Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
The Future Of Hepatitis C Therapy
With such high rates of success with current treatments, it may seem like the hepatitis C story is in its final chapters, but it is not over yet. A vaccine against hepatitis C would cause the prevalence of the disease to plummet, but efforts to produce a vaccine, while still under way, have not yet been successful. While hepatitis A and B have vaccines, the hepatitis C virus is more variable than either of these viruses, which, along with other factors, complicates vaccine development efforts. Additionally, the current drugs show great promise, but the costs of the more successful FDA-approved DAA treatments are extremely high, which present a significant obstacle to many with the disease. But the research has come a long way. From the early investigations into a mysterious new virus, to the identification of the culprit, and the rigorous work to develop an effective treatmentthe story of hepatitis C is definitely a thriller.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Declination Form Osha
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often does not have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged.
This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- feeling and being sick
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
Spread Of Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hepatitis B And C Spread
Who Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C
- All people born between 1945 and 1965
- Anyone who has ever injected drugs, even if once or many years ago
- People with HIV infection
- People who had a blood transfusion organ transplantation before 1992
- People who have been exposed to blood on the job through a needle stick or other injury
- People receiving hemodialysis
- People who have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
Who Should I Tell About My Childs Hepatitis C Diagnosis
Choosing whether to tell people about your/your childs hepatitis C status is a very personal decision and there is no right or wrong answer. There can be a stigma associated with hepatitis C and sometimes family and friends dont fully understand what it is. Some people, however, find that support from family and friends is important and helps them to cope with the diagnosis better.
It is also up to parents when to tell children about their health. It is helpful that even young children receive some information about what they can do to prevent passing the infection on to others. This includes children not letting anyone touch their blood if they have a cut or a nose bleed and telling an adult when they are bleeding. Whether or not to tell a childs school is also a difficult decision for some parents. There is a worry that the school may stigmatise or treat a child with hepatitis C differently but they should ensure confidentiality at all times.
Also Check: Genotype Test For Hepatitis C
Recommended Reportable Laboratory Markers
The following laboratory markers are recommended for reporting to public health to aid in case ascertainment, case classification, and monitoring cure continua for hepatitis C:
- HCV RNA , including quantitative, qualitative, and genotype testing
- HCV antigen when and if a test is approved by FDA and
- If any of the above positive results are reported, also report the following:
- Pregnancy status,
- Concurrent ALT and total bilirubin results,
- Other hepatitis serological results .
Jurisdictions are strongly encouraged to incorporate the reporting of negative/undetectable HCV RNA test results into their surveillance regulations and systems to support improved understanding of their local epidemic. Such reporting may increase awareness regarding
- acute infections and cleared infections,
- completeness of testing, and
- availability of reflex testing.
Jurisdictions might also wish to receive negative anti-HCV results to assist in identifying cases of test conversion and examine trends in screening however, they must be mindful of their ability to process and store high volumes of data. Further, caution must be taken in the collection and use of these results, as people with non-reactive anti-HCV tests do not have a reportable condition. Jurisdictions must have legal authorization for receipt of these data.
How Does Hepatitis C Affect The Liver
When infected, the liver becomes inflamed, which may cause the healthy, soft tissues in the liver to harden and scar. If not stopped, inflammation and scarring can lead to serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver or liver tumors. If the damage is severe enough, the liver may not perform all of its functions normally.
Recommended Reading: Drug Treatment For Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms Of Hcv
Many cases of HCV are not found because there are no symptoms, or the symptoms are vague and may seem like the flu. Symptoms may start from two weeks to six months after exposure, though the average is six to seven weeks.
Some people with HCV may have:
- Muscle and joint aches.
- Changes in the color of urine and stool.
- Jaundice . Jaundice may also cause itching.
- Take your medical history.
- Do a physical exam.
- Order blood tests.
- Many blood tests are used to look for HCV, so your doctor may choose to do one or many at once.
- In the past, this was the widely used treatment for HCV.
- Patients stay on these drugs for 2448 weeks.
- It only cures 2040% of patients and is associated with significant side effects.
- These are newer option to care for HCV. They are sometimes called direct-acting antivirals .
- These treatments do not use interferon.
- Patients stay on these for 1214 weeks.
- Most cases on these treatments have a greater than 90% chance of cure.
- Patients on these have fewer side effects, are better tolerated and have much better success rates than earlier treatments.
- These drugs are very high priced and not all health plans cover them.
A variety of drugs that work in different ways are used together to treat HCV so that the virus can be attacked in different ways to increase your chance of a cure. Your gastroenterologist or liver specialist, called ahepatologist, will help guide you through complex treatment options.
Zeroing In On The Hepatitis C Virus
The era of direct-acting antivirals that specifically target HCV began in 2011 with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval of the first protease inhibitors. These drugstelaprevir and boceprevir, along with several similar drugs approved latertargeted the HCV protease that is critical for viral replication. When used in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, protease inhibitors yielded SVR rates of up to 75 percent. However, this triple therapy was accompanied by additional side effects to those already present with peginterferon and ribavirin. Nevertheless, the success of HCV-specific protease inhibitors showed that the virus had vulnerabilities that could be exploited by a well-designed and properly administered drug.
More new anti-HCV drugs were developed and tested over the next several years. These new drugs included sofosbuvir and dasabuvir, which interfered with the activity of the HCV polymerase, an enzyme that is responsible for the viral replication. Members of a second class of drugs, ledipasvir and daclatasvir, targeted the NS5A region of the virus, which makes a structural protein critical for viral replication. Many of these drugs were initially tested in conjunction with peginterferon and ribavirin, or in combination with a protease inhibitor. Generally, the results were SVR rates of at least 80 percent.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis A Curable Or Treatable
Meaning Of Hcv Viral Load
The number of HCV RNA international units per milliliter of blood must be measured before treatment and during the course of treatment, to assess response. Before treatment, however, the HCV viral load is not related to the patient’s liver disease severity or HCV prognosis. This is important for patients and providers to understand.
Note: In hepatitis B, unlike hepatitis C, a higher HBV DNA viral load does correlate with increased disease severity and increased likelihood of outcomes such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
Are There New Treaments Currently Under Investigation For Hcv
There are two new types of compounds currently under development by several pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies in the United States.
- Protease inhibitors: Protease inhibitors are compounds that interfere with the ability of certain enzymes to break down proteins. Protease inhibitors can keep a virus from making copies of itself within an infected cell.
- Polymerase inhibitors: Polymerase inhibitors are molecules that bind to polymerase enzymes, which are responsible for the formation of new RNA from an existing strand of RNA. By binding to the HCV RNA-dependent polymerase enzymes, these inhibitors prevent the formation of new RNA.15
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine In Newborns
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HCV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis C usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Because symptoms of hepatitis C are usually absent, persons with risk for HCV infection should be tested. The blood test for hepatitis C infection is called the hepatitis C antibody test. People who have hepatitis C infection will show positive antibodies on this test. In many cases, it is necessary to confirm a positive hepatitis C antibody test with a more specific test, such as a test for HCV virus RNA.
If you think you have hepatitis C or have risk for hepatitis C, you should contact your doctor. The Communicable Disease Control Unit may be able to help answer your questions.
I Have Hepatitis C How Can I Find Out If My Baby Is Infected
There is a low chance around 6 to 10 % of a mother with hepatitis C passing the virus to her baby. If your child does test positive for hepatitis C the good news is that most children with hepatitis C usually grow normally and healthily like any other children and although it isnt available for children at the moment, there are drugs which can cure hepatitis C can cure up to 90% of adults with hepatitis C. There is also a small chance that your baby may naturally clear the infection themselves.
Read Also: How Much Is A Hepatitis B Shot
What Causes Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus . The virus is passed from person to person through contact with blood infected with HCV. Mothers infected with HCV can pass the virus on to their children at birth. While this is the most common way for a child in the United States to become infected with HCV, it is unusual. A mother infected with HCV has about a 5 percent chance of passing the virus to her child. About a quarter of infants infected with the virus clear it without treatment by the time they reach age 3.
Older children, especially teenagers, can contract HCV through injection drug use. The virus can spread through other forms of contact with potentially infected blood . Tattoos and body piercings appear to be safe as long as they are done with sterile instruments.
What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
Doctors refer to hepatitis C infections as either acute or chronic:
- An acute HCV infection is a short-term illness that clears within 6 months of when a person is exposed to the virus.
- A person who still has HCV after 6 months is said to have a chronic hepatitis C infection. This is a long-term illness, meaning the virus stays in the body and can cause lifelong illness. An estimated 3.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic HCV.
Read Also: How To Do Hepatitis B Test
Surveillance Activities For Chronic Hepatitis C
Due to varying levels of resources, jurisdictions might be at different stages of implementing surveillance activities for chronic hepatitis C. The following section provides best practice models for core and enhanced surveillance activities for consideration by jurisdictions. Enhanced surveillance activities should be identified based on local priorities.
Best Practice Models for Core and Enhanced Chronic Hepatitis C Surveillance
Core Surveillance
Case Ascertainment and Reporting
- Create an electronic system for systematically collecting and storing hepatitis C test results and other case data longitudinally for unique persons.
- Establish a method to receive hepatitis C laboratory data and enter into the hepatitis C system/registry, preferably through an automated ELR system. ELR is the most efficient way to receive these data, especially if the ELR system can automatically enter the hepatitis C records into the surveillance system.
- Jurisdictions with an existing ELR system for other conditions can incorporate hepatitis C testing.
- If ELR is not possible, work with high volume testers to receive data another way .
Investigations
Quality Assurance
Analyses
Policy
Data Sharing
Enhanced Surveillance
Case Ascertainment and Reporting
Analyses
Treatments For Chronic Hepatitis C
If the infection has lasted more than six months, doctors may start treatment with two drugs: peginterferon and ribavirin. Doctors do not treat children with hepatitis C until they reach age 3 because of concerns of possible toxicity and the low chance that a child younger than 3 will have significant liver damage from HCV.
Some children with other medical conditions, such as those with thalassemia, other viral infections, or serious kidney disease, may need to be treated differently. You should tell your doctor if your child has any other medical conditions before starting treatment for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: The Cause Of Hepatitis C
What Are The Stages Of Liver Damage
There are different stages of liver fibrosis, each of which can be described with a fibrosis score. Your healthcare professional uses this score to determine how much liver scarring you have, based on several factors. Ask your healthcare professional any questions you may have about your fibrosis score.
Tap through the following graphic to see the different stages of fibrosis from F0 to F4 .
What Are The Treatment Options For Hcv
Currently, the standard of care for the treatment of HCV is pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin. This combination therapy is typically a 24-week or 48-week course. Research has shown that combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin can result in undetectable levels of HCV in 40-50 percent of people with genotype 1 and 70-80 percent of people with genotypes 2 and 3.11,12,13,14
Recommended Reading: How Long Can You Live If You Have Hepatitis B
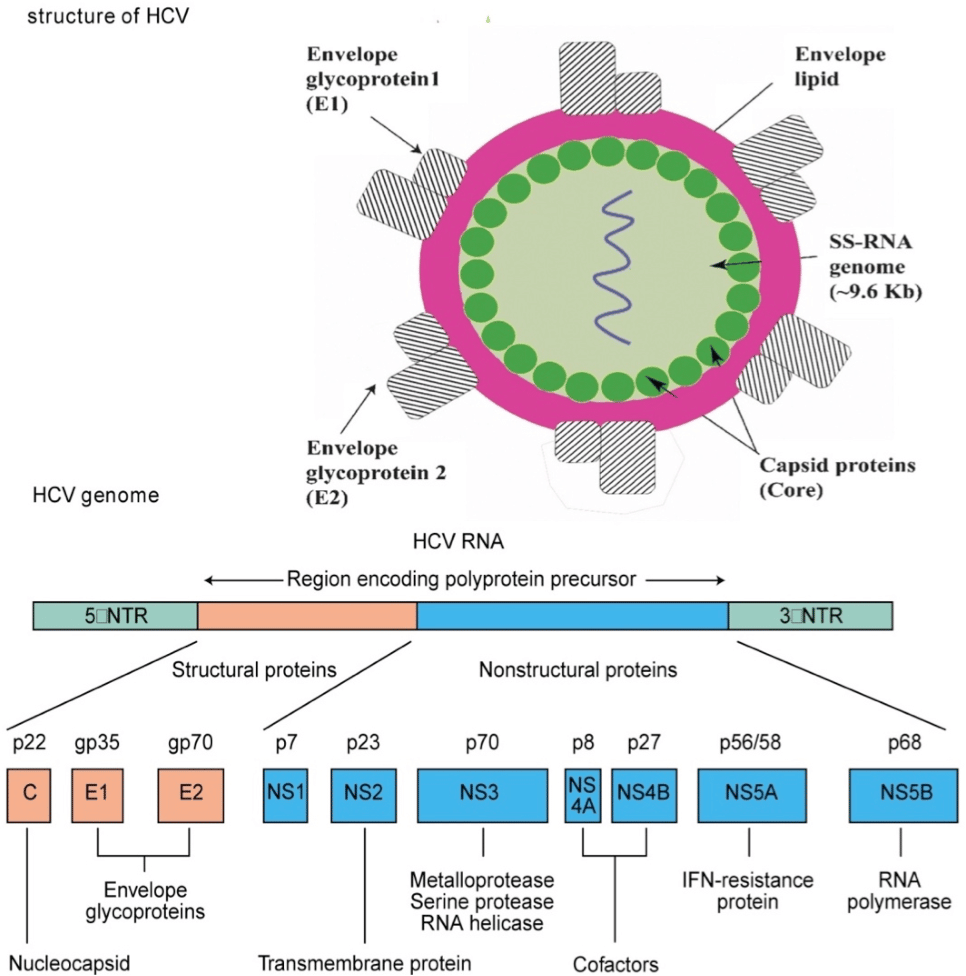
About The Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus that predominantly infects the cells of the liver. This can result in inflammation and significant damage to the liver. It can also affect the livers ability to perform its essential functions. Although it has always been regarded as a liver disease – hepatitis means inflammation of the liver – recent research has shown that the hepatitis C virus affects a number of other areas of the body. These can include the digestive system, the lymphatic system, the immune system and the brain.
Hepatitis C was first discovered in the 1980s when it became apparent that there was a new virus causing liver damage. Before being properly identified in 1989 it was originally known as non-A non-B hepatitis. In 1991 a screening process was developed making it possible to detect HCV in blood samples. As a relatively new disease there are still many aspects of hepatitis C which are yet to be fully understood.
There are an estimated 150 million people worldwide chronically infected with hepatitis C. The level of infection, known as prevalence, varies widely from country to country. In some countries, such as Egypt, it is as high as15%. In the United States it is believed to be 1% and in the UK it is believed to be around 0.5%. The virus can only be transmitted by infected blood.