Hbsag Structure And Variants
The preS/S ORF encodes three different structurally related envelope proteins, termed the large , middle-sized and small protein, that is synthesized from alternative initiation codons. The three proteins share the same carboxy-terminus but have different amino terminal extensions. In particular, the S protein corresponding to the HBsAg consists of 226 amino acids , the M protein contains an extra N-terminal extension of 55 aa, and the L protein has a further N-terminal sequence of 108-119 aa compared with the M protein. The enhancer and basic core promoter regions of S region overlap with the X gene.
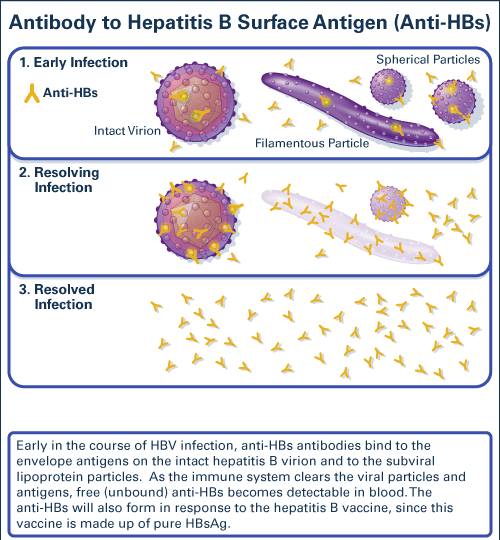
HBsAg is an envelope glycoprotein that is currently the primary element for diagnosis and target of immunoprophylaxis of HBV infection. The dominant epitopes of HBsAg, which are the targets of neutralizing B-cell responses, reside in the a determinant within the major hydrophilic region .
Several mutations in the S region have been described and those most frequently reported in the literature are listed in Table Table1.1. In most cases, they were aa substitutions due to a single mutation, but nucleotide deletions have also been reported. The majority of mutations were located in the S region, but some mutations were also identified in the pre-S1 or pre-S2 regions. Mutations in the S region have been found in various HBV genotypes, while those in pre-S1 or pre-S2 have been frequently observed in patients with HBV genotype C .
What Exactly Is Hbsag And Hbsab What Exactly Is The Difference Between Hbsag And Hbsab Are They Antibodies That Protect Against The Hbv Or Is It The Actual Virus
Ag is the antigen and Ab is the antibody.
Explanation:
First it is important to know the difference between and antibody and an antigen :
- Antibody = protein produced by the immune system to neutralize all molecules foreign to the body.
- Antigen = a foreign and/or toxic molecule that induces an immune response.
Now the difference in this example:
- HBsAb = Hepatitis B surface antibody that is produced because the body has been exposed to the Hepatitis B virus .
- HBsAg = Hepatitis B surface antigen, this is the part of the virus that induces an immune response.
Presence of either HBsAb and/or HBsAg mean different things:
- Presence of HBsAb = the body has been exposed to HBV. It usually appears about one month after the virus has disappeared. This means someone is no longer contagious when HBsAB is present. Also, it protects the body from getting HBV in the future.
- Presence of HBsAg = early sign of an active infection with HBV, people are contagious in this stage.
- Presence of both HBsAb and HBsAg = sometimes this occurs and means that the body is fighting off the infection, but people are still contagious.
There is also another test for HBV that tests for the presence of the Hepatitis B e-antigen . This antigen is only present during an active HBV infection. It can be used to determine how contagious someone is and to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Also Check: Can You Get Hepatitis A After Vaccination
Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Mmab
Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Immunohistochemistry on an FFPE Infected Liver Tissue
| Analyte Specific Reagent: analytical and performance characteristics are not established | |
| Summary and Explanation | Hepatitis B virus is spherical in shape with a diameter of 42 nm. It contains a 27 nm partially double-stranded DNA core enclosed within a lipoprotein coat. |
| Antibody Type | |
| Hepatitis B Infected Liver | |
| Presentation | Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen is a mouse monoclonal antibody derived from cell culture supernatant that is concentrated, dialyzed, filter sterilized and diluted in buffer pH 7.5, containing BSA and sodium azide as a preservative. |
| Availability | |
| 5 |
Synonyms: HBcAg, anti-Hep B cAg, anti Hep B cAg, anti-HBcAG, anti HBcAG, Hepatitis B Virus Core Antigen, anti-Hepatitis B Virus Core Antigen, anti Hepatitis B Virus Core Antigen, hcv core, e antigen precursor core antigen hepatitis B virus, subtype adr and others, Hepatitis B virus, HBV serum, hepatitis, Hepatitis B core antigen HBV, Hepadnavirus, HBV related antigen, anti HBc, anti HBe, HBeAg
Don’t Miss: What Medications Treat Hepatitis C
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Does A Hepatitis B Surface Antigen W/refl Confirm Mean You Have The Virus
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
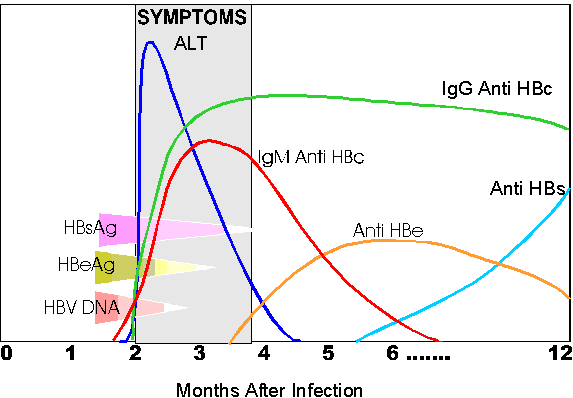
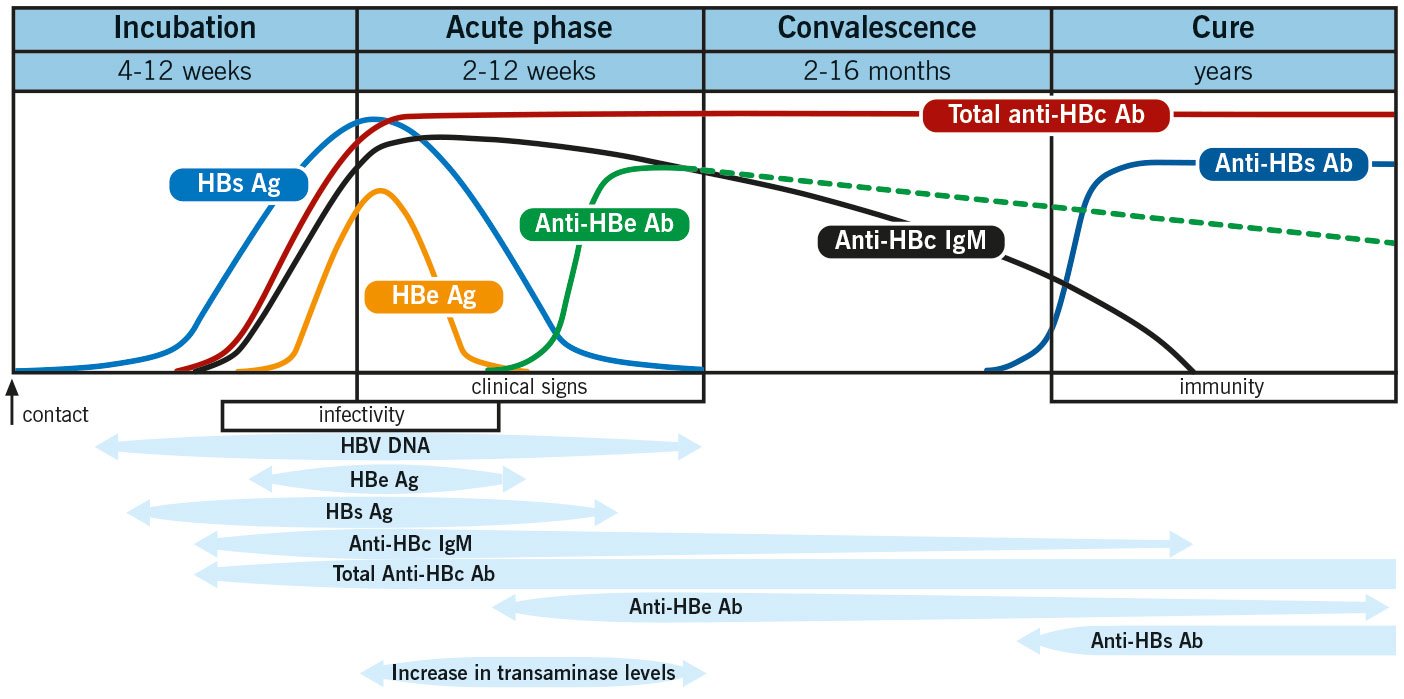
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Correlation Between Hbsag Titers And Hbv Dna
The correlations between serum HBsAg titers and serum HBV DNA in each phase of CHB are shown in Figure Figure1B-F.1B-F. There was a strong correlation in the IC phase , a modest correlation in the ENH and IT phases, but a poor correlation between serum HBsAg titers and serum HBV DNA in the LR and LC phases.
The ratio of HBsAg to HBV DNA in each phase of CHB was also determined .2). The HBsAg/HBV DNA ratio was significantly higher in the LR phase compared to the IT, IC, ENH and LC phases .
You May Like: How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis C Untreated
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis B
In most of the adult cases of hepatitis B , the virus is completely cleared from the body upon treatment. However, the remaining 5% can go on to develop chronic forms of the disease. It has been observed that within 6 months of the treatment, most people not only clear the virus but also become immune to the same. In general, there are 3 distinct types of hepatitis B infections seen:Healthy Chronic Carriers These people carry the virus but dont develop any symptoms. They are not infectious to others but have a higher risk of developing hepatic conditions such as cirrhosis. However, if the immune system in such individuals gets suppressed owing to an infection or treatment via immunosuppressant drugs, there are chances that they may develop hepatitis B infection. Chronic Infectious Carriers They are the contagious carriers of the disease as they have virus replicating in their systems. They show signs of hepatitis such as damaged liver that progresses into liver cirrhosis. Only 5% of the cases can show remission of the virus.Chronic Mutant The chronic mutant form is a result of a mutated strain of the virus that causes permanent alteration to the hepatitis B viruss genetic makeup. Those with it have the risk of being infectious to others and it is observed to be more resistant to treatment than other forms of hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
You May Like: Diet For Dogs With Chronic Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Screening Test
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, HBsAg antibody, and hepatitis B core antigen antibody. This allows healthcare providers to know if you could benefit from vaccination or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care or treatment.
If you are pregnant, donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive treatment, or have end-stage renal disease, you may be screened routinely. You will also be screened if you are in a higher risk group for HBV.
HBeAg or hepatitis B e antigen
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels During Natural History Of Chronic Hepatitis B: A Chinese Perspective Study
Correspondence to: Yi-Da Yang, Professor, State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Disease, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 79 Qingchun Road, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang Province, China.
Telephone: +86-571-87236755 Fax: +86-571-87236755
Also Check: How Can I Catch Hepatitis
Study Selection And Characteristics
A total of 11,589 citations were identified, and 293 full-text articles examined which identified 40 studies meeting pre-defined criteria . Of the included studies, 33 compared RDTs and/or EIAs against an immunoassay reference standard, of which five focused on accuracy in HIV-positive individuals . Seven studies compared RDTs and/or EIAs against a NAT reference standard, of which 3 had data from HIV-positive patients . Studies were all either cross-sectional or case-control, predominantly in the laboratory setting, and performed in a broad range of populations, including healthy volunteers, blood donors, pregnant women, incarcerated adults, HIV and hepatitis patient cohorts with confirmed HBV infection. The prevalence of HBV ranged from 1.9 to 84% in populations tested. A mixture of serum, plasma and whole blood was used for RDTs, while studies of EIAs were performed on serum or plasma samples. Study characteristics are presented in Tables , and .
Fig. 1
Three studies had data from 442 HIV-positive patients in Uganda and South Africa, with pooled sensitivity and specificity of 57.9% and 95.8% , respectively. The corresponding pooled sensitivity and specificity for the 202 HIV-negative patients across two of these studies were 83.3% and 85.7% , respectively .
Can Hcv Cause Psychosis
At least 50% of patients infected with HCV suffer from a psychiatric illness, and the lifetime prevalences of psychotic, anxiety, affective, personality, and substance use disorders are all higher among patients with HCV,10,47 as compared to the general US population studied in the Epidemiologic Catchment Area study.
Also Check: What Are The Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Also Check: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
Vaccine For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Vaccine
It takes only a few shots to protect yourself and your loved ones against hepatitis B for a lifetime.
The hepatitis B vaccine is a safe and effective vaccine that is recommended for all infants at birth and for children up to 18 years. The hepatitis B vaccine is also recommended for adults living with diabetes and those at high risk for infection due to their jobs, lifestyle, living situations, or country of birth. Since everyone is at some risk, all adults should seriously consider getting the hepatitis B vaccine for a lifetime protection against a preventable chronic liver disease.
The hepatitis B vaccine is also known as the first anti-cancer vaccine because it prevents hepatitis B, the leading cause of liver cancer worldwide.
You cannot get hepatitis B from the vaccine. All hepatitis B vaccines that have been used since 1986 are made synthetically meaning the hepatitis B vaccines do not contain any blood products. Learn more.
If you have a current HBV infection or have recovered from a past HBV infection, the hepatitis B vaccine series will not benefit you or clear the virus. However, the vaccine can provide a lifetime of protection for loved ones who do not have hepatitis B and get the vaccine as soon as possible. Testing is the only way to know if you or your loved ones have a current infection or have recovered from a past infection.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Recommendations
Three-Dose Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system “encodes” antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C High Viral Load
Immunohistochemical Stains For Viral Antigens In Chronic Hepatitis B
Immunohistochemical stains for HBcAg and HBsAg are a useful diagnostic adjunct in biopsies of patients with chronic HBV infection. In addition to confirming HBV as the cause of liver disease in any given case, positive staining for HBcAg is also indicative of active viral replication. Such staining is usually confined to hepatocyte nuclei however, in cases with abundant HBcAg production, the cytoplasm may be stained as well . Extensive positivity for HBcAg may be seen in perinatally infected patients who have developed tolerance to the virus, as well as in immunosuppressed patients . Immunostaining for HBsAg is cytoplasmic but may also be membranous the latter is seen in cases of active viral replication in parallel with HBcAg positivity.18
Monica A. Konerman, Anna S. Lok, in, 2018
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis
Question 5 How Can Quantitative Hbsag Levels Help Distinguish The Different Phases Of Hbv Infection
Quantitative HBsAg results, along with selected immunologic and virologic characteristics, may help differentiate infection phases and inform prognosis and therapeutic decision-making. For example, the HBeAg-negative inactive carrier state may be identified by low HBV DNA and low HBsAg in patients with certain genotypes.2 Low serum HBsAg levels measured 1 year after documented HBeAg seroconversion may predict subsequent HBsAg loss in HBV genotype B or C infection.5 It has been documented that a drop in HBsAg levels in patients who are on NA treatment can predict subsequent HBsAg loss. The observed decrease in HBsAg concentration may help predict HBsAg loss and support the decision to discontinue peg-IFN and/or NA therapy.
Peg-interferon and/or NA treatment may lead to reductions in HBsAg. In general, sustained responders display greater and/or more rapid HBsAg decline than non-responders.1-2,4-6 The quantitative HBsAg level that best predicts sustained virologic response has yet to be well established. However, some experts consider 2 or more measurements of HBsAg below the assayâs lower limit of detection obtained â¥6 months apart to be a potentially useful endpoint for antiviral therapy.9-11
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis C Considered An Std
Negative But Other Hepatitis Tests Are Positive
Your HBsAb test may be negative even when other hepatitis B tests are positive, showing active or chronic infection. Further testing is necessary, especially for the hepatitis B surface antigen , which shows that the virus itself is circulating in your bloodstream and that you have an active or chronic infection.
Also Check:
The Hbsag Test Procedure
Since a test for Hepatitis B is a blood test, a blood sample is taken by a lab technician as follows:
- An elastic band is wrapped around the upper arm
- The needle site is cleaned with alcohol
- The needle is inserted into the vein
- A tube is attached to the needle to fill it with blood
- The band is removed from the arm once enough blood is collected
- A gauze pad is applied over the needle site as the needle is removed
- A bandage is applied over the site
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis Is An Inflammation Of The Liver