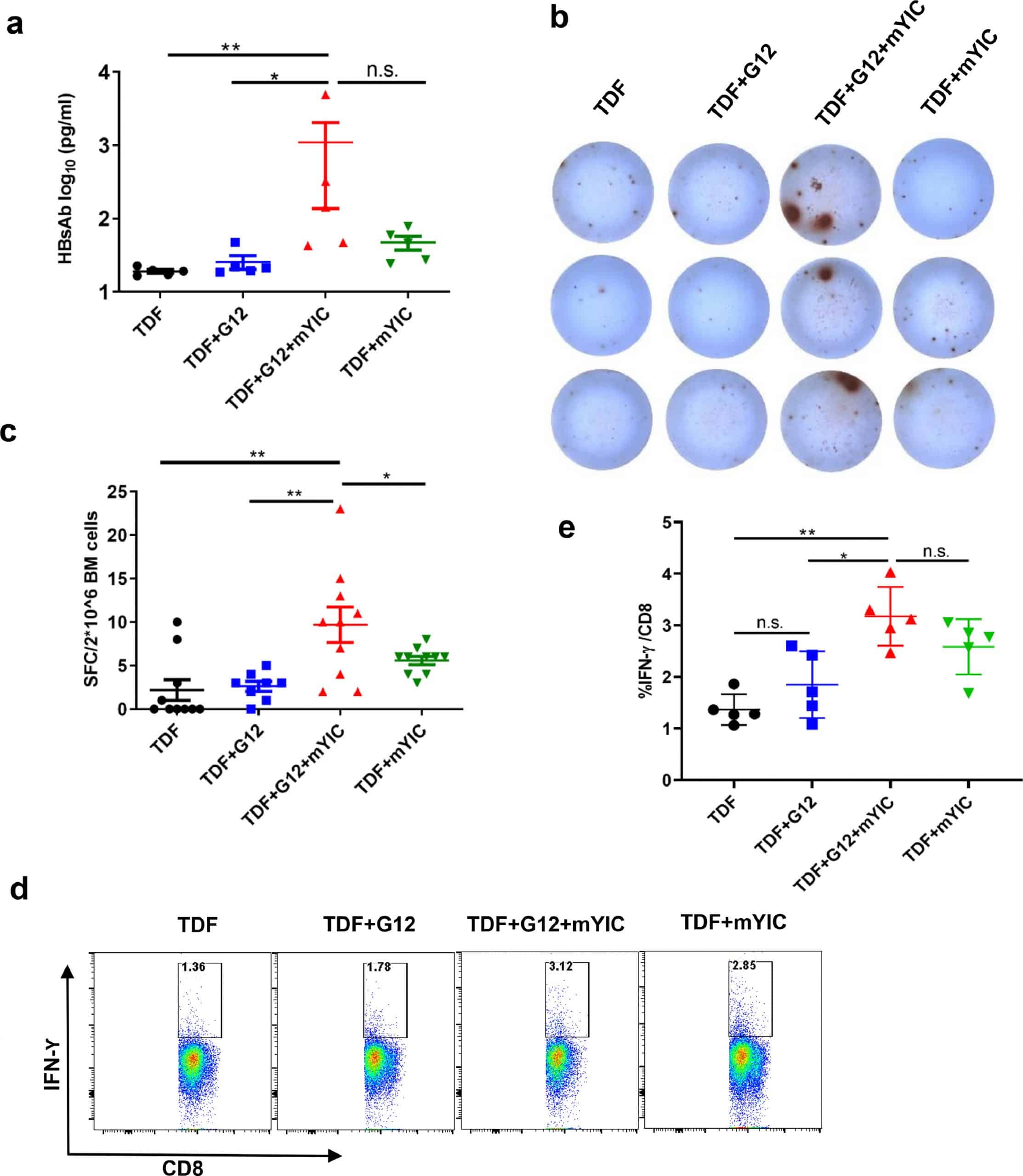
Median gap time between last and preceding vaccine dose was 2.4 months. After log-transformation in anti-HBs and gap time, because their non-normal distribution, linear regression models were tested. No association between gap time and anti-HBs was found in unadjusted , but it was detected in adjusted models . Sex did not modify the relationship between anti-HBs and gap time of the last two doses . The risk of anti-HBs < 10 UI/L was influenced by this interval of doses .
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
How Do T Cells And B Cells Work
Your T cells and B cells work together. They each have different roles in your immune system.
Your T cells help kill infected cells and control your bodys immune response to foreign substances. Most of your T cells need the help of another immune cell to become activated. After your T cells are activated, they multiply and specialize into different types of T cells. These types include:
- Cytotoxic T cells: Cytotoxic T cells attach to antigens on infected or abnormal cells. Then, they kill the infected cells by making holes in their cell membranes and inserting enzymes into the cells.
- Helper T cells: Helper T cells help your other immune cells. Some helper T cells help B cells make antibodies against foreign invaders. Others help activate cytotoxic T cells.
- Regulatory T cells: Regulatory T cells make substances that help end your immune systems response to an attack. Sometimes, they prevent harmful responses from occurring.
B cells have receptors on their surfaces where antigens attach. B cells learn to recognize the different antigens and produce specific antibodies to attack each one. The B cells respond to antigens in two ways:
Recommended Reading: How To Order Hepatitis B Titer
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Approvals And Informed Consent
This study was approved by the Alaska Area and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention institutional review boards, as well as the Yukon-Kuskokwim Health Corporation and the Norton Sound regional health boards. Additionally, the study was approved by the Southcentral Foundation and the Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium. At the 35-year follow-up, the continued study objectives were described, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant. In addition, this study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki as reflected in a priori approval by the appropriate institutional review boards.
Understanding Changes In Biomarkers During Disease Progression
Understanding the changes in HBV biomarkers over the course of a persons infection and recovery is key to interpreting the test results. Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 depict the typical biomarker changes over the course of hepatitis B disease.
Figure 3-1. Typical serologic course of acute hepatitis B to recovery
Acute, resolved, and chronic hepatitis BApproximately 90% of people > 5 years of age with acute hepatitis B will spontaneously clear their infection . People with resolved hepatitis B will remain positive for total anti-HBc and develop anti-HBs that protect against future HBV infection . Chronic hepatitis B is defined as an HBV infection lasting > 6 months. During the typical course of chronic infection, the total anti-HBc and HBsAg markers will always be present, whereas anti-HBc IgM will disappear . Hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B e antibody are variably present. HBV DNA levels vary during the course of chronic infection. Any detectable HBV DNA level is considered positive for surveillance purposes.
HBV-infected people with mutations in HBsAg that cannot be detected by current serologic assays may present with a negative HBsAg result despite high blood levels of HBV DNA. Some laboratories have the capacity to detect HBsAg mutants. Any HD interested in determining which laboratories can detect HBsAg mutants should follow-up with the major laboratories that perform HBsAg testing in their jurisdiction.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Rite Aid
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Can I Take The Test At Home
Samples for hepatitis B testing can be collected at home. At-home hepatitis B testing requires a patient to collect a blood sample, typically from a fingerstick using a very small needle provided in the test kit. Once a blood sample is collected, it is prepared according to the instructions contained in the test kit and mailed to a laboratory for testing.
Because there are numerous types of tests for HBV, it is important to look closely at the specific components of any at-home test kit. Many at-home test kits only look for hepatitis B surface antigen .
Also Check: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can You Donate Plasma With Hepatitis C
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Effects On Liver
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Test Code: 499
Methodology: Immunoassay
Clinical Significance: The detection of anti-HBs is indicative of a prior immunologic exposure to the antigen or vaccine. To determine immune status as 10 mIU/mL as per CDC guidelines, please order Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, Quantitative.
Alternative Name: Anti-HBS Anti-HBS Qual Anti-HBSAG Australian Antibody HB Surface Ab
Supply: T01 â Red/Gray SST 8.5mL
Preferred Specimen: Serum
Transport Container: Serum Separator Tube
Transport Temperature: Room Temperature
Specimen Stability: Room Temperature: 5 days
Rejection Criteria: Gross Hemolysis, Gross Lipemia
For additional supply or collection device information, please contact DLOâs Customer Service at 891-2917, option 2.
The information contained here on the Diagnostic Laboratory of Oklahoma website is not to be construed as medical recommendations or professional advice. Neither DLO nor its affiliates, agents or any other party involved in the preparation or publication of the works presented is responsible for any errors or omissions in information from the use of such information. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information contained herein with other reliable sources and to direct any questions concerning personal health care to licensed physicians or other appropriate health care professionals.
Also Check: What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis
Also Check: Where To Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
Cases And Clusters Of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis B data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis B that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation based on the degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
- People of childbearing age who are or have the potential to become pregnant, indicating the potential for perinatal transmission
- Children 24 months of age to detect perinatal transmission
- People in age and demographic groups for whom infection may be acute due to recent transmission, including those
- 70 years of age
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B And C Difference
Levels Of Hepatitis B Antibody Titers Are Affected By Age And Doses Gap Time In Children From A High Endemic Area Of The Western Amazon
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Shot For Hepatitis C
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Cvs
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
What Does A High Level Of Lymphocytes Mean
High levels of lymphocytes in your blood are called lymphocytosis. Lymphocytosis is usually due to an infection or illness. Your body sometimes produces extra lymphocytes to help fight infections and illnesses. But a more serious condition can also cause a high lymphocyte count, including:
- Autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
- Rare inherited conditions such as severe combined immunodeficiency , ataxia-telangiectasia, DiGeorge syndrome and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.
- Radiation or chemotherapy treatments.
Don’t Miss: Common Ways To Get Hepatitis B
Case Reporting And National Notification
Cases of acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B, and hepatitis B during pregnancy should be reported to HDs as specified by state, territorial, or local regulations. Acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B are nationally notifiable conditions . Hepatitis B cases are identified using an event code corresponding to the hepatitis B condition . Data are sent weekly or more frequently, depending on the infrastructure of the jurisdiction sending the data. Cases might be re-classified or removed as needed after the initial transmission to CDC, as long as the changes occur before surveillance data are finalized each year.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Recommended Reading: How Many Doses Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Submission And Collection Notes
Detailed instructions for ordering Hepatitis B testing are available to assist with completing the Hepatitis Serology boxes in section 3 of the General Test Requisition.
For testing all Hepatitis markers, HIV, HTLV, Syphilis and Rubella, you only are required to submit two FULL red top or serum separator tubes .
Do NOT submit glass tubes.
Hepatitis B Prevention Strategies
HepB vaccination is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention efforts. A comprehensive strategy to eliminate HBV transmission includes universal vaccination of infants beginning at birth, routine vaccination of previously unvaccinated children less than age 19 years, and vaccination of adults at risk for HBV infection, including those requesting protection from HBV without acknowledgement of a specific risk factor. It also includes universal testing of pregnant women for HBsAg to identify newborns who require immunoprophylaxis for prevention of perinatal infection and to pregnant women who can benefit from antiviral therapy to reduce perinatal transmission.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Or C
Postexposure Management Of Health Care Personnel After Occupational Exposure To Blood And Body Fluids By Health Care Personnel Hepb Vaccination And Response Status
| HepB Vaccination and Response Status | Postexposure testing results for source patient | Postexposure testing results for HCP | HBIG* postexposure prophylaxis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complete vaccination | Yes |
*HBIG should be administered intramuscularly as soon as possible after exposure when indicated. The effectiveness of HBIG when administered greater than 7 days after percutaneous, mucosal, or nonintact skin exposures is unknown. HBIG and HepB vaccine should be administered in separate anatomic injection sites.Should be performed 1 to 2 months after the last dose of the HepB vaccine series using a quantitative method that allows detection of the protective concentration of anti-HBs .§A responder is defined as a person with anti-HBs greater than or equal to 10 mIU/mL after 3 or more doses of HepB vaccine.¶A nonresponder is defined as a person with anti-HBs less than 10 mIU/mL after 2 complete series of HepB vaccine.**HCP who have anti-HBs less than 10 mIU/mL, or who are unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated, and sustain an exposure to a source patient who is HBsAg-positive or has unknown HBsAg status, should undergo baseline testing for HBV infection as soon as possible after exposure and follow-up testing approximately 6 months later. Initial baseline tests consist of total anti-HBc testing at approximately 6 months consists of HBsAg and total anti-HBc.