Epidemiology Of Hdv At The Fingertips In The 1980s1990s
In the 1980s, initial surveys showed that HDV infections were endemic worldwide, but there were great variations in prevalence and some intriguing contrasts. In poor areas of South America, Africa, and India, HDV was transmitted primarily by superinfection as a secondary event in the context of HBV endemicity. In the Amazon basin, HDV occurred frequently in children and adolescents chronically infected early in life with HBV . By adulthood, most of the HBsAg carriers had contracted HDV and many died in periodic outbreaks of fulminant hepatitis D. Unique to this area were infections sustained by HDV genotype 3 and liver histology, displaying a cytopathic noninflammatory process of liver microsteatosis. HDV continues to be an important health issue in the Brazilian Amazon despite the implementation of HBV vaccination in rural areas in blood collected from HBsAg carriers along the banks of the Purus River in 20052006, the prevalence of anti-HD was 41.9% . Outbreaks of severe and fulminant hepatitis developing on a background of high-HBV endemicity have been reported in the last 20 years, also from Russia , Greenland , and Mongolia .
Schematic representation of the main areas of HDV globally onto which the predominant hepatitis D virus genotype for each geographical area has been superimposed.
What Is Hepatitis D Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
Hepatitis D, also known as delta hepatitis affects only those who have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus if you contract both, the one-two punch can cause serious liver problems.
The hepatitis D virus depends on another virus, namely the one that causes hepatitis B, to reproduce itself. This means hepatitis D can only infect people who are already infected with the hepatitis B virus, or who are exposed to hepatitis B at the same time theyre exposed to hepatitis D.
When you are infected with hepatitis B and D at the same time, its called coinfection.
If you already have chronic hepatitis B and are then exposed to the hepatitis D virus, its called a superinfection. In either case, this double whammy can lead to serious problems.
Hepatitis D can cause significant liver damage and even death, so prevention of this dual infection is crucial.
Hepatitis D can cause an acute or chronic infection, or both. The acute infection lasts a short time, and the chronic infection lasts longer than six months.
Reviewa Review On Hepatitis D: From Virology To New Therapies
Hepatitis D virus is a defective virus, dependent on hepatitis B virus for its assembly.
-
Hepatitis D virus infection affects 6272 million people worldwide.
-
Chronic hepatitis D is the most severe chronic viral hepatitis.
-
Current interferon-based antiviral treatments have dismal efficiency and are poorly tolerated.
-
Host-targeting molecules inhibiting the viral life cycle are currently in clinical development.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
Experimental Drugs For The Treatment Of Hepatitis D
Accepted for publication 23 February 2021
16 April 2021Volume 2021:13 Pages 461468
Lisa Sandmann,1 Markus Cornberg1,21Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endocrinology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany 2Centre for Individualised Infection Medicine , Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research, Braunschweig, GermanyCorrespondence: Markus CornbergHannover Medical School, Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endocrinology, Carl-Neuberg-Str. 1, Hannover, 30625, GermanyTel +49511 532 6821Email Abstract: Chronic hepatitis D virus infection is the most severe form of viral hepatitis. Antiviral treatment is urgently needed to prevent patients from developing end stage liver disease or hepatocellular carcinoma. Treatment options were limited to off-label use of pegylated interferon alfa until conditional approval of bulevirtide by the EMA in July 2020. However, several other antiviral compounds are currently investigated and represent promising agents for the treatment of chronic HDV infection.Keywords: hepatitis delta, HBV/HDV coinfection, interferon, bulevirtide, lonafarnib
Functions Of The Sea Rvc
In its capacity as an advisory body to WHO, the SEA RVC shall have the following functions:
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C Curable Now
Open Questions And Future Directions
-
Can hepatitis D virus establish transcriptionally silenced but reactivatable episomes in hepatocytes as an additional mechanism of persistence?
-
To what extent do the eight HDV genotypes differ in replication efficacy and sensitivity against the upcoming novel treatments?
-
Do HDV-targeted therapies lead to a restoration of HDV-specific immunity?
-
Are these restored immune responses required for treatment response? Are they required for prevention of viral relapse? Of note, there may be differences in treatment regimens that are associated with alanine aminotransferase flares combination therapy) compared with treatment regimens without ALT flares .
-
How can a synergistic potential of antiviral drugs and immune-modulators be translated into curative regimens?
-
Are there baseline or on-treatment predictors to sustained HDV virological response for the different treatment strategies?
-
Is a sustained HDV virological response without hepatitis B surface antigen loss a realistic and achievable aim for treatment regimens without IFNs?
-
Are drugs aiming at HBsAg loss effective and safe in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus/HDV coinfection?
-
Last but not least, since HDV is prevalent in low-income countries and migrant populations, it will be important to establish new concepts to foster diagnosis and access to care.
Epidemiological Changes In The Last Two Decades In Europe
In 1983, the prevalence of anti-HD was 24.6% in carriers with liver disease in Italy. In a survey in 1987, the endemicity of HDV remained stable, with 23% of the carriers showing anti-HD and a 40% peak prevalence among cirrhotic patients. However, in two subsequent Italian surveys, the rate of anti-HD had declined to 14% in 1992 and 8.3% in 1997 . In Spain, rates of anti-HD declined from 15% in 19751985 to 7.9% in 19861992 in Taiwan, the rate of HDV superinfections diminished from 23.7% in 1983 to 4.2% in 1996. In Turkey, the prevalence of anti-HD in chronic HBsAg liver disease diminished from 31% to 11% in 19802005.
Epidemiology of hepatitis D virus in Europe in 2012. Prevalence of immigrants among HDV+. Data from Buti et al. , data from Cross et al. 2008, data from Wedemeyer and Manns 2010, data from Rizzetto and Ciancio 2012, and data from Brancaccio et al. 2014.
The issue of HDV infection has been reinvestigated in the United States. In a recent study, 50% of the chronically HBV-infected IDUs in Baltimore, MD, had anti-HD , and an 8% prevalence of anti-HD was found in 499 HBsAg carriers in northern California . In this study, HDV-positive patients had higher rates of cirrhosis than those with HBV monoinfection 69% were Caucasian non-Hispanic, 10% came from Asia and the Pacific Islands.
Don’t Miss: Cost Of Hepatitis C Medications
No Identifiable Source Of Infection
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
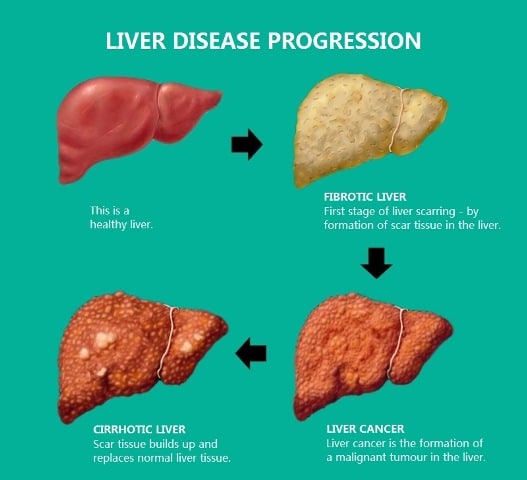
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Chronic hepatitis D can lead to cirrhosis, which is when the liver slowly breaks down. Scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, which blocks the flow of blood. Gradually, the liver is able to function less and less.
If cirrhosis is diagnosed early and the underlying cause is treated, the damage can be halted and in some rare cases, reversed.
Read Also: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Another Person
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
People who have acute hepatitis D usually have symptoms, which can include the following:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Jaundice, which causes a yellowish tint to the whites of the eyes and skin
- Discolored stools and urine
- Pain over the liver, in the upper part of the abdomen
In contrast, the majority of people with chronic hepatitis D will have few symptoms until complications develop. This could be several years after the initial infection. These symptoms can include the following:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Swelling of the ankles and abdomen
Hispanic Americans And Hepatitis B
Adult Hispanic Americans have a low rate of chronic hepatitis B infection, according to CDC statistics, and they die from hepatitis Brelated causes at the same rate as adult white Americans. Among adults ages 19 to 49, vaccination coverage was lower for Hispanic than for white Americans in 2015, but among Hispanic and white adolescents ages 1317 years and children age 19 to 35 months, it was the same in 2016.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Hepatic Encephalopathy
Public Health Significance And Occurrence
Hepatitis D virus infection requires concomitant Hepatitis B virus infection. HDV occurs world wide, with an estimated 10 million people infected.
It occurs epidemically or endemically in populations at high risk of HBV infection among haemophiliacs, injecting drug users and others who come in frequent contact with blood in institutions for the developmentally disabled and to a lesser extent, among men who have sex with men.
A decline in prevalence of both acute and chronic Hepatitis D in many parts of the world has been attributed to decreasing prevalence of chronic HBsAg carriage in the general population. Better sanitation and social standards may also have contributed.
In recent years about 30 cases of HDV infection have been notified in Australia each year, with around 10 of these from Queensland.
Clinical Presentation And Natural History
Hepatitis D is transmitted parenterally, sharing the same routes of transmission as HBV, HCV, and HIV, especially injection drug use. Only a small inoculum appears to be sufficient for infection, but perinatal transmission appears to be uncommon.45 Intrafamilial spread, as well as sexual transmission, is thought to be an underappreciated mode of transmission, especially in endemic regions. As HDV can be transmitted only in the presence of HBV, the percentage of individuals in a population who are infected with HBV, and the physical proximity of this HBV-infected network, are thought to have a direct influence on the risk and rapidity of HDV transmission.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis A Sexually Transmitted
Enteric Routes: Transmission Of Hepatitis A And Hepatitis E
The Hepatitis A and hepatitis E viruses are both transmitted by enteric, that is digestive or by fecal, routes. This is also known as the fecal-oral route. To be exposed to these viruses, you must ingest fecal matter that is infected with the virus. While there are several ways in which this fecal-oral route can be established, poor hygiene and poor sanitary conditions in some countries lead to higher rates of infection of these viruses.
As a result, some areas of the world, like India, Bangladesh, and Central and South America, are particularly prone to the hepatitis E virus. About one-third of people in the United States have been exposed to the hepatitis A virus.
It is believed that the hepatitis F virus may also be spread by enteric routes.
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Ab Total Reactive
How Is Hepatitis D Diagnosed
Doctors may suspect a person has hepatitis D when the symptoms of acute hepatitis B are unusually severe, chronic hepatitis B gets worse much faster than usual, or when chronic hepatitis B suddenly gets much worse, which would indicate a superinfection.
If hepatitis D is suspected, the doctor will take a medical history to understand factors that may have led to the infection. A physical exam will look for signs of liver damage, which could include jaundice, swelling in the feet or ankles, and swelling or tenderness in the abdomen.
If its suspected that a person may have hepatitis D, a blood test that confirms the presence of the antibodies that are produced in response to the infection is required to confirm the diagnosis.
There may be additional tests to determine if there is liver damage as a result of hepatitis B and hepatitis D. The tests can include the following:
- An elastography, a special ultrasound that can measure the stiffness of the liver
- A liver biopsy, in which a long needle is used to take a small piece of tissue that will be examined under a microscope to look for signs of disease or damage
- A blood test to measure liver enzyme levels, elevated levels of which often indicate inflammation or damage to the liver cells
How Is Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A
The hepatitis A virus is usually spread by putting something in your mouth that is contaminated with the virus. The virus is found in the stool of people with hepatitis A and is spread when someone’s stool accidentally contaminates food or water. This can happen when an infected person does not adequately wash their hands after using the bathroom then touches other things such as food. When other people eat that food, they can get infected with hepatitis A. Usually the transmission is between people in very close personal contact.
Foods themselves can be contaminated with hepatitis A virus, such as raw oysters harvested from sewage-contaminated water. When people eat food contaminated with hepatitis A virus, they can get infected with the virus.
Hepatitis A is usually spread through:
- household contact with an infected person
- sexual contact with an infected person
- eating or drinking contaminated food or water
- sharing eating utensils that are contaminated
- touching contaminated surfaces and then placing your hands near or in the mouth
Read Also: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Means
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Hepatitis D only occurs in patients with hepatitis B. Thus, healthcare workers, including the nurse practitioner should consider serological testing for HDV in patients with hepatitis B. This can be obtained by detection of total anti-HDV antibody followed by confirmatory staining for HDAg in liver tissues and/or measurement of serum HDV RNA. As HBV replication is suppressed in chronic HDV infection, hepatitis B e-antibodies are typically present.
As HDV depends on HBV, prevention can be achieved with hepatitis B vaccination. If the host is immune to HBV, they are subsequently protected against HDV. Patients who are at risk of contracting HDV infection should be encouraged to receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
At the moment there is no specific treatment for hepatitis D but unlike hepatitis B, the former is a benign infection.
Research And Statistics: How Many People Have Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D was first identified as a distinct form of hepatitis in 1977. A systematic review and meta-analysis published on April 23, 2020, in the Journal of Hepatology estimated its worldwide prevalence at 12 million people. 30220-8/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> 14)
Hepatitis D is rare in the United States, and most cases occur among people who migrate or travel to the United States from countries that have a higher rate of HDV.
Hepatitis D is not a nationally notifiable condition, so the actual number of people who have it is unknown.
Study results published in Clinical Infectious Diseases found that approximately 0.11 percent of the more than 21,000 subjects had antibodies, which would indicate they had hepatitis D infection. That would correspond to approximately 357,000 people in the United States with a past or ongoing HDV infection.
The researchers found that the prevalence of hepatitis D is highest in Asian Americans and people born outside the United States.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis Be Cured Permanently
Treatment And Medication Options For Hepatitis D
Medications are not effective against acute hepatitis D, but fortunately, the acute infection tends to subside on its own.
As for chronic hepatitis D, appropriate treatment depends on the phase of the disease and how severe the infection is.
If a persons liver is severely damaged, a liver transplant may become necessary.
While treatment options for hepatitis D are limited, new medications are being studied.