Lc And Hcc Development
During the 2-year follow-up, periodically monitored imaging examinations and alpha-fetoprotein diagnosed 2 ETV-treated patients with HCC after more than 6-month drug treatment, one of whom had LC at baseline. Two patients were older than 40 and achieved BR after 3 months. Both patients had high HBV DNA level , and achieved CVR after 18-month therapy, indicating poor effect of ETV in these 2 patients. Furthermore, both patients had high baseline HBsAg, and neither of them achieved HBeAg or HBsAg seroclearance. In addition, 2 patients in ETV group were detected to develop LC during the 2-year follow-up, with no patient in TDF group. Despite these 2 patients were HBeAg-positive and had high HBV DNA and HBsAg level at treatment initiation, both of them achieved sustained virological response and sustained BR after 3-month antiviral therapy, but neither of them achieved HBeAg or HBsAg seroclearance. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that there was no independent factor in the development of HCC and LC.
Entecavir + Tenofovir Works Well For Hepatitis B Patients With Prior Treatment Failure
A dual regimen of entecavir plus tenofovir for 48 weeks led to virological response and was generally well-tolerated as second-line therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients who had failed previous nucleoside/nucleotide treatment, according to a poster presentation at the 64th AASLD Liver Meeting last week in Washington, DC.
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection is treated with oral nucleoside/nucleotide analogs including entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine , adefovir , and telbivudine . While these drugs can reduce HBV viral load to an undetectable level while on therapy, they typically do not lead to post-treatment sustained virological response or hepatitis B antigen loss.
HBV can develop resistance mutations that compromise long-term efficacy especially of the oldest drug, lamivudine and limit future treatment options, but entecavir and tenofovir have a higher barrier to resistance.
Maciej Jablkowski of the Medical University of Lodz in Poland and colleagues conducted the ENTEBE study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of entecavir plus tenofovir in chronic hepatitis B patients who had failed previous nucleoside/nucleotide therapy.
This multicenter Phase 3b trial enrolled 92 participants. Three-quarters were men, 76% were white, and the median age was 43 years. A majority were hepatitis B e antigen positive and 76% had normal alanine amino transferase at baseline. People with decompensated liver disease were excluded.
Researchers Suggest Finite Therapy Could Be An Option With Entecavir Or Tdf In Certain Cases
byZaina Hamza, Staff Writer, MedPage Today July 20, 2022
Chronic hepatitis B patients who discontinued tenofovir disoproxil fumarate after achieving viral suppression had higher rates of clinical relapse compared to those who stopped entecavir, a global retrospective study found.
At 6 and 24 months, clinical relapse rates after stopping TDF grew from 31% to 58%, which was significantly higher than after entecavir cessation , reported Harry Janssen, MD, PhD, of the Erasmus MC University Medical Center in Rotterdam, The Netherlands, and colleagues from the RETRACT-B study group.
In the study of 1,402 patients who discontinued either of the two treatments after viral suppression, hepatitis B surface antigen loss occurred in 6.8% over 18 months of off-treatment follow-up, with no significant differences between the TDF and entecavir groups, according to the findings in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Both agents are recommended in international guidelines as first-line treatments in chronic hepatitis B, have good safety profiles, and have shown comparable rates of viral suppression, according to Janssen and co-authors.
“Over the past decade, there has been strong interest in understanding whether one drug is superior to the other in terms of preventing or delaying HCC development or viral relapse following treatment discontinuation,” the group noted.
Disclosures
Primary Source
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Read Also: Hepatitis C Ab W/reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
Characteristics Of The Study Patients
Among 414 patients treated with ETV or TDF at the center, between January 2017 and May 2019, who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 124 patients were administered with TDF and the remaining 290 patients were administered with ETV. The baseline demographic clinical characteristics of all 414 patients are shown in Table 1, demonstrating baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of the two groups were not comparable at baseline. More patients in TDF group had high baseline HBV DNA, HBeAg, and HBsAg levels, and were HBeAg seropositive while patients treated with ETV were older, had higher ALT level and more male at the beginning of treatment. To eliminate the influence of the baseline characteristics, we performed the PSM method to match 124 patients in the TDF group with 124 patients in the ETV group by age, sex, baseline HBV DNA levels, baseline HBsAg level, HBeAg status, and cirrhosis. There was no statistical significance detected in post-matched patients .
Table 1. The baseline characters of pre- and post-matched patients.
Predictive Factors On The Long
Sixty seven patients had low baseline serum HBV DNA levels , 173 patients showed IVR-3 and 89 patients were negative for HBeAg. The patients with low serum HBV DNA levels, IVR-3 or HBeAg negativity had a significantly higher probability of achieving a VR. In patients with low baseline serum HBV DNA levels, the cumulative VR rates were 84%, 94%, 97% and 100% at 6, 12, 24 and 36 months, which were in contrast with the rates, 40%, 72%, 80% and 83% in patients with high baseline serum HBV DNA levels . The cumulative VR rates were 64%, 89%, 94% and 100% in patients with IVR-3 and 5%, 32%, 46% and 51% in patients without IVR-3 at 6, 12, 24 and 36 months, respectively . A similar pattern was observed according to HBeAg status .
Fig. 4
Cumulative virologic response rate according to HBV DNA levels and IVR-3. a Cumulative VR rates in the patients with high baseline serum HBV DNA levels at 6, 12, 24 and 36 months were 40%, 72%, 80% and 83%, respectively. They were 84%, 94%, 97% and 100%, respectively, in the patients with low baseline serum HBV DNA levels. b Cumulative VR rates in the patients without IVR-3 at 6, 12, 24 and 36 months were 5%, 32%, 46% and 51%, respectively. And in the patients with IVR-3, they were 64%, 89, 94 and 100%, respectively
You May Like: Signs Of Hepatitis C In Men
Incidence Rates Of Hcc In The Etv And Tdf Groups
Figure 3 shows the cumulative incidence rate of HCC. Like LC-related complications, the cumulative incidence and annual incidence of HCC were analyzed only in the ETV and TDF groups due to the short duration of TAF treatment. Annual incidence rate of HCC was 0.552 per 100-person years in the ETV group and 0.299 per 100-person years in the TDF group. This difference between groups was not significant .
Fig. 3.
Cumulative incidence rates of hepatocellular carcinoma. ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
HCC occurred in 10 of the 163 ETV-treated patients , 3 of the 154 TDF-treated patients , and no TAF-treated patient during the follow-up period. However, these differences among groups were not statistically significant .
Tenofovir Alafenamide Versus Entecavir For The Treatment Of Chronic Hepatitis B
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government.Know the risks and potential benefits of clinical studies and talk to your health care provider before participating. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : May 1, 2019Last Update Posted : February 10, 2022 |
| Drug: Tenofovir alafenamideDrug: Entecavir | Phase 4 |
Recommended Reading: What Does Reactive Mean In Hepatitis B
Safety And Efficacy Of Etv And Tdf At 48 Weeks
At 48 weeks after ETV or TDF administration, cholesterol increased by 6 mg/dL in the ETV group and decreased by 10 mg/dL in the TDF group . However, there were no significant differences in changes in ALP, eGFR, or LC complications between these 2 groups . Differences in HBeAg seroconversion, CVR, and ALT normalization were not significantly different between the ETV and TDF groups, indicating that these 2 drugs had similar efficacy .
Table 3.
Safety and efficacy of ETV and TDF at 48 weeks
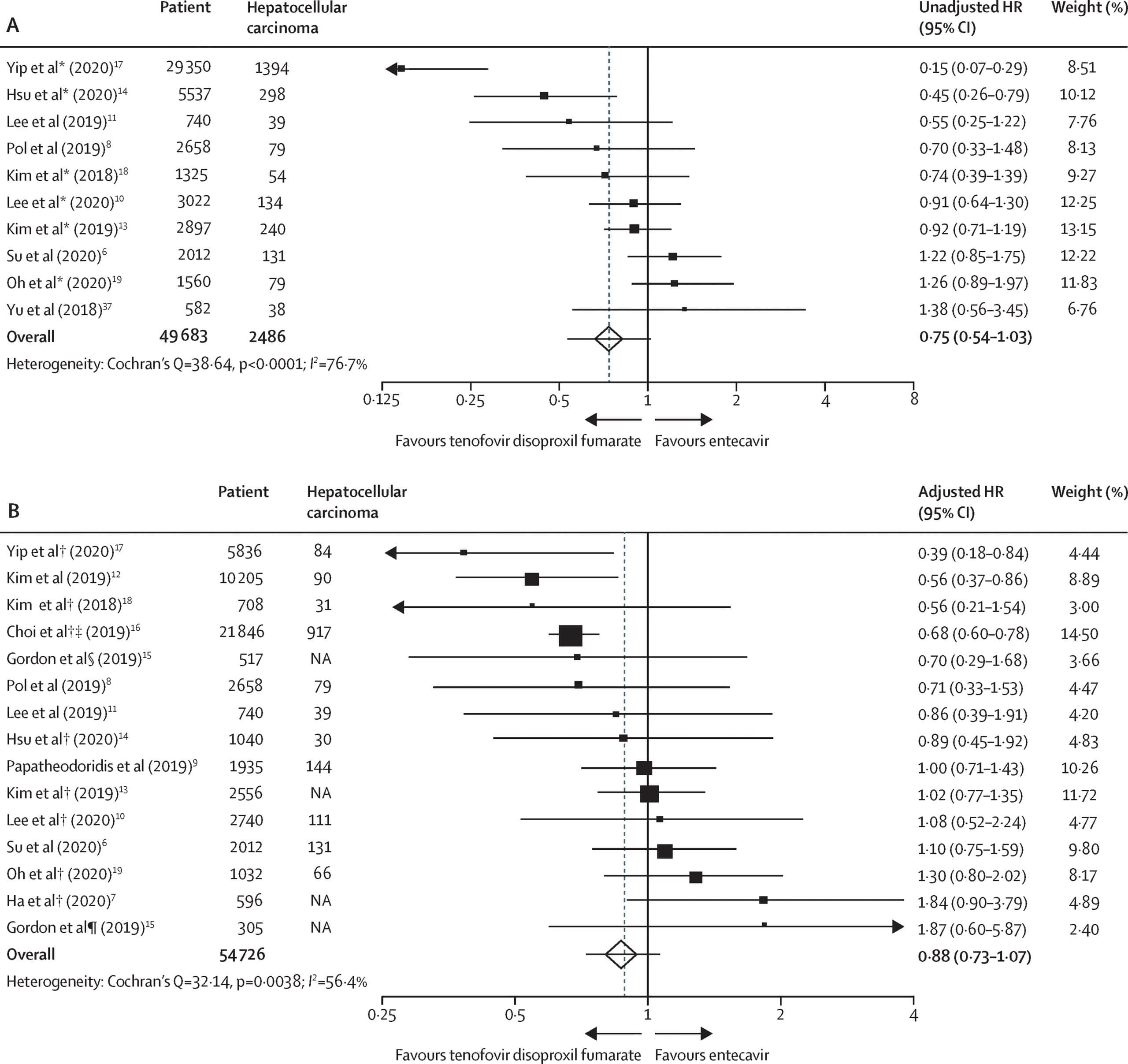
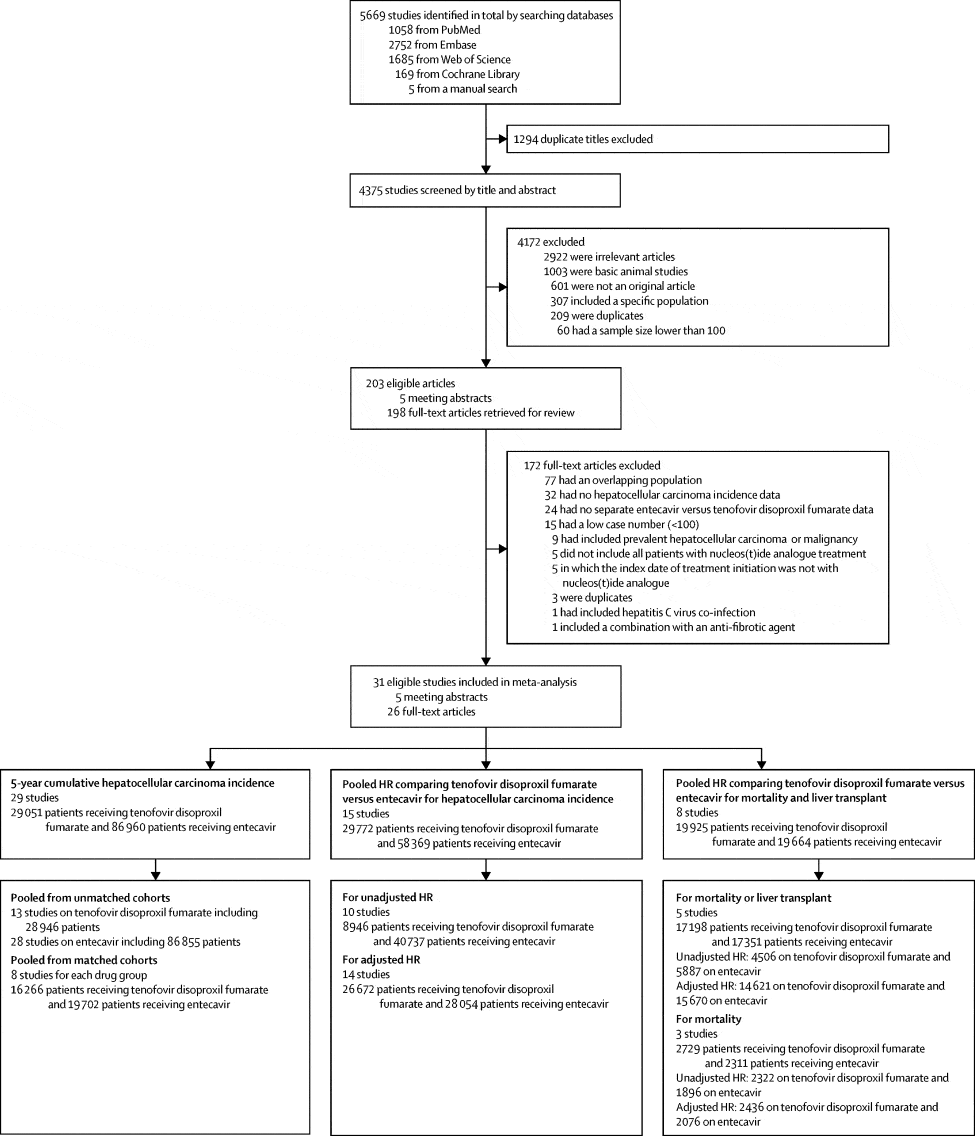
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence With Tenofovir Versus Entecavir In Chronic Hepatitis B: A Systematic Review And Meta
- Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, TaiwanSchool of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, TaiwanSchool of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, TaiwanGraduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences, China Medical University, Taichung, TaiwanDivision of Gastroenterology, Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital, New Taipei, Taiwan
- Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, TaiwanSchool of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- AffiliationsDepartment of Infectious Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, ChinaNational Local Joint Engineering Research Center of Biodiagnosis and Biotherapy, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, TaiwanSchool of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, E-Da Hospital, Kaohsiung, TaiwanSchool of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- Mindie H NguyenCorrespondenceCorrespondence to: Prof Mindie H Nguyen, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Stanford University Medical Center, Palo Alto, CA 94304, USA
- Contributed equally
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Newborn
Population And Baseline Characteristics
A total of 701 patients with CHB who were treated with ETV, TDF, or TAF were identified . We excluded 338 patients who were treated with antiviral agents for < 48 weeks , had their prescription changed or stopped taking the drug , had incomplete electronic medical records , had low-level viremia at baseline , or were diagnosed with CKD . A total of 363 patients were therefore enrolled in the study. Baseline characteristics and laboratory characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the ETV, TDF, and TAF treatment groups
Fig. 1.
Flowchart of participant enrollment. CHB, chronic hepatitis B ETV, entecavir TDF, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate TAF, tenofovir alafenamide CKD, chronic kidney disease.
Median age of patients was 51 years and 66.4% of patients were male. There were some differences among the 3 groups. Median duration of treatment with ETV, TDF, and TAF was 75.0 months , 43.0 months , and 13.0 months , respectively . There were also significant differences in the number of patients previously treated with NAs. The proportion of NA naive patients was 93.3, 73.4, and 78.2% in the ETV, TDF, and TAF groups, respectively .
Basic Characteristics Of Patients Included
During the study period from January 2008 to December 2013, a total of 13,355 consecutive adult patients with CHB and no history of HCC or decompensated liver cirrhosis were treated with ETV or TDF. After removing patients based on exclusion criteria, 12,388 were considered eligible for analysis . The basic demographic and clinical characteristics of all patients included in the study are summarized in Table I. When these 2 groups were
You May Like: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis C
Safety And Efficacy Of Etv And Taf At 48 Weeks
Table 4 shows the results of laboratory parameters used to assess the safety of ETV and TAF. There were no differences between these 2 groups in cholesterol, ALP, or creatinine levels, or the incidence of LC complications. In terms of efficacy, there were no differences in HBeAg seroconversion, CVR, or ALT normalization between the 2 groups .
Table 4.
Safety and efficacy of ETV and TAF at 48 weeks
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Is Not Associated With A Lower Risk Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Compared To Entecavir In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Hye Won Lee1,2,3Seung Up Kim1,2,3
1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea.
2Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea.
3Yonsei Liver Center, Severance Hospital, Seoul 03722, Korea.
Correspondence to: Seung Up Kim, MD, PhD, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1, Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea. E-mail: ksukorea@yuhs.ac
Received: First Decision: Revised: Accepted: Academic Editors: Copy Editor: Production Editor:
© The Author 2022. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
You May Like: Hiv And Hepatitis B And C Are Incurable
Significance Of This Study
What is already known on this subject?
-
The treatment with highly potent antiviral drugs tenofovir and entecavir for patients with chronic hepatitis B has led to a decrease in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver-related events.
-
Although there has been no head-to-head randomised controlled trial that directly compared TDF and ETV, virologic, serologic and biochemical responses are reported to be similar but whether there is a difference between the two agents in the extent of decreasing incidence rates of HCC and mortality has not been clarified thus far.
What are the new findings?
-
No difference was observed between TDF and ETV in the incidence rates of HCC and all-cause mortality or liver transplantation in the entire cohort and in the subgroups of patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
-
HCC develops consistently even after treatment with highly potent antiviral drugs and in patients without cirrhosis, which indicate the importance of regular surveillance for HCC in all patients with CHB.
Data Collection And Definition
Data were collected from electronic medical records at the Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong and included clinical information, and laboratory data. Medical history, such as LC, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, history of taking lipid-lowering agents, tuberculosis, malignancy, chemotherapy, and immunosuppressive therapy was included in the demographic data. Patients underwent routine blood chemistry test and virological assessments, including hemoglobin, platelets, international normalized ratio of prothrombin time, liver function tests, serum HBV-DNA level, and status of HBeAg every 36 months. According to our outpatient protocol, patients were also followed up every 612 months with ultrasonography and serum alpha-fetoprotein level to screen for HCC.
We calculated eGFR using the modification of diet in renal disease GFR equation as 186 × 1.154 × 0.203 × 1.212 × 0.742 . HBV DNA was measured by a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay, and CVR was defined as an HBV DNA level below 20 IU/mL. Diagnosis of LC was clinically defined taking into account platelet count, serum albumin level, prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and radiological image findings included splenomegaly and liver surface nodularity. Endoscopic findings such as esophageal or gastric varices were considered in the diagnosis of LC.
Don’t Miss: How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Tenofovir Versus Entecavir On Recurrence Of Hepatitis B Virusrelated Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Surgical Resection
Chanyoung Jo
Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Department of Gastroenterology, Liver Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Address Correspondence and Reprint Requests to:
Young-Suk Lim, M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine
88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu
Chanyoung Jo
Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Department of Gastroenterology, Liver Center, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Address Correspondence and Reprint Requests to:
Young-Suk Lim, M.D., Ph.D.
Department of Gastroenterology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine
88 Olympic-ro 43-gil, Songpa-gu
Safety And Efficacy Of Etv Tdf And Taf Treatment At 48 Weeks
To evaluate the safety of ETV, TDF, and TAF treatment at 48 weeks after administration, changes in cholesterol, ALP, creatinine, and the presence of LC-related complications were evaluated . At 48 weeks, cholesterol level had decreased in the TDF group and mildly increased in the ETV and TAF groups compared to baseline . eGFR changes were not significantly different between the 3 groups at 48 weeks, nor were ALP changes . There was no significant difference in LC complications after 48 weeks among groups . In the ETV group, 3 patients developed LC complications, 2 developed variceal bleeding, and 1 patient developed ascites. There was only 1 case of variceal bleeding in the TDF group and no LC complications after 48 weeks in the TAF group.
Table 2.
Comparison of safety and efficacy in laboratory parameters and LC-related complications between baseline and 48 weeks in the ETV, TDF, and TAF groups
Read Also: Is There Cure For Hepatitis C
Conflict Of Interest Statement