Hbv Resistance Against Nas
If a confirmed re-increase of HBV DNA > 1 log during ongoing treatment with NAs is observed, HBV resistance development can be suspected . This virologic breakthrough is often followed by a biochemical breakthrough, which is characterized by a re-increase of formerly normal ALT levels . Resistance of HBV against NAs is mediated by variants in the HBV polymerase gene, which decrease the susceptibility of the virus. NAs show similar mutation pathways and cross-resistance within their group, which is due to their conformational similarities . Monotherapy with lamivudine, adefovir, or telbivudine is frequently associated with spontaneous resistance development and should therefore be avoided . Entecavir has a very high genetic barrier against resistance, but resistance occurs often in patients with preexisting lamivudine resistance. Tenofovir is the only NA for which no resistance development was shown, even though there seems to be a certain cross-resistance to adefovir, which may lead to a slightly reduced susceptibility, leading to a slower decline in HBV DNA and to incomplete virologic responses in some patients .
Transient Hepatitis B Virus Production
HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pHBI together with pGL3 to normalize the transfection efficiency and an shRNA-expressing plasmid using GenJet In Vitro DNA Transfection Reagent according to the manufacturers instructions. At 7 days post-transfection, the culture supernatant was used to measure the level of HBV production by real-time PCR, and cell lysates were used to check the transfection efficiency by a Luciferase Assay System .
Practical Management Of Drug Resistance
In cases of a confirmed virological breakthrough and exclusion of non-adherence , the patient should be either switched to another antiviral monotherapy with a high genetic barrier to resistance or a second antiviral drug with a complementary resistance profile should be added . Although it appears reasonable from a virological point to reduce resistance by combination therapy, there are no clear long-term data favoring the add-on over the switch concept . Table 2 summarizes current recommendations for the management of treatment failure.
Table 2
Don’t Miss: Symptoms Of Acute Hepatic Porphyria
Choosing Oral Antivirals Versus Peginterferon
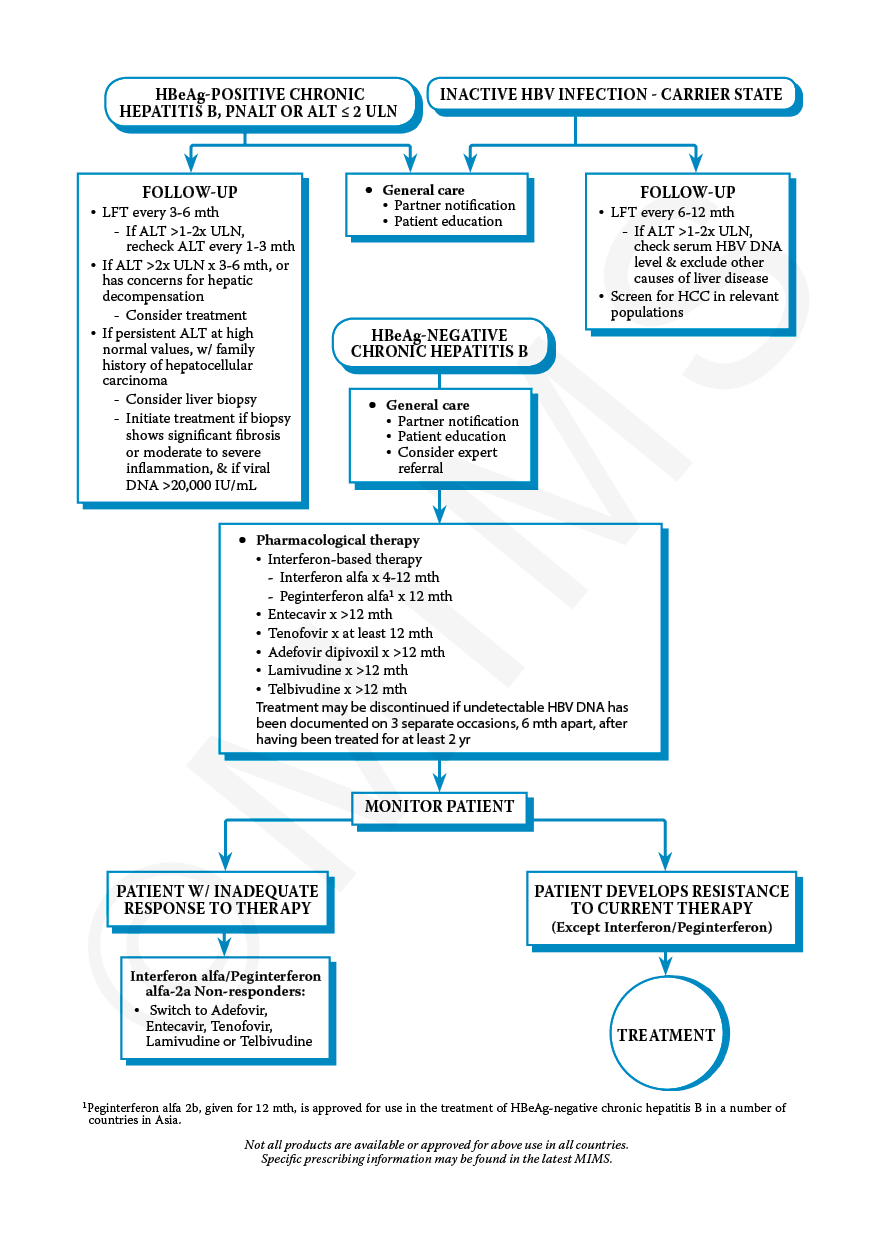
A primary decision point when choosing an initial therapy in a patient with chronic hepatitis B is whether to use an oral antiviral agent or an interferon-based agent . When an interferon-based agent is used, peginterferon is clearly preferred over interferon, primarily due to more convenient dosing, improved efficacy, and better tolerance. Thus, the following discussion will focus on comparing oral antivirals with peginterferon.
The availability of safe, well-tolerated, highly potent, oral antivirals that have a high genetic barrier to drug resistance, when taken together with the key disadvantages of peginterferon, have made the oral antivirals the preferred treatment for most individuals with chronic HBV infection. The oral antivirals have similar efficacy as peginterferon after 48 to 52 weeks of therapy for persons positive for hepatitis B e Ag and those negative for HBeAg . Long-term follow-up studies have shown that sustained treatment with oral antiviral therapy in persons with chronic HBV markedly reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis, decompensated liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma . There are also long-term follow-up studies that suggest interferon or peginterferon treatment for chronic HBV reduces the risk of HCC and improves survival, but these data are less robust than with oral antivirals, especially with peginterferon.
Treatment Options For Hepatitis B
People living with chronic hepatitis B infection should expect to live a long and healthy life. There are decisions people can make to protect their livers such as seeing a liver specialist or health care provider regularly, avoiding alcohol and tobacco, and eating healthy foods. There are also approved drugs for both adults and children that control the hepatitis B virus, which helps reduce the risk of developing more serious liver disease, but there is still no complete cure.
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories:
- Immune modulator Drugs These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot over 6 months to 1 year.
- Antiviral Drugs These are drugs that stop or slow down the hepatitis B virus from reproducing, which reduces the inflammation and damage of your liver. These are taken as a pill once a day for at least 1 year and usually longer.
It is important to know that not everyone with chronic hepatitis B infection needs to be treated. This can be difficult to accept when first diagnosed because taking a drug to get rid of the virus seems like the first step to getting better. Current treatments, however, are generally found to be most effective in those who show signs of active liver disease .
Hepatitis B Drug Watch
Visit the HBF Drug Watch for a complete list of the approved treatments for hepatitis B and promising new drugs in development.
Read Also: How Does Someone Get Hepatitis B
Key Points About Drug
- Drug-induced hepatitis is a redness and swelling of the liver.
- It is a rare condition caused by harmful amounts of certain medicines, vitamins, herbal remedies, or food supplements.
- In most cases, you may be taking a medicine for several months before it reaches a toxic level and affects your liver.
- You may also get the condition if you take too much of some medicines, such as acetaminophen. This can happen quickly.
- You must stop taking the medicine that is causing the disease.
Prediction Of Hbeag Seroconversion
Several baseline factors including low HBV DNA levels, high ALT levels and presence of HBV genotype A are predictive for HBeAg seroconversion . Additionally, an early decrease in HBV DNA levels during treatment is associated with a higher rate of patients losing HBeAg . As HBsAg loss during NA treatment occurs almost exclusively in patients who were initially HBeAg positive, HBeAg seroconversion can be considered a predictor for HBsAg loss .
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis C Do
Hepatitis B Treatment Outcomes
Effective hepatitis B treatment suppresses hepatitis B virus reproduction, and reducing hepatitis B viral load can reduce inflammation and bring liver enzyme levels back to normal. Less often, treatment can lead to loss of hepatitis B antigens and promote production of antibodies .
The most effective antiviral drugs usually produce low or undetectable hepatitis B viral load in most people who receive treatment. However, people with HBeAg-negative hepatitis B are more likely to respond to treatment. For example, one study found that among HIV-negative people treated with tenofovir, around 95% of HBeAg-negative people and 75% of HBeAg-positive people had undetectable hepatitis B virus DNA after one year. A majority of both groups still had hepatitis B suppression after eight years on treatment.
Most people taking antivirals alone do not experience hepatitis B antigen loss or seroconversion. Pegylated interferon strengthens the immune response against hepatitis B, but usually does not lead to a cure. Some studies show that adding pegylated interferon to antivirals increases the likelihood of these outcomes. For people with co-infection, seroconversion appears to be more likely if they are also on HIV treatment.
There is currently no treatment that cures a majority of people with hepatitis B. Researchers are working on new types of treatment including direct-acting antivirals that attack different steps of the hepatitis B lifecycle and drugs that improve immune response.
Preferred Initial Hbv Therapy
When initiating treatment for chronic HBV, the recommended approach, in most circumstances, is to use a potent oral antiviral that has a high genetic barrier to resistance, typically with long-term administration of the medication. Three oral antivirals are recommended as a preferred option for initial therapy: entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide, or tenofovir DF. For most individuals undergoing treatment for chronic HBV, any one of these three agents can be used. Some special situations, as outlined below, warrant preference of one of these agents over another. Combination therapy, including use of two oral antivirals, one antiviral plus peginterferon, or two antiviral is not recommended for initial treatment.
Don’t Miss: The Effects Of Hepatitis C
Medications For Hepatitis B
Several drugs are currently available for treatment of hepatitis B. Most of these are antiviral drugs that directly stop hepatitis B from reproducing. Hepatitis B treatment may also include pegylated interferon, which stimulates the body’s immune response against the virus.
Most hepatitis B drugs are nucleoside or nucleotide analogues, similar to one class of drugs used to treat HIV. In fact, some commonly used anti-HIV drugs are also active against hepatitis B. This can make treatment of both viruses easier, since it requires fewer drugs, but it must be done carefully to avoid either virus becoming resistant. These are:
- lamivudine .
- emtricitabine .
- tenofovir disoproxil or TDF .
- tenofovir alafenamide or TAF .
Other antiviral drugs are used to treat hepatitis B but not HIV:
- adefovir
- telbivudine .
Maoto Suppresses Extracellular Hepatitis B Virus Production In Hepad387 Cells
To confirm the effect of maoto, we evaluated it in HepAD38.7 cells in more detail . We first confirmed that the maoto extract did not show any cytotoxicity at a concentration of 100 µg/ml . Then, the effect of maoto on HBV production was evaluated at various concentrations under 100 µg/ml . Consistent with the results in Figure 1C, maoto inhibited extracellular HBV production in HepAD38.7 cells in a dose-dependent manner . Maoto did not affect HBeAg production, which is thought to correlate with HBV pgRNA production, in the tested concentration range . These results confirmed the inhibitory effect of maoto on extracellular HBV production without any cytotoxicity and suggest that maoto inhibits a step in the HBV production process after HBV pgRNA expression.
Also Check: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Injections: Interferon And Pegylated Interferon
Pegylated interferon is given as an injection once per week. It can be used alone or with an oral hepatitis B medication. Patients with both chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection may need pegylated interferon alone or combined with an oral hepatitis B pill.
- Pegylated interferon therapy is usually given for 48 weeks.
- Pegylated interferon may cause many side effects, such as flu-like symptoms, rashes, irritability, and depression.
- Side effects to interferon require close monitoring with routine blood tests.
What Will I Need To Do If I Am On Hepatitis B Medications
- Take oral medications every day to avoid developing resistance.
- See your provider on a regular basis
- If you have cirrhosis or high risk of liver cancer, get liver imaging on time as prescribed by your provider
- Have periodic laboratory tests to monitor HBV viral load and liver enzymes to monitor disease activity and response to medications
- You may need blood tests every 3-6 months initially and at least once a year thereafter if virus is undetected in blood.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Long Term Effects Of Hepatitis C
Treating Hepatitis B With Tenofovir
Violetta Shamilova, PharmD, is a board-licensed pharmacist. She is an assistant professor at the Touro College School of Health Sciences, and has worked at CVS pharmacy for five years. She completed the certified APhA Delivering Medication Therapy Management Services course.
Tenofovir, also called tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is an antiviral drug for treating chronic hepatitis B in adults and children who are 12 years and older. It is also used, in combination with other drugs, to treat the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. It’s sold under the brand name Viread by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Experimental Markers For Response To Na Treatment
Using highly potent NAs, suppression of serum HBV DNA can be achieved in almost all patients, including those with and those without long-term response. Reliable markers for treatment response could help to tailor NA treatments and to estimate their duration. Markers for response to NAs which are currently investigated are host or virus related. Thus, HBeAg seroconversion was shown to be predictable by a decrease in the levels of HBeAg after 6 months of entecavir treatment . Higher serum levels of the interferon-inducible protein 10 have recently been shown to be associated with a greater decrease in HBsAg levels during treatment with entecavir in a cohort of 114 European patients, an observation which had also been previously made in a smaller cohort of patients receiving treatment with different NAs . Other viral markers like core-related antigen or cytokines such as interleukin-22 which show an association to response to NA treatment are currently being investigated .
As for HBeAg seroconversion, variants within the host’s innate immune system were shown to be associated with HBsAg loss . Thus, it could be shown that the single nucleotide polymorphism TLR4 rs4986790 is significantly associated with spontaneous HBsAg loss . Novel treatment approaches targeting TLR 7 have been shown to induce strong decreases in serum HBsAg levels, which supports the concept of an important role of the innate immune system in HBsAg clearance .
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative Titer
Hepatitis B Virus Preparation And Infection
HepAD38.7 is a specialized cell line that produces HBV in the absence of tetracycline . The cells were cultured without tetracycline, and the culture supernatant was collected every 3 days for up to 60 days. The culture supernatants were filtered through a 0.22 µm filter, and viruses were purified by polyethylene glycol precipitation. The virus was used to infect HepG2-NTCP cells and PXB-cells at 2 × 103 genome equivalents /cell. Infection was performed in the presence of 2% DMSO and 4% PEG 8000. After 24 h of infection, the cells were washed three times to remove remaining extracellular HBV particles.
Which Agents Are Used As First
Currently, pegylated interferon alfa , entecavir , and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate are the first-line agents in the treatment of hepatitis B disease. These are the main treatment drugs approved globally for this disease, although ongoing trials are investigating new types of medications, such as tenofovir disoproxil in combination with emtricitabine . Encapsidation inhibitors, entry inhibitors, TLR7 agonists, and therapeutic vaccines are all in development.
In 2009, international phase III trials with clevudine for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection were halted owing to a very high risk of myopathy.
Lamivudine , telbivudine, and adefovir are of historical interest. These agents are currently considered second- or third-line therapy, or nonpreferred treatment.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent hepatitis B. Its usually divided into three doses, which are given over the course of six months. In many countries, infants receive their first dose of the vaccine at birth.
The Centers for Disease Control recommends that all children under the age of 19 be vaccinated if they havent already received the vaccination. Adults can also get the hepatitis B vaccine, and its generally recommended if you have an increased risk of infection due to:
- traveling to or living in a region where hepatitis B is common
- being sexually active with more than one partner
- working in a medical setting
- using intravenous drugs
If youve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and havent been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though youll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
They can also prescribe a medication called
Recommended Reading: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis B
Combined Use Of Maoto And Lamivudine Decreases Hepatitis B Virus Replication More Efficiently Than The Individual Use
Considering that maoto suppresses an HBV infection step different from that of lamivudine , i.e., the reverse transcription step, we reasoned that a combined use of 3TC and maoto would suppress HBV replication more effectively. We therefore compared the effect of maoto alone, 3TC alone, and the combined use on HBV replication. Compared to maoto or 3TC alone, the combined use decreased HBV replication more efficiently as expected . These results suggest the potential of maoto for increasing the efficacy of current anti-HBV drugs when used in combination.
Figure 4 Combined use of maoto and 3TC decreases hepatitis B virus replication more efficiently than the individual use. Cells were treated with distilled water , 30 µg/ml maoto alone, 250 nM lamivudine alone, or maoto and 3TC for 9 days with refreshing the medium and drugs every 3 days as shown in Figure 3A. HBV DNA in culture supernatants of the cells after 9 days of maoto treatment was measured by real-time PCR. Values are expressed as the mean percentage + S.E. of three independent experiments. *P< 0.05 **P< 0.01 ****P< 0.001 N.S., no significance.
Evaluation Of Hepatitis B Virus Dna

HBV extracellular DNA and core-associated DNA were isolated as described previously with minor modifications . Briefly, the culture supernatant was treated with DNase at 37°C for 30 min, and extracellular DNA was extracted by a QIAmp DNA Mini Kit according to the manufacturers protocol. For isolation of core-DNA, the cells were lysed in lysis buffer . After removal of the nuclear pellet by centrifugation, the supernatant was treated with 20 U/ml DNase , 5 µg/ml RNase , 5mM MgCl2 and 5mM CaCl2 at 37°C for 3 h to degrade the nucleic acids outside the nucleocapsids. The DNase was then inactivated by the addition of 10 mM EDTA. After the inactivation of DNase, proteinase K , sodium dodecyl sulfate and NaCl were added to disrupt the nucleocapsids. Finally, core-DNA was isolated by a QIAmp DNA Mini Kit . The amounts of extracellular DNA and core-DNA were measured by real-time PCR using Fast SYBR Green Mater Mix with the HBs-specific primers. The thermal profile was as follows: 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 s and 60°C for 20s.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse