How Is It Treated
Acute hepatitis B: There are no drugs to treat acutehepatitis B. Doctors usually suggest rest, goodnutrition, and fluids. Some people may need to be inthe hospital.
Chronic hepatitis B: People with chronic hepatitis Bvirus infection should receive care from a provider whohas experience treating hepatitis B. These providerscan be:
- Some internists or family medicine providers
- Infection specialists
- Gastroenterologists
If you have chronic hepatitis B, get checked regularlyfor signs of liver disease. Discuss treatment with yourhealth care provider. Not every person with chronichepatitis B needs treatment. If you show no signs ofliver damage, your provider will continue to check youfor liver disease.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B, but the risk is higher in:
- Infants born to mothers who have hepatitis B
- People who inject drugs or share needles, syringes, and other types of drug equipment
- Sex partners of people with hepatitis B, especially if they are not using latex or polyurethane condoms during sex
- Men who have sex with men
- People who live with someone who has hepatitis B, especially if they use the same razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- Health care and public-safety workers who are exposed to blood on the job
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you may not have symptoms until complications develop. This could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis B screening is important, even if you have no symptoms. Screening means that you are tested for a disease even though you don’t have symptoms. If you are at high risk, your health care provider may suggest screening.
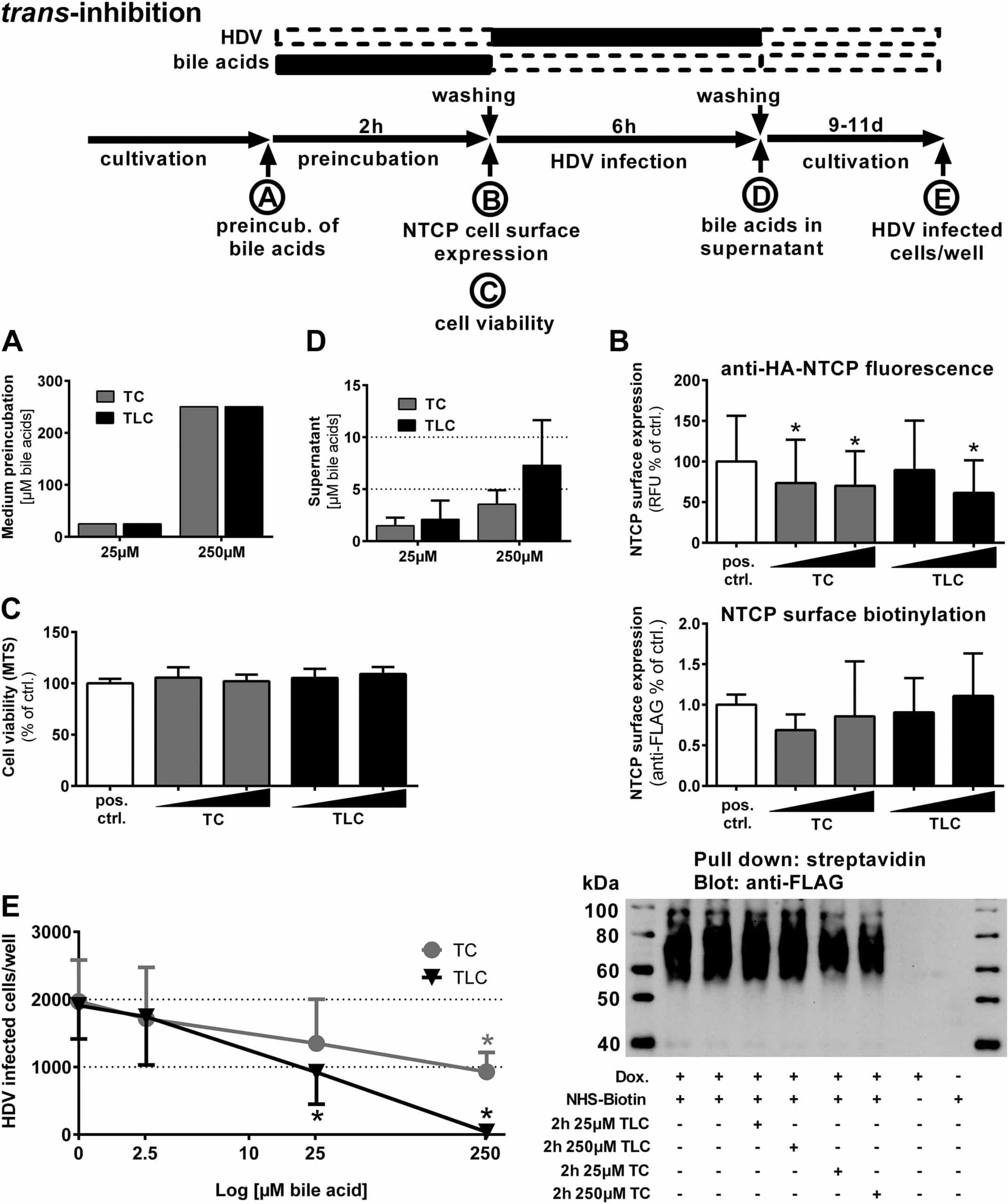
Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
Some individuals infected with HBV have an increased risk of developing liver cancer . Identifying who is at the highest risk of developing liver cancer is important so that healthcare professionals can take steps to monitor the patient appropriately and detect any disease at an early stage.
Fortunately, if detected early, there are many effective therapies available. It might be beneficial for some patients to have regular abdominal imaging with ultrasound every six months to screen for liver cancer. However, not everyone with hepatitis B needs to have regular ultrasound surveillance and patients should discuss this with their healthcare providers.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Through Saliva
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
After the virus enters the body, there is an incubation period lasting 1.5 to 6 months until illness begins. During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HBV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis B usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Chronic HBV infection can lead to serious liver disease, liver scarring , and hepatocellular cancer.
Because symptoms of hepatitis B are usually absent, persons with risk for HBV infection should be tested. If you think you have hepatitis B, or are at risk for hepatitis B, you should contact your doctor.
Hepatitis B In The United States
In the United States, about 862,000 people have chronic hepatitis B.6 Asian Americans and African Americans have higher rates of chronic hepatitis B than other U.S. racial and ethnic groups.10 Researchers estimate that about half of the people living with chronic hepatitis B in the United States are Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders.11 Chronic hepatitis B is also more common among people born in other countries than among those born in the United States.7
The hepatitis B vaccine has been available since the 1980s and, in 1991, doctors began recommending that children in the United States receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The annual rate of acute hepatitis B infections went down 88.5 percent between 1982 and 2015.12 In 2017, the annual number of hepatitis B infections rose in some states.13 Experts think the rise was related to increases in injection drug use. Injection drug use increases the risk of hepatitis B infection.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Catch It
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Ab
Melting Curve Analysis For The Detection Of Hbv Ymdd Mutants
YMDD mutants were analyzed by melting curve analysis. The melting peaks of the wild-type and mutant HBV strains were typically observed at different temperatures, as shown in Figure Figure1A.1A. The melting temperatures of the YIDD and YVDD mutants were approximately 9°C and 2.5°C lower than that of the wild-type, respectively. Because the melting curve showed a double peak in the case of YIDD or YVDD mutant mixed with the wild-type YMDD, as shown in Figure Figure1B,1B, this type of melting curve was considered to be the mixed mutant-type.
Melting curve analysis using the LightCycler probe hybridization assay. The melting curves were converted to melting peaks by plotting the negative derivative of fluorescence with respect to temperature . The melting temperature for each of the YMDD mutants is indicated with a vertical line. A: Representative results for differentiating HBV YMDD mutants. YMDD, YVDD and YIDD mutants showed distinct Tm values B: The shoulder curve indicated the mixed mutant-type. Representative results show YMDD + YIDD mutants.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
You May Like: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis A
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
What Is The Hepatitis B Carrier State
Some persons infected with hepatitis B virus never fully recover andcarry the virus for the rest of their lives. These persons are known ascarriers, and they can infect other household and sexual contactsthroughout their lives. Among adults who have hepatitis B, 5% to 10%develop a lifelong infection among children, the risk for lifelonginfection is much higher. In the United States today, an estimated onemillion persons have life long hepatitis B virus infections.
Don’t Miss: What Are Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
Who Is At Risk Of Hepatitis B
Anyone can get hepatitis B if not vaccinated. However, in the U.S., you may be at a higher risk if you:
- Have sex partners that have hepatitis B
- Have HIV or another STD
- Inject drugs or share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Live with someone who has hepatitis B
- Are undergoing dialysis
- Travel to areas that have moderate to high rates of hepatitis B
- Work in health care or public safety and are exposed to blood or body fluids on the job
- Are an infant born to an infected mother
Read Also: Hepatitis C Screening 1945 To 1965
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
How Do Interferons Work
Interferons work in a few ways. For one, they change the way white blood cells destroy invading cells. This change triggers the bodys built-in immune response to fight viruses such as hepatitis C.
Interferons also help stop the spread of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C spreads by multiplying, or copying, its cells. Interferons would help stop the virus from multiplying, which helped slow the spread of the virus.
Interferons have other broad actions that dont target any virus in particular. This is one reason why these drugs can cause many side effects.
Read Also: How Often Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Need To Be Given
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
Who Should Be Vaccinated
Preventing hepatitis B is important because of the high risk oflifelong infection leading to serious liver problems. The followingpersons should be vaccinated against hepatitis B:
- All babies, beginning at birth.
- Adolescents who have sex or inject drugs .
- Persons who engage in any of the high-risk behaviors listed in thispamphlet.
- Persons whose jobs expose them to human blood.
You May Like: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Intercourse
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Many Doses Of Hepatitis B Vaccine For Adults
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. This means their immune system was not able to get rid of the hepatitis B virus and it still remains in their blood and liver.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is also directly related to the age at which one first becomes exposed to the hepatitis B virus:
- 90% of infected newborns and babies will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of infected children will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of infected adults will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
Learning that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting. Because most people do not have symptoms and can be diagnosed decades after their initial exposure to the hepatitis B virus, it can be a shock and a surprise to be diagnosed with a chronic hepatitis B infection. The good news is that most people with chronic hepatitis B should expect to live a long and healthy life.
There are effective drug therapies that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging a liver. There are also promising new drugs in the research pipeline that could provide a cure in the very near future. Although the risk of developing a serious liver disease or liver cancer is higher for those living with chronic hepatitis B than those who are not infected, there are still many simple things a person can do to help reduce their risks.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy With Hepatitis B
Why Would My Doctor Prescribe Interferons
Until recently, treatments for hepatitis C focused on interferons and ribavirin. These drugs were used in an attempt to cure the hepatitis C infection. However, they were only effective some of the time.
Effective treatment with these medications would prevent liver disease and cirrhosis . In addition, effective treatment would decrease the risk of liver cancer and help prevent liver failure.
But today, interferons arent typically prescribed to treat hepatitis C. In recent years, DAAs have become available, and they have a cure rate of up to 99 percent . These drugs require a shorter treatment time and typically have fewer side effects than interferons. However, theyre very expensive, and most of them only treat certain types of hepatitis C.
The type of DAA your doctor might prescribe would depend on your insurance coverage and the type of hepatitis C you have. Some examples of DAAs include:
Complications Of Hepatitis B
Most people do not have any lasting problems after having a hepatitis B infection.
If left untreated, chronic hepatitis B can cause liver damage and increase your risk of getting liver cancer.
It is important to take any medicine you have been prescribed and go for regular check-ups to make sure your liver is working properly.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2022 Next review due: 01 July 2025
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis Do To Your Body
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
How Is Hepatitis B Virus Spread
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood and body fluids of personswith hepatitis B. Contact with even small amounts of infected blood cancause infection. You can get hepatitis B by direct contact with the bloodor body fluids of an infected person, for example, by sharing needles or byhaving sex with an infected person. A baby can get hepatitis B from aninfected mother during childbirth.
You May Like: How Can A Person Contract Hepatitis