What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
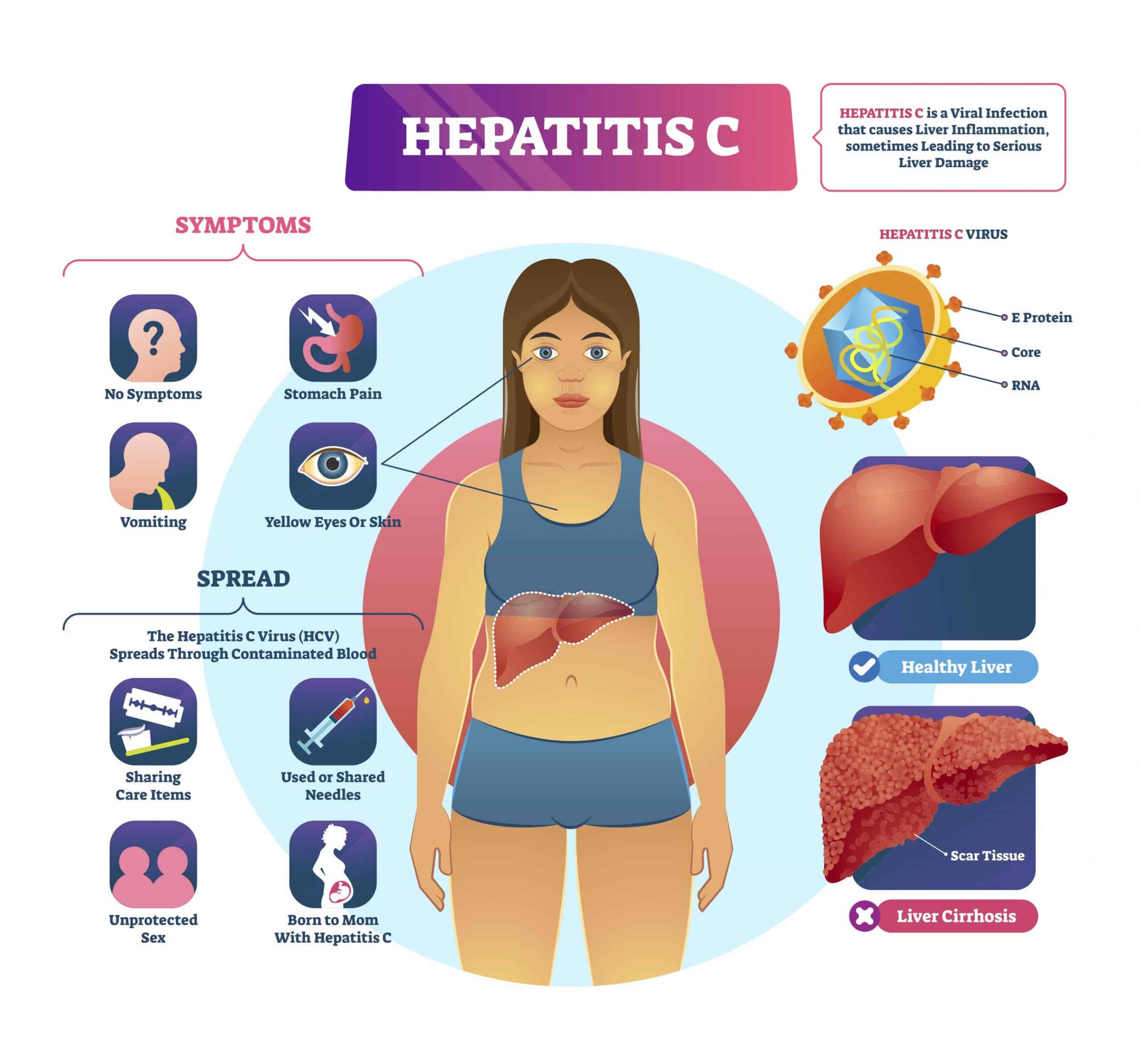
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Parenteral Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis B Hepatitis D And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B, C, and D viruses are all transmitted by what is known as the parenteral route. Parenteral simply means that these viruses can be introduced by all routes except through the intestinal tract, which leaves the door wide open in terms of possible exposure. Let’s look at the possible transmission routes for each of these types of hepatitis virus more closely.
Whos At Risk For Hepatitis C
You might be more likely to get it if you:
- Inject or have injected street drugs
- Were born between 1945 and 1965
- Got clotting factor concentrates made before 1987
- Received a blood transfusion or solid organ transplants before July 1992
- Got blood or organs from a donor who tested positive for hepatitis C
- Are on dialysis
- Get a body piercing or tattoo with nonsterile instruments
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Cure Latest News 2022
How Can I Protect Myself Against Viral Hepatitis
There are many ways you can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis:
- Get the vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Use a condom during sex.
- Don’t share needles to take drugs.
- Practice good personal hygiene such as thorough hand-washing with soap and water.
- Don’t use an infected person’s personal items.
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation.
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
It is very important that you take these preventive measures if you participate in risky behaviors. Take preventive steps, too, if you work in places like a nursing homes, dormitories, daycare centers, or restaurants where there you have extended contact with other people and a risk of coming into contact with the disease.
What Is Viral Hepatitis

Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Disease Caused By Hepatitis B
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Sexual Transmission And Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be transmitted through sexual activity. Unvaccinated adults who have multiple sex partners, along with sex partners of people with chronic hepatitis B infection, are at increased risk for transmission. Injection-drug use and sexual contact are other common modes of hepatitis B transmission in the United States.
Among adults seeking treatment in STD clinics, as many as 10%40% have evidence of past or current hepatitis B virus infection. Many of these infections could have been prevented through universal vaccination during delivery of STD prevention or treatment services. Offering vaccination to all adults as part of routine prevention services in STD treatment facilities has been demonstrated to increase vaccination coverage among adults at risk for hepatitis B infection, as the behavioral risk factors for STDs and hepatitis B are similar.
You May Like: Cost Of Hepatitis C Medications
Baby Boomers Are At Higher Risk
If you were born between 1945 and 1965, you might not realize that you are more likely to have hepatitis C. The reason is that intravenous drug use was popular in the 1960s and 1970s, and this practice occurred more commonly in young adults that were born between 1945-1965. Also, blood transfusions in the 1960s and 1970s not infrequently spread hepatitis C since the diagnostic test for hepatitis C was not yet discovered and blood could not be screened. All baby boomers should have a one-time test for hepatitis C to rule out infection.
Hepatitis C is a tricky disease. Its highly contagious, very dangerous and usually exists without presenting any symptoms at all. While hepatitis C can be transmitted in many different ways, its important to do what you can to help prevent contracting or spreading the disease, whenever possible, such as avoiding sharing needles at any time. Be sure to talk with your doctor if you have questions, fears or would like to be tested.
Related Services
Building Healthy Sexual Relationships
Rule number one for a healthy sexual relationship: Be open and honest. I believe in transparency, says Talal. This conversation can be difficult, but its important to have. Part of discussing your status is talking about what exposure you may have had to hepatitis C, even in the distant past.
Its a good opportunity for you to share both your sexual history and your past experiences with other ways the virus can be transmitted, such as injecting drugs or being exposed to items that may have infected blood on them, including needles, razors, and toothbrushes.
Dr. Sherman explains that even if you consistently use condoms during sex, other activities, such as sharing needles or straws to inject or snort drugs, increase your risk of spreading hepatitis C. People do not want to hear about this, he says. Its difficult to get the word out about risk.
If you and your partner find that hepatitis C is disrupting your relationship or sex life, you might also want to consider working with a marriage and family therapist or sex therapist.
Also Check: How Hepatitis B Is Caused
For Safer Sex Treat Hepatitis C
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you can lower your odds of spreading the virus by seeking medical treatment. Direct-acting antiviral medications can cure more than 90 percent of hepatitis C cases with eight to 12 weeks of treatment, according to the CDC. These newer hepatitis C treatments are not only effective but also generally have fewer, much less severe side effects than previous drugs.
Just be aware that during treatment, transmission can still occur. And a cure doesnt grant you protection against the virus for life. If you continue to engage in high-risk behavior, you can get reinfected, warns Kenneth Sherman, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine and the director of the division of digestive diseases at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine.
How To Prevent Hepatitis C
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Avoiding contact with infected blood is the only way to prevent the condition.
The most common way for people to contract hepatitis C is by injecting street drugs. Because of this, the best way to prevent hepatitis C is to avoid injecting.
Treatments can help many people quit. People in the U.S. can call the National Helpline for help with finding treatments.
If a person finds it difficult to stop, they can reduce the risk of contracting hepatitis C by never sharing drug equipment, ensuring a clean, hygienic environment, and always using new equipment, including syringes, ties, alcohol swabs, cottons, and cookers.
People who may come into contact with infected blood, such as healthcare workers and caretakers, should always wash the hands thoroughly with soap and water after any contact, or suspected contact, with blood. They should also wear gloves when touching another persons blood or open wounds.
People can also reduce their risk by making sure that any tattoo artist or body piercer they visit uses fresh, sterile needles and unopened ink.
The risk of contracting hepatitis C through sexual contact is low. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, reduces the risk of most sexually transmitted infections.
People who have hepatitis C can reduce the risk of transmitting it to others by:
There are many misconceptions about how hepatitis C spreads. People cannot transmit or contract the virus through:
Also Check: What Are Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread only through exposure to an infected person’s blood.
High-risk activities include:
- Sharing drug use equipment. Anything involved with injecting street drugs, from syringes, to needles, to tourniquets, can have small amounts of blood on it that can transmit hepatitis C. Pipes and straws to smoke or snort drugs can have blood on them from cracked lips or nosebleeds. Get into a treatment program if you can. At the very least, don’t share needles or equipment with anyone else.
- Sharing tattoo or piercing tools. Nonsterile items and ink can spread contaminated blood.
- Blood transfusions in countries that donât screen blood for hepatitis C.
- Nonsterile medical equipment. Tools that arenât cleaned properly between use can spread the virus.
- Blood or cutting rituals. Sharing the tools or exchanging blood can transmit hepatitis C.
Medium-risk activities include:
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
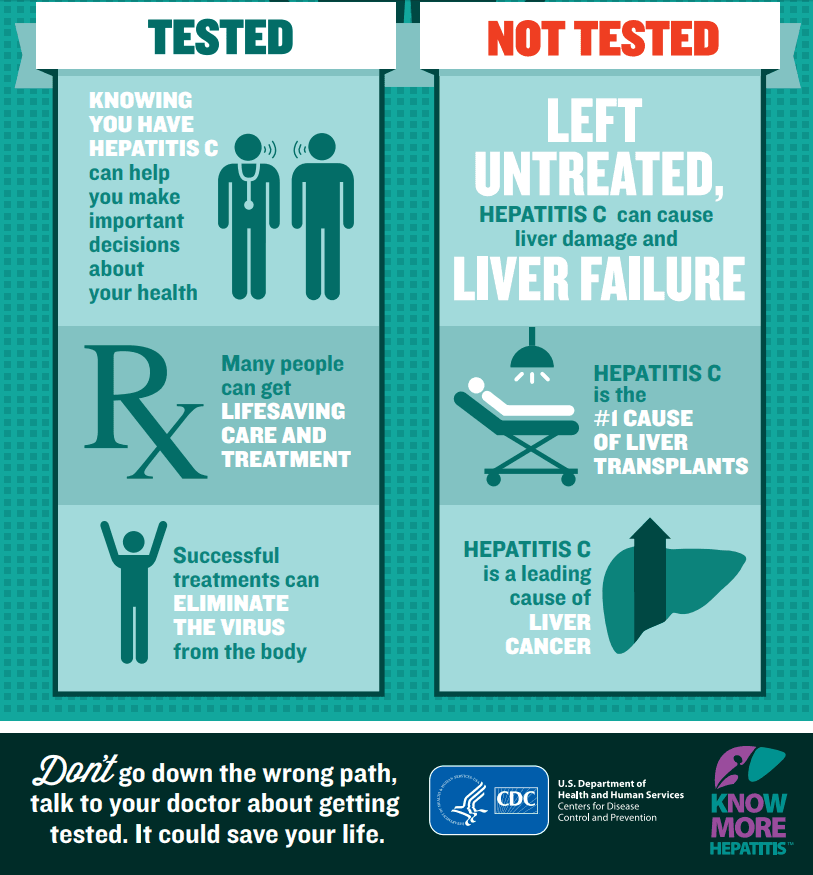
Hepatitis C infection can be treated with special drugs that eliminate the virus from the body and prevent liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. People with hepatitis C should avoid drinking alcohol or taking any medications or dietary supplements that may be harmful to the liver. Hepatitis A and B vaccine may also be recommended. Many of the treatments available today are once-a-day pills taken for a few months ask your doctor about treatment options and steps you can take to protect your liver from damage.
Also Check: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
Other Rare Potential Forms Of Transmission
Although the risk is very low, there are several other ways a person may be exposed to HCV. These include coming into contact with unsterilized tools used during tattooing, body piercing, or manicuring. Another low-risk method of transmission is sharing personal items that may come in contact with blood. These include toothbrushes or razors.2,4,5
HCV is not transmitted by hugging, kissing, or sharing utensils.
If you think you may have been exposed to HCV or are concerned about your risk, talk with your doctor. HCV is curable with treatment.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C Infection
There are two types of hepatitis C infection:
- Acute: a short-term infection that occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to the virus. However, about 75 to 85 percent of people with the acute form go on to develop the chronic form.
- Chronic: a long-term illness that can continue throughout a persons life. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and other serious problems, such as liver failure or cancer. About 15,000 people a year die from liver disease associated with hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Load Quest
Where Can You Get More Information
Your doctor, nurse, or health care clinic listed in the telephone directory can provide you with more information.
Persons who inject drugs can substantially reduce their risk of getting and transmitting HIV, viral hepatitis and other blood borne infections by using a sterile needle and syringe for every injection. The Massachusetts Department of Public Health supports programs where persons who inject drugs can access sterile needles and syringes through syringe services programs . Through these programs you can get sterile needles and syringes free of cost, dispose of used needles and syringes, and get connected to other services such as testing for hepatitis C, HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, overdose education, and narcan . To find an MDPH-supported SSP program near you, please click here.
Hepatitis C and Related Resources in Massachusetts This provides information about MDPH-supported programs including testing for hepatitis C, linkage to treatment for individuals with hepatitis C infection, and other resources such as overdose prevention programs.
Additional information about substance use disorder treatment programs may be obtained from the MDPH.
Viral Hepatitis Information from the CDC. The CDC provides resources on a variety of topics, including general information regarding transmission and prevention, statistics about HCV, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
Q: Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
A: We recommend testing for the following:
- Persons who have used injection drugs not prescribed by a doctor, even once
- Persons who received blood before 1992
- Persons who have received an organ transplant before 1992
- Persons who have received long-term hemodialysis
- Persons who were treated for clotting problems with a blood product made before 1987
- Persons who have signs and symptoms of liver disease
- Healthcare workers after accidental exposure to blood
- Children born to hepatitis C virus-positive women
There Is A Test For Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C antibody test determines if a person has been infected with the virus. A positive, or reactive result, means antibodies were found and you were infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Additional tests are required to confirm if you have active infection at present.
Read Also: When To Stop Lactulose In Hepatic Encephalopathy
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus. Today, most people become infected with HCV by sharing needles or other equipment to inject drugs. For some people, HCV infection is a short-term or acute illness but for more than half of people who become infected with HCV, it becomes a long-term, chronic infection. Chronic HCV infection is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, even death. The majority of infected people might not be aware of their infection because they do not have any symptoms. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The best way to prevent HCV infection is by avoiding behaviors that can spread the disease, especially injecting drugs.
No Identifiable Source Of Infection
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Transmission Routes Cdc
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Recent Increases In Hepatitis C Infections
Between 2013 and 2020, the reported number of acute HCV infections more than doubled. High rates of new infections were predominantly among young adults aged 20-29 years and aged 30-39 years. The number of cases continues to increase, in 2020 an estimated 66,700 new HCV infections occurred in the United States. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis B And C