How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will look at your health history and give you a physical exam.
Some lab blood tests used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis include:
- Liver function tests. These check for inflammation or damage to your liver.
- Complete blood count or CBC. Looks at the number and types of cells in your blood.
- Coagulation panel. This test looks at how well the clotting proteins are working.
- Electrolyte panel. Checks to see if you have an electrolyte imbalance.
- Autoimmune antibodies. These are used to see if you have autoimmune hepatitis or another liver disease with similar symptoms.
- Other liver tests. These are done to check for other possible types of liver disease.
You may also have imaging tests such as:
Genetics And Predisposing Factors
Autoimmune hepatitis is thought to result from an environmental trigger in a genetically predisposed individual, leading to loss of tolerance of T lymphocytes with subsequent hepatocyte attack.
It is a polygenic disease and does not follow a Mendelian distribution. Therefore there is no need to screen family members of patients with AIH. There is a strong genetic association with the alleles of the major histocompatibility complex class II. The presence of human leukocyte antigen genes HLA DRB1*03 and HLA DRB1*04 predisposes to AIH type 1 and affect the disease course and response to treatment. Individuals who are positive for HLA DRB1*03 are younger, respond less favorably to corticosteroid therapy, and progress more often to liver failure. On the other hand, the presence of HLA DRB1*04 is associated with higher rates of concomitant autoimmune disorders.
Autoimmune hepatitis can also be associated with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy syndrome, an autosomal recessive disease characterized by hypoparathyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy is the only AIH-associated disease that follows a Mendelian pattern of inheritance and genetic counseling should be offered for patients and family members.
Table 1: Drugs Associated With Drug-Induced Autoimmune-Like Hepatitis
| Association |
|---|
Complementary And Alternative Medicines
Many complementary and alternative medicines available suggest they can ease the symptoms of liver disease. As with any other medicine, you should use them with care. Your doctor or a registered dietitian will have full access to your medical history and be able to offer advice on treatments that are specific to you and will not interact with any of your other medications.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take To Cure Hepatitis C
Do Medicines Used To Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis Have Side Effects
Medicines for autoimmune hepatitis can cause side effects. Your doctor will monitor any side effects and help you manage them while you take these medicines. Your doctor also may adjust the doses or change the medicines you take. You may need to stop taking corticosteroids or azathioprine if you have severe side effects.
Side effects of corticosteroids may include
- changes in how you look, which may include weight gain, a fuller face, acne, or more facial hair
Corticosteroids and azathioprine suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, which increases your risk for infections. These medicines can also increase your risk of developing cancers, especially skin cancers.
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
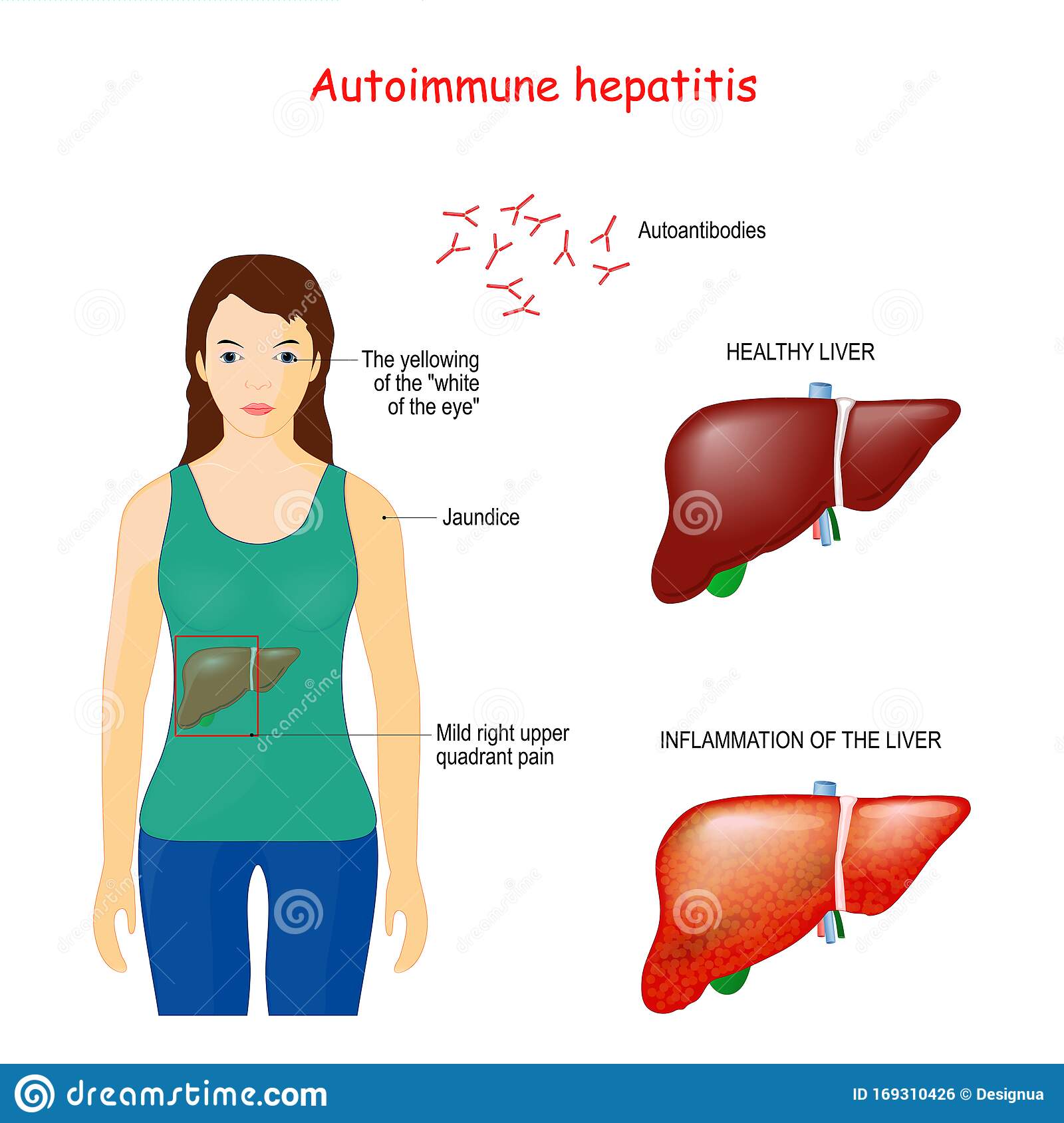
The liver is a large organ that sits up under your ribs on the right side of your belly . It helps filter waste from your body, makes bile to help digest food, and stores sugar that your body uses for energy. Autoimmune hepatitis occurs when your bodys infection-fighting system attacks your liver cells. This causes swelling, inflammation and liver damage.
It is a long-term or chronic inflammatory liver disease.
Autoimmune hepatitis:
- May occur at any age
- Affects women more than men
- Is often linked to other diseases where the body attacks itself
Also Check: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic
Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Serious
Autoimmune hepatitis AIH is a substantial inflammation of the liver mediated by an autoimmune response against the hepatocytes themselves, which manifests clinically as positive autoantibodies, hyper-IgGemia and gamma-globulinemia, and on liver histology as interface hepatitis. Autoimmune hepatitis is a more serious and complex liver disease, which often leads to cirrhosis and even liver failure if not treated properly. AIH can manifest clinically as a chronic process, and some patients have an acute, fulminant process. some data show that about 30% of patients are already cirrhotic by the time they are found to have AIH, and all patients with AIH About 1-2% of all AIH patients will develop into hepatocellular carcinoma, so it is a more serious and complicated liver disease.
About Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune liver diseases are typically long-lasting and recurring conditions. This means that you may experience persistent immune system attacks that destroy liver cells. As cells die, scar tissue known as fibrosis forms. Autoimmune diseases tend to progress slowly, and you may have long periods without symptoms. When scarring becomes extreme, liver function weakens and eventually may result in a condition known as cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is also known as liver failure or end-stage liver disease. The only cure for this condition is organ transplantation. While the only cure for severe cirrhosis is transplantation, we can help you manage the symptoms of the disease with medication before or instead of transplantation.
Our liver specialists work closely with other experts at Mount Sinai to provide a comprehensive approach to treating you if you have multiple autoimmune conditions. Our goal is to keep your immune system active and related symptoms under control.
Mount Sinai liver specialists work with colleagues in rheumatology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, radiology, and pathology to manage autoimmune liver disease. We use state-of-the-art methods of diagnosis and treatment.
If end-stage liver disease develops and you need liver transplantation, we have the expertise to help you. We have extensive experience treating patients with autoimmune liver disease. After living with chronic liver disease, through treatment, we can help restore your quality of life.
Read Also: How You Get Hepatitis B
What Is A Possible Complication Of Autoimmune Hepatitis And Cirrhosis
People with autoimmune hepatitis and cirrhosis are at risk of developing liver cancer. A health care provider will monitor the person with a regular ultrasound examination of the liver. Ultrasound uses a device, called a transducer, that bounces safe, painless sound waves off organs to create an image of their structure. A specially trained technician performs the procedure in a health care provider’s office, an outpatient center, or a hospital, and a radiologista doctor who specializes in medical imaginginterprets the images anesthesia is not needed. The images can show the liver’s size and the presence of cancerous tumors.
Researching Autoimmune Liver Disease
The focus of our research at Mount Sinai has been to identify ways to slow the progression of autoimmune liver diseases. We evaluate the genetic and environmental influences of liver disease. We also research treatments with minimal side effects. Our studies have led to several clinical trials and global collaborations.
Our research teams dedication means you have access to comprehensive, groundbreaking care. We have made strides in diagnosis to post-transplantation care. Our team also supports patient-directed self-help groups for those with autoimmune diseases.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Totally
Why Choose Upmc For Liver Disease Care
Doctors at the UPMC Center for Liver Diseases treat the full range of liver conditions, no matter the severity of your disease.
Our world renowned hepatologists will work with you to:
- Diagnose your liver disease early.
- Treat your liver disease at any stage, with lifestyle changes, medicine, or surgery.
- Improve your quality of life.
Our doctors work closely with experts at the UPMC Liver Transplant Program, one of the most experienced transplant centers in the country. Together, we care for those with severe liver damage and disease.
How Common Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
Researchers arent sure how common autoimmune hepatitis is in the United States. Studies conducted in northern European countries have found that between 10 and 24 of every 100,000 people in that region have autoimmune hepatitis. Researchers have found that the disease is more common among Alaska Natives, affecting about 43 of every 100,000 people.1
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Caused By Alcohol
What Is An Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease causes your immune system to attack healthy cells in your body by mistake. It can affect different parts of your body. There are more than 80 types of autoimmune diseases.
Verywell / Danie Drankwalter
Fortunately, autoimmune hepatitis is treatable with corticosteroids and outcomes are good in patients who seek early treatment.
Hepatitis Cases In Children
The number of cases of hepatitis in children has increased recently. Public health doctors and scientists are looking into what could be causing this.
See a GP if your child has symptoms of hepatitis, including yellowing of the eyes and skin .
Good hygiene, including supervising hand washing in young children, can help to prevent infections that can cause hepatitis.
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Go Away On Its Own
Potential Outcomes Of Immunosuppressant Therapy
The goal of treatment is disease remission. In remission, patients experience the improvement of symptoms, the normalization of abnormal liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels, and the reduction or elimination of inflammatory activity on liver biopsy.
Most patients who embark on a course of immunosuppressant therapy respond well initially. More than 90% of adults started on corticosteroid treatment experience improvements in liver chemistries and gamma globulin levels within 2 weeks.
Remission, if it is to be achieved, typically requires 18-24 months of immunosuppressant therapy. Remission can be achieved in about 65% of patients within 18 months and 80% of patients within 3 years. Once a drug-induced remission is achieved, an attempt should be made to withdraw immunosuppression. However, a sustained remission after total drug withdrawal is seen in 13% of patients at 5 years. Patients who relapse need to restart long-term immunosuppressant therapy in an effort to normalize their biochemical abnormalities and to delay the progression of liver disease. Many such patients are maintained on chronic maintenance therapy with azathioprine.
About 13% of patients experience an incomplete response to treatment, without worsening of their condition. Most incomplete responders need long-term immunosuppression in an attempt to stabilize levels of aspartate transaminase and alanine aminotransferase andby extensionprevent disease progression.
References
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis is a serious, long-lasting disease. Right now, there is no cure for autoimmune hepatitis. Fortunately, most children with autoimmune hepatitis respond well to treatment.
The goal of autoimmune hepatitis treatment is remission. This means symptoms become less severe and liver damage slows or stops. Some children are able to stop taking medicine after two or three years. These children will still need to be watched for a return of autoimmune hepatitis symptoms and other health issues.
Two main types of medicine are used to help control autoimmune hepatitis in children:
- Corticosteroids . Prednisone helps stop the immune system from attacking the liver. It also reduces liver inflammation. Budesonide is another corticosteroid that is sometimes used it has less side effects, but it is mostly given later on when the disease is under control already.
- Immunosuppressants. Azathioprine or mercaptopurine are often added to the treatment they work together with prednisone to get the immune system under control. There are other medications to suppress the immune system that can be used if the standard treatment is not working well.
Dont Miss: What Is The Medication For Hepatitis C
Don’t Miss: What Are Treatments For Hepatitis C
What Are The Causes
There is still no known direct cause for autoimmune hepatitis. note that people who have a family history of autoimmune conditions, or those with other autoimmune diseases, may be more likely to get autoimmune hepatitis.
According to the , some common medicines may cause autoimmune liver injury, including the antibiotics minocycline and nitrofurantoin. However, in these cases, the symptoms typically clear up once the person stops taking the medication.
No matter what triggers the disease, the cause of the symptoms is damage to the liver. The immune system in the body gets wrong signals about normal cells, mistaking them for invading cells. It attacks these cells and damages the liver tissue, leading to symptoms over time.
If a person suspects they may have liver damage, they should see a doctor.
Doctors will ask about:
The goal of treatment is to suppress symptoms and control the disease, as best as possible.
The first treatment many doctors provide is corticosteroids or immune system-suppressing drugs. These medications work to lower activity of the immune system in general, which may help slow the attack on the liver.
Treatment will also include regular blood tests to be sure the body is responding well to the treatment.
Quadrants And Regions Of Abdomen
| Quadrants and regions of abdomen |
|---|
| Side-by-side comparison of the quadrants and regions of the . |
The human is divided into quadrants and regions by and for the purposes of study, , and . The division into four quadrants allows the localisation of and , , lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which and may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant. These terms are not used in , since most other animals do not stand erect.
The left lower quadrant includes the left and half of the . The equivalent in other animals is left posterior quadrant. The left upper quadrant extends from the to the left . This is the left anterior quadrant in other animals. The right upper quadrant extends from umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent in other animals is right anterior quadrant. The right lower quadrant extends from the umbilical plane to the right . This in other animals is the right posterior quadrant.
The nine regions offer more detailed anatomy and are delineated by two vertical and two horizontal lines.
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
Autoimmune Liver Diseases Occur When The Bodys Immune System Attacks The Liver Causing Inflammation If Left Untreated The Liver Inflammation May Eventually Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver Which May Lead To Liver Cancer And Liver Failure
Overview and Symptoms
Although a number of autoimmune conditions may involve the liver, the three most common autoimmune liver diseases are autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. These conditions may occur individually or as part of overlap syndromes.
What Are The Current Treatment Options
Very mild cases or inactive phases of the disease may not require treatment. However, for more serious cases, treatment to fight acute episodes is important.
For many individuals, lifelong medication use may be required to keep the bodys autoimmune response under control and preserve liver health.
The two main medications used to treat autoimmune hepatitis are:
- prednisone: a corticosteroid
- azathioprine: an immunomodulator or steroid-sparing agent
Other medications may be added in severe cases. If medications are no longer effective and liver failure is likely, a liver transplant may be necessary.
If possible, your treatment should be supervised by a hepatologist, which is a physician who specializes in liver health.
Read Also: Chronic Hepatitis C With Hepatic Coma
What Are The Complications Of Autoimmune Hepatitis In A Child
Autoimmune hepatitis can cause scar tissue to start forming on the damaged liver . This makes it harder for the liver to work properly. Over time, lots of scar tissue can build up in the liver . This can block the blood flowing through the liver and may lead to problems such as bleeding in the esophagus or stomach, or water in the belly . Cirrhosis also can cause the liver to fail signs may be jaundice , bleeding/bruising, or confusion.
What Are The Types Of Autoimmune Hepatitis
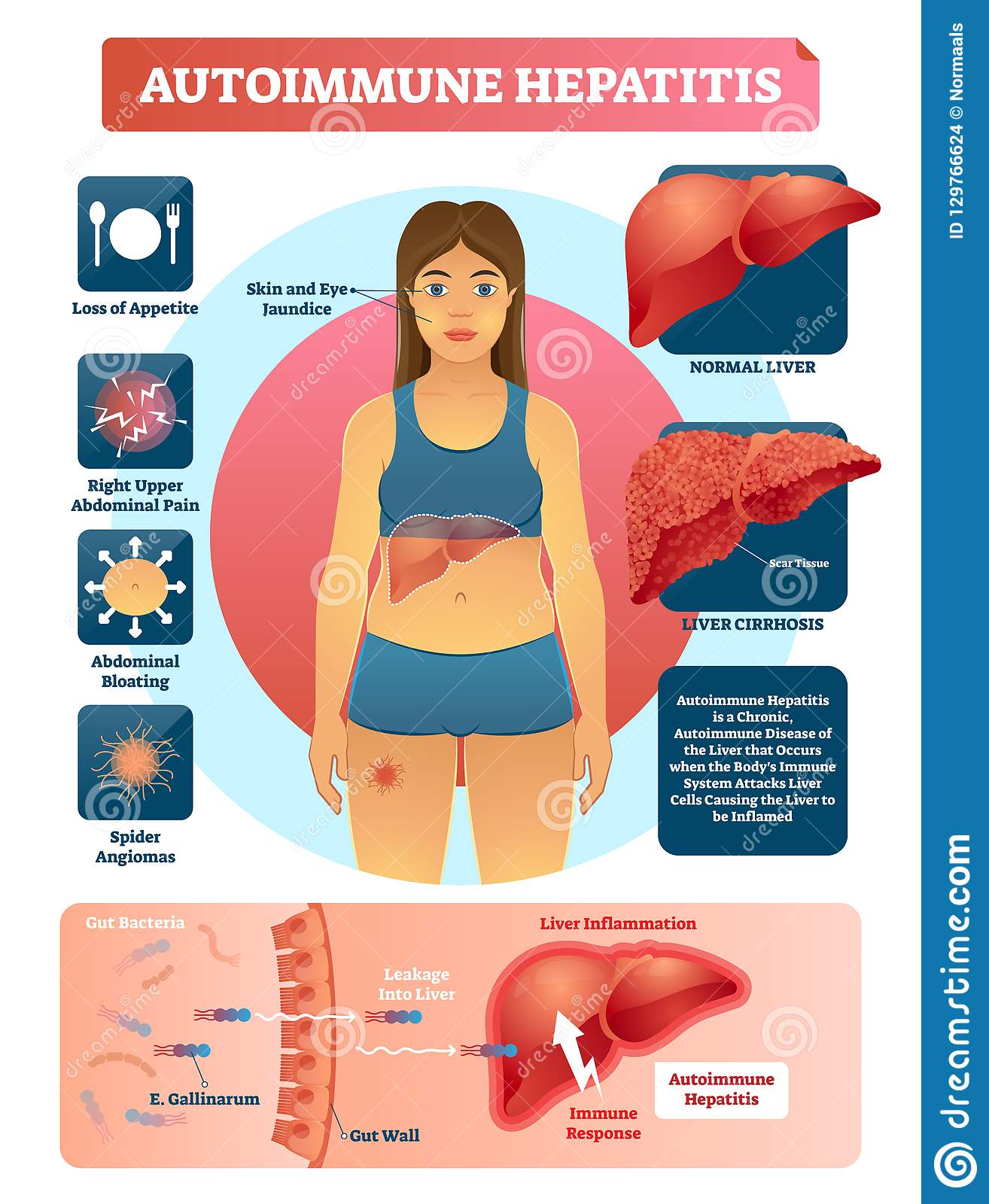
Autoimmune hepatitis is classified into several types. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common form in North America. Type 1 can occur at any age however, it most often starts in adolescence or young adulthood. About 70 percent of people with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis are female.1
People with type 1 autoimmune hepatitis commonly have other autoimmune disorders, such as
Type 2 autoimmune hepatitis is less common and occurs more often in children than adults.1 People with type 2 can also have any of the above autoimmune disorders.
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis From Sex
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Treatment In Homeopathy
When The Liver Is Under Attack
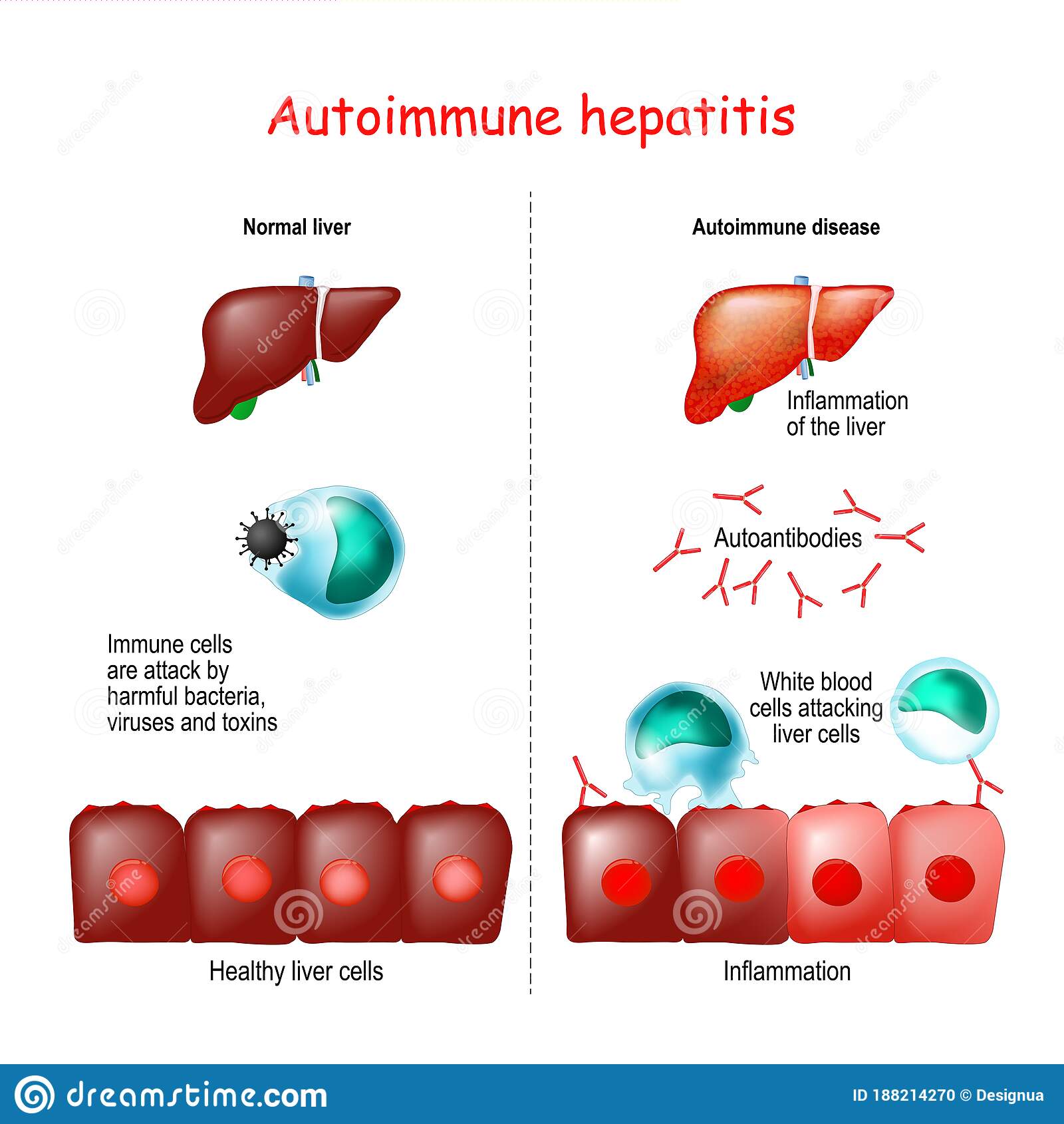
In people with autoimmune hepatitis, immune cells inappropriately mistake the livers normal cells as abnormal and attack them. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, scarring , impaired liver function, and even cirrhosis , which can result in liver failure, and death if not treated. Some people may eventually need a liver transplant. The liver disease specialists at NewYork-Presbyterians Center for Liver Disease and Transplantation are experienced in diagnosing and treating autoimmune hepatitis.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Vaccine
What Causes Autoimmune Hepatitis In Children
It is not known exactly why the immune system begins attacking liver cells in children with autoimmune hepatitis.
Experts are looking at a number of possible causes, including:
- Genetics. Physical traits passed down from parents
- Environment. Causes of disease from outside the body, such as toxic substances, certain medicines, or germs
- Problems with the immune system. For example, in patients with autoimmune hepatitis, it seems that some cells that regulate the immune system are fewer or weaker, while other cells that make the immune system attack are more frequent or more active.
Inside the Liver Center: Meet Dr. Weymann
Dr. Weymann leads a team of highly skilled specialists dedicated to caring for children suffering from a wide range of liver diseases. Named to the Best Doctors in America list, Dr. Weymann understands that liver problems can be life-threatening and life-changing. Quick evaluation, correct diagnosis and early treatment can impact long-term health.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Hepatitis