What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Prevention Is The Best Medicine
Even though hepatitis C rarely spreads within a household, if you or a family member have the disease, it’s wise to take precautions to prevent its spread especially if anyone in your home is immune compromised, or has cuts or open sores that increase the risk of infection.
In general, use these common sense preventive tips:
- Unless you are in a long-term, monogamous relationship, practice safe sex.
- Clean up spilled or dried blood with a bleach-based cleaning solution and wear rubber gloves.
- Do not share razors.
- Do not share toothbrushes. “Though hepatitis C is not transmitted through saliva, there might be blood on the toothbrush,” Reau says.
Note that hepatitis C is not transmitted by sharing eating utensils, hugging, kissing, coughing or sneezing.
Recommended Reading: What Medications Treat Hepatitis C
Am I Eligible For Treatment
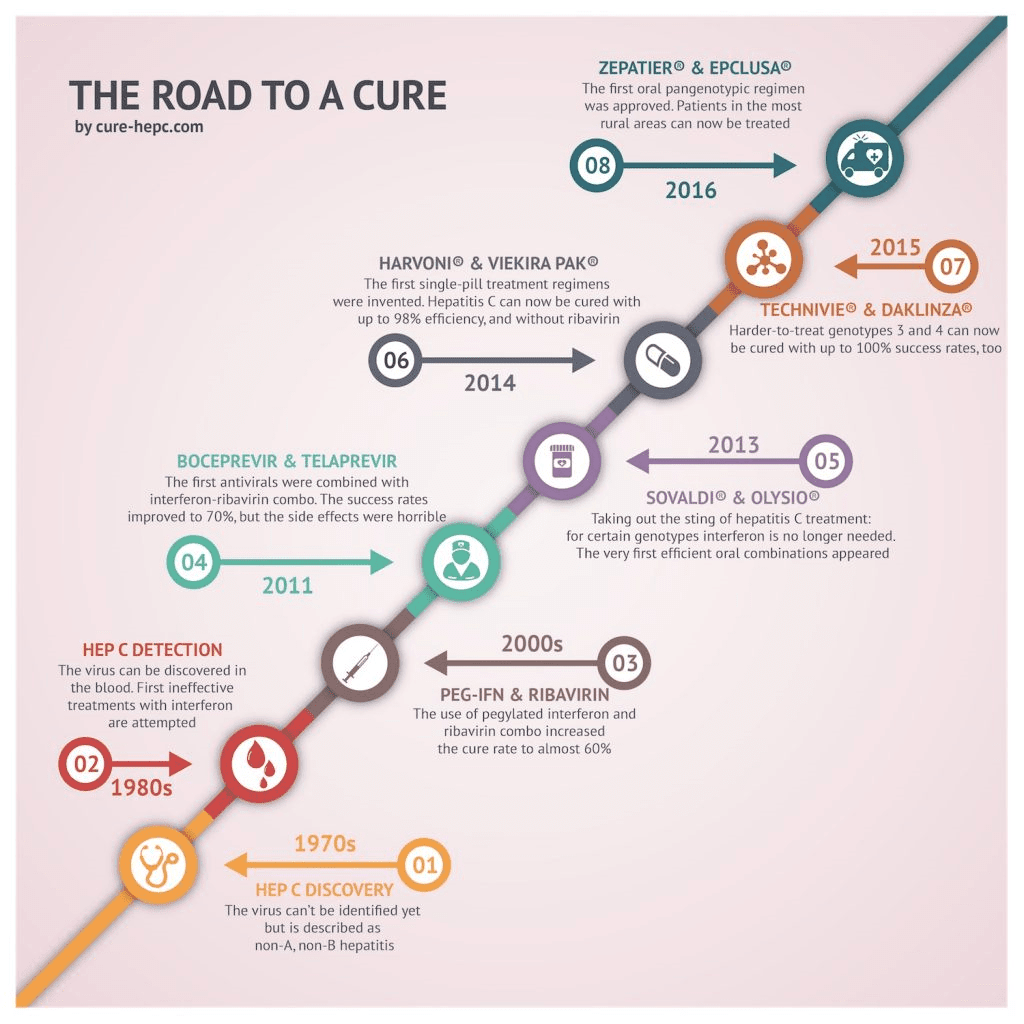
In the past, when treatment for Hepatitis C basically consisted of interferon and ribavirin, side effects precluded many patients from being eligible. However, with the current availability of interferon-free treatment regimens, many of these people can now receive treatment for their Hepatitis C infection.
Some things your Hepatitis C provider will want to know when discussing your eligibility for treatment, as well as deciding which treatment regimen is best for you, include the following:
- What medications do you currently take? Some medicines interact with Hepatitis C medications, which can affect the level of either one meaning that the level of the Hepatitis C medicine or your other medicine may become too high or too low. There can be risks of toxicity if too high, or the medication may be less effective if too low. If available, your Hepatitis C provider will select a treatment option with no interactions. If not available, he or she can talk to your other healthcare providers about the possibility of changing your current medicines before Hepatitis C treatment begins. As an example, people taking amiodarone should not take Sovaldi or Harvoni due to serious risks of a slow heart rate deaths have been reported. People taking amiodarone would need to take some other Hepatitis C treatment.
- Are you pregnant? Antiviral medications may not be recommended if you are pregnant, because these medications can cause birth defects in babies.
Why Should People Take Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis C
The purpose of taking antiviral medications for hepatitis C is to:
- remove all the hepatitis C virus from your body permanently
- stop or slow down the damage to your liver
- reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis
- reduce the risk of developing liver cancer
- reduce the risk of liver failure and the need for a liver transplant
Don’t Miss: How Can I Get Hepatitis
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not been sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Your Insurance Company Could Say No
Some insurance companies try to combat the high cost of hepatitis C drugs by rejecting coverage for them. More than one-third of people were denied coverage for these drugs by their insurance company, according to a 2018 study in Open Forum Infectious Diseases. Private insurance companies rejected more claims for these drugs over 52 percent than Medicare or Medicaid.
Medicare and Medicaid are more likely to approve hepatitis C drug coverage. But with Medicaid, you might have to meet certain requirements to receive these drugs, such as:
- getting a referral from a specialist
- having signs of liver scarring
- showing proof that you have stopped using alcohol or illicit drugs, if this is a problem
Recommended Reading: Can Chronic Hepatitis B Be Cured
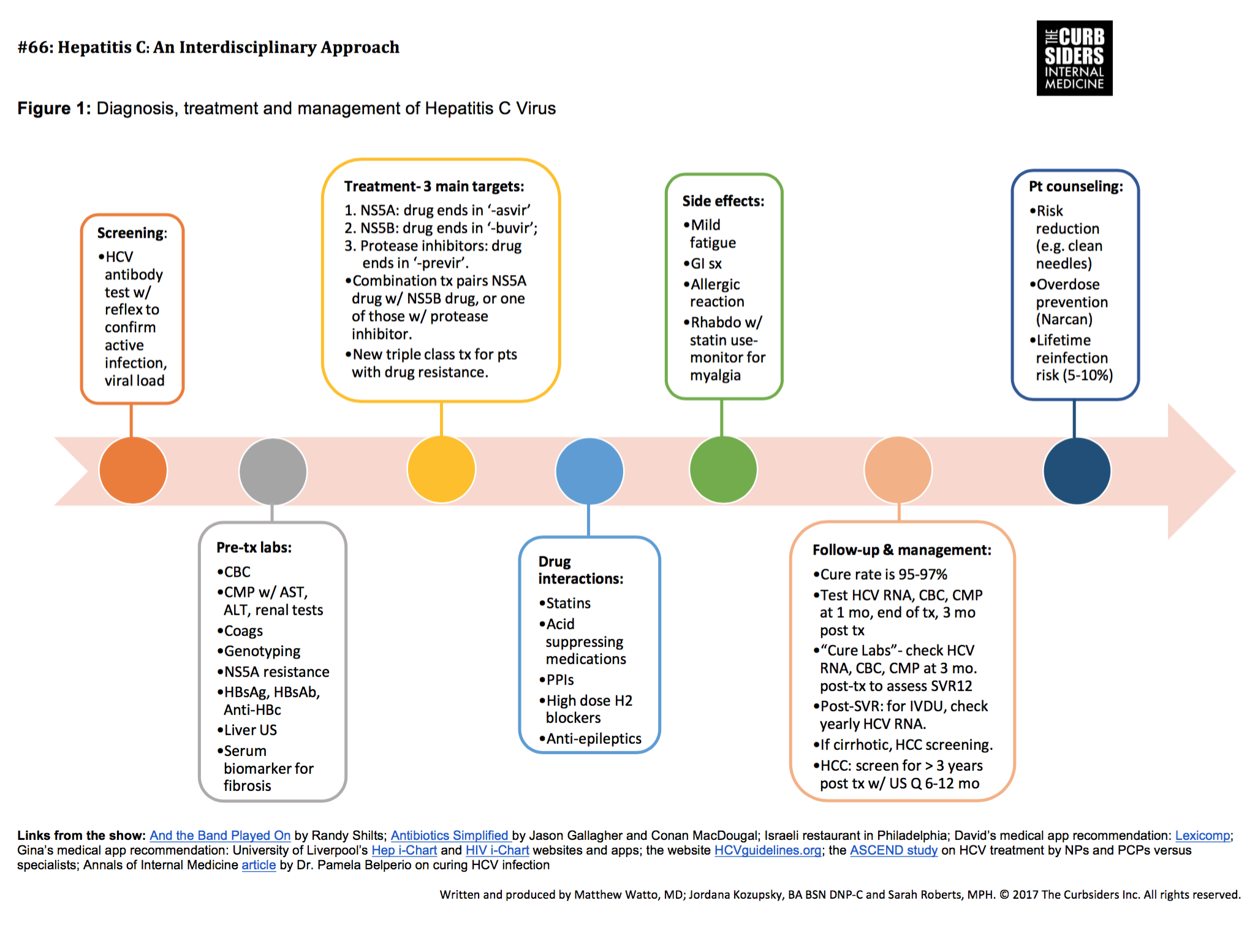
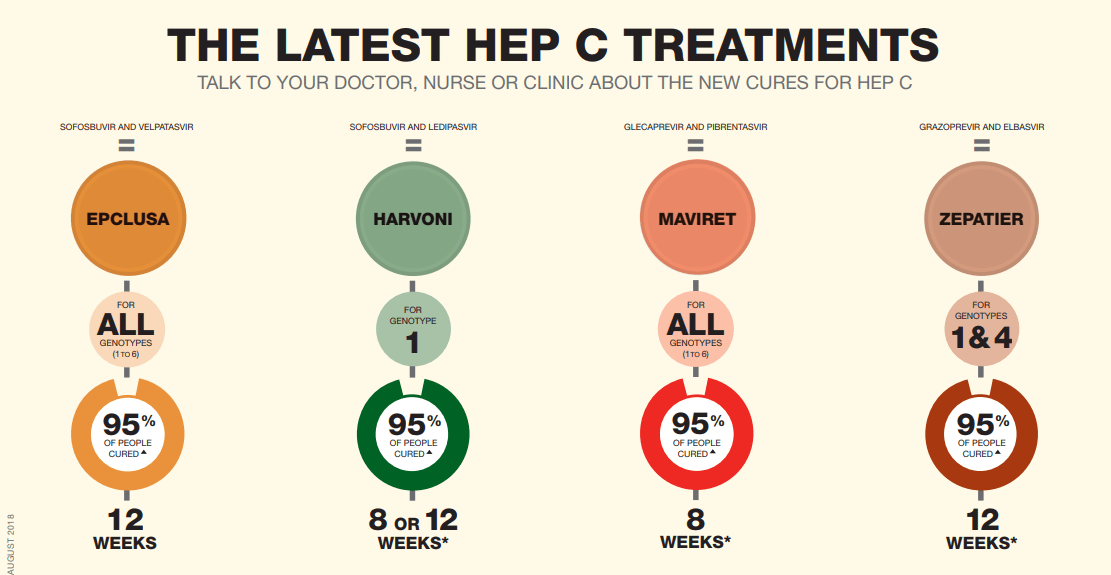
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. The only way to prevent infection is to avoid contact with infected blood.
Hepatitis C cannot be spread by coughing, sneezing or sharing eating utensils. People should not be kept away from school, work, or other social settings because they have hepatitis C.
Here are some precautions that may prevent the spread of hepatitis C:
- Do not share personal care items, such as toothbrushes or razors, with others.
- Practice safe sex by using condoms.
- Dont share needles or syringes.
- Wear gloves when handling another persons blood.
- Use sterile equipment for body piercings or tattoos.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow recommended safety measures.
People who are at greater risk for contracting hepatitis C should have their blood tested. The Centers for Disease Control recommends that Americans born between 1945 and 1965 be screened at least once for the disease.
Don’t Miss: Google What Is Hepatitis B
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
Cdc: Less Than 1 In 3 People With Health Insurance Get Hepatitis C Treatment Within Year Of Diagnosis
MIAMI It’s estimated more than 2 million people in the United States are living with hepatitis C. Now, new government data shows many patients are not getting treatment for the deadly, but curable infection.
It’s been nearly a decade since breakthrough treatment for hepatitis C became available in the United States. A new report from the CDC shows less than one in three people with health insurance get the antiviral treatment within a year of being diagnosed.
Dr. Carolyn Wester, director of CDC’s Division of Viral Hepatitis, said, “It can cure more than 95% of people who take it with just 8 to 12 weeks of oral only treatment.”
Without treatment, hepatitis C can lead to advanced liver disease, liver cancer and even death. Experts say insurance restrictions may be part of the reason for low treatment rates. Treatment can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
Dr. Wester said, “We need to remove eligibility restrictions, burdensome prior authorization requirements, and ensure that individuals with ‘hep C’ are accessing treatment in the settings where they receive care, like primary care offices and substance use disorder treatment centers.”
New hepatitis C infections are increasing due to rising rates of injection drug use in the nation’s opioid crisis. The new report shows treatment rates are lowest among adults under 40.
The CDC says making sure everyone has access to treatment is critical for a person’s health and to prevent new infections.
- In:
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Have Symptoms
Are There Ways To Cure Hepatitis C Other Than With Medications
Patients sometimes ask whether there are ways to treat hepatitis C other than taking medicines. Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent hepatitis C. Once a person is infected, the only way to treat it is with prescribed antiviral medications.
Some patients worry that having hepatitis C means they will need a liver transplant. Only a very small fraction of people with hepatitis C require a liver transplant. By far, most people with hepatitis C never need a liver transplant. A transplant is performedonlywhen damage to the liver is extremely advanced and the liver is unable to perform its basic functions. A transplant provides a new working liver, but a transplant does not get rid of the hepatitis C virus in the patient. Patients with a liver transplant still need antiviral medication to cure their virus.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B What Is It
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Who Treats Hepatitis C
If you think you are at risk of having Hepatitis C, talk to your current healthcare provider about getting tested. Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C infection, you may want to see a specialist. Specialists who work with people with Hepatitis C include the following healthcare providers:
- Doctors who specialize in liver diseases
- Doctors who specialize in stomach and intestinal diseases
- Doctors who specialize in infectious disease
- Nurse practitioners whose practice concentrates on people with liver diseases
Nurse practitioners are registered nurses who are prepared through advanced education and clinical training to assume some of the duties formerly assumed only by physicians. They work in a medical care team, and can provide a wide range of health care services, including the diagnosis and management of common, as well as complex medial conditions.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis Vaccine For Adults Schedule
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Are pregnant
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have HIV
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
You May Like: Hepatitis A And B Shots
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
- sofosbuvir
How Do People Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C virus is found in the blood of people with HCV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Until reliable blood tests for HCV were developed , people usually got hepatitis C from blood products and blood transfusions. Now that blood and blood products are tested for HCV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
Currently, people usually get hepatitis C by sharing needles for injection drug use. An HCV-infected woman can pass the infection to her baby during birth. It is also possible to get hepatitis C from an infected person through sexual contact, an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis B And C Curable
How Can I Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Although there is currently no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C, there are things you can do to avoid becoming infected or re-infected and prevent the spread of hepatitis C virus. Hepatitis C is not spread through food or close personal contact such as handshaking, hugging and kissing. Hepatitis C is spread when the blood from an infected person enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person. To avoid this happening:
- do not share needles or other equipment to inject drugs or any other substances
- do not use personal items that may have come in contact with an infected persons blood such as shavers or toothbrushes
- avoid touching blood or open wounds
- avoid sexual practices that might risk blood contact including trauma, during menstruation, or in presence of genital ulcers.
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Vaccine Side Effects