Why Hepatitis C Lead To Kidney Disease
The speculations of the question of, why and how hepatitis C affects the kidneys are many. The main reason for this is the behavior of HCV in the body.
When a person is infected by HCV, the immune system is triggered to get rid of the infection. In the case of HCV, the immune system is triggered to become more active than usual leading to the deposition of complexes in the kidney. This lead to the following:
- Abnormal kidney functions
- Inflammation in the kidneys
Note: As it is seen that Hepatitis C causes the stimulation of the immune system, there is no doubt about the fact that HCV can lead to the rejection of a transplanted kidney. Therefore, it is of the utmost importance that the patients who have undergone a kidney transplant must be screened for Hepatitis C.
Consider Having Your Kidneys Tested If Diagnosed With Hep C
In spite of its name, the disease hepatitis C , is a multiorgan disease affecting organs beyond the liver. Chronic hepatitis C virus has the potential to affect wide-ranging organ systems, including the kidneys, the skin, the hematological system, and even cause autoimmune disease and diabetes. When it comes to the kidneys, hepatitis C tends to affect the “filter” of the kidneys, in various ways, creating different disease processes.
This realization that hepatitis C can have a major impact on kidney function and cause kidney disease is an essential take-home message, both for the healthcare provider managing the hepatitis C disease process, as well as for patients. It tells us that patients with hepatitis C should be evaluated for problems that might suggest kidney disease. Conversely, patients presenting to a nephrologist with certain signs or symptoms might need to be worked up for hepatitis C.
Outcomes Of Interest And Follow
The CKD was defined as having eGFR 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or any urine protein/creatinine ratio 150 mg/g in 2 separate occasions three months apart. The eGFR was calculated by Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation . Annual changes in eGFR were recorded for every patient. The developments of new CKD , absolute/relative changes of eGFR and percentages of patients having 50% decline of eGFR at 3rd years from the baseline were accurately recorded during the follow-up period.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis C In Post
There are limited data on the use of the new DAAs together with the calcineurin inhibitors like cyclosporins and tacrolimus in HCV-infected post renal transplant recipients. Prescribing information from boceprevir and telaprevir showed significant increase in plasma concentration of cyclosporin, sirolimus or tacrolimus, thus the plasma concentration level of these drugs should be monitored closely. The AASLD/IDSA guideline does not recommend the co-administration of simeprevir and cyclosporine based on a pharmacokinetic study of simeprevir, daclatasvir and ribavirin in recurrent hepatitis C patients after orthotopic liver transplant, where the simeprevir plasma concentration was found to be raised by 6-fold in the presence of cyclosporin. According to the AASLD/IDSA guidelines, no dose adjustment is required for combination therapy of sofosbuvir and simeprevir when co-administered with tacrolimus based on studies in liver transplant patients.
Hepatitis C And Renal Transplant
Hemodialysis is a risk factor for HCV infection. KDIGO guidelines recommend all renal transplant candidates should be screened for HCV and state that HCV infection is not a contraindication to renal transplant. A meta-analysis on 13 observational studies by Fabrizi et al found that most studies showed an increase in all-cause mortality and all-cause renal graft loss among renal transplant recipients with HCV. This is likely due to post-transplant immunosuppression and undiagnosed HCV infection prior to transplant. Hepatitis C infection in the setting of post renal transplant had been reported to cause specific diseases in the liver and the transplanted kidney.
In a cohort study of 614 renal transplant recipients, 2.45% were diagnosed with MG post transplant. In eleven of them were de novo MG and 6 out of the 11 de novo MG cases were associated with HCV infection. All but one of the HCV infected recipients were not treated before the transplant. Other studies also found that HCV is a strong aetiologic factor for development of MG post transplant.
Read Also: Minute Clinic Hepatitis B Vaccine
Why A Liver Virus Would Damage The Kidney
Damage to the kidney from hepatitis B virus is not usually a result of direct infection. In fact, the immune system’s abnormal reaction to certain parts of the virus may play a larger role in disease causation.
These viral components will typically get attacked by your antibodies in an attempt to fight the infection. Once this happens, the antibodies will bind with the virus, and the resultant debris will get deposited in the kidney. It can then set off an inflammatory reaction, which could cause kidney damage. Hence, rather than the virus directly affecting the kidney, it is your body’s response to it that determines the nature and extent of kidney injury.
Kidney Disease From Hep C Treatment
In a nutshell, treat the cause. In those found to have severe kidney damage which could be causally linked to hepatitis C, the treatment should focus on treating hepatitis C. However, it’s not always that straightforward. Not every patient with hepatitis C is necessarily a candidate for treatment since response rates vary and the side effects of therapy have to be kept in mind.
Certain patients could already be past the point of no return when it comes to both salvaging liver or kidney function. Kidneys don’t especially have much of a regenerative capacity. So if severe scarring has already occurred in the kidneys, it’s unlikely that the patient would recover kidney function even with treatment of hepatitis C. Regardless, there could be perfectly valid reasons , to still treat hepatitis C.
An important point to remember is that the presence of kidney disease itself changes treatment choices for hepatitis C as well. This is because therapy is often different based on the level of kidney damage. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment path for you.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Hepatitis B
Assessment Of Hepatitis C And Liver Disease Status In Renal Patients
The clinical tools used in assessing HCV and the liver disease in non-uremic patients are generally applicable to renal patients apart from a few notable differences. HCV infected patient on hemodialysis tend to have normal alanine transaminase possibly due to high lactate level, which cause rapid consumption of NADH co-enzyme or enzyme during dialysis.
All anti-HCV-positive CKD patients should be assessed for HCV RNA viral load, HCV genotyping as well as liver fibrosis. HCV genotype is a strong predictor of response to anti-HCV treatment. KDIGO recommended special steps in drawing blood sample for HCV RNA tests in hemodialysis patients because heparin is an inhibitor of polymerase chain reaction. In order to avoid contamination with heparin which is used in hemodialysis session, the blood sample for HCV RNA should be taken from a peripheral vein before the dialysis session.
We look into several studies that analysed liver biopsy findings in this group of patients. These studies revealed that about 22%-81% of HCV positive ESRD patients had histological evidence of liver fibrosis on biopsy while a smaller percentage of approximately 13%-25% had biopsy proven cirrhosis.
Patients with clinical or histological evidence of cirrhosis should have further assessments to look for the complications of cirrhosis such as upper endoscopy for varices and liver ultrasound for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance.
Treatment Of Hcv Infection
Greater eradication of HCV infection by antiviral therapy has been documented in hemodialysis patients than in those with normal renal function , possibly reflecting the high antiviral drug plasma levels achieved because of reduced renal clearance. Actually, the clearance of PEG-IFN is reduced by 45% in patients with ESRD , being mainly affected by the permeability and pore size of dialyzers . This accounts for the high incidence of adverse effects in dialysis patients .
A meta-analysis of 24 prospective studies, including 529 HCV-positive patients on dialysis, showed that monotherapy with IFN allowed SVR in 39% of cases, but 19% of patients were withdrawn from treatment because of side effects . Similar efficacy results were reported in 4 trials with 116 patients given PEG-IFN monotherapy but the drop-out rate was 27% . Overall, there was, however, very high between-study variability as far outcomes independent of the antiviral therapy used, possibly because of the fact that only few of them were randomized or had controlled design. This precludes any conclusions about the indication of preferably using IFN or PEG-IFN in hemodialysis patients with HCV infection.
Better SVR response to these antiviral agents can be anticipated in dialysis patients if pretreatment viral load is low, the degree of cirrhosis is moderate, and the infection results from HCV genotype other than type 1 .
Table 3.
Results of combined treatment of IFN or PEG-IFN with RBV in dialysis patients
You May Like: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
How Can I Protect Myself From Hepatitis C Infection
If you dont have hepatitis C, you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink
- not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
Hepatitis C can spread from person to person during sex, but the chances are low. People who have multiple sex partners, have HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases, or who engage in rough or anal sex have a higher chance of getting hepatitis C. Talk with your doctor about your risk of getting hepatitis C through sex and about safe sex practices, such as using a latex or polyurethane condom to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C.
If you had hepatitis C in the past and your body fought off the infection or medicines cured the infection, you can get hepatitis C again. Follow the steps above, and talk with your doctor about how to protect yourself from another hepatitis C infection.
If you think you may have been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent liver damage.
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Dont Miss: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Dog Food
Recommended Reading: Which Hepatitis Is An Std
Side Effects Of Antiviral Therapy
Treatment with IFN and ribavirin is associated with frequent and sometimes serious side effects. Among the latter are autoimmune diseases , significant hemolytic anemia and severe depression. In a recent meta-analysis of eleven clinical studies published by Fabrizi et al, the summary estimate for dropout rate was 0.18 , with a large heterogeneity across studies, mainly due to anemia and infections .
Except from hemolytic anemia, side effects are mainly related to IFN. The majority of the patients receiving IFN presents with a flu-like syndrome, characterized by diffuse myalgia, headache, fatigue and fever. Generally, these symptoms are self-limited and managed by common analgesics. Depression can be induced by IFN in 20% to 30% of the cases, usually after three months of treatment. Being mild to moderate in intensity, IFN-induced depression can generally be handled with conservative measures, by non-psychiatrist professionals. However, if severe depression develops, HCV treatment must be stopped and the patient should be immediately referred to a psychiatrist. IFN-induced cytopenias , are relatively common, typically dose-dependent and rarely associated with clinically significant complications, even in CKD patients. IFN dose reductions and the use of growth factors usually allow the continuation of therapy.
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But its important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Read Also: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you havent been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Chronic Hepatitis C After Kidney Transplantation
Although some studies have failed to find a negative impact on clinical outcomes after KT, the majority of studies so far reported indicate that HCV infection is associated with increased liver-related mortality and fibrosis progression among HCV-infected KT patients, with a significant reduction in patient and graft survival, possibly related to accelerated fibrogenesis and increased liver damage induced by the use of immunosuppressive regimens. Recent evidence also suggests that KT recipients with chronic HCV infection have an increased risk of post-transplant de novo glomerulonephritis, diabetes mellitus, and azathioprine hepatotoxicity.
In contrast to what is observed in CKD patients under dialysis, HCV-positive KT recipients more often present with false-negative anti-HCV results, even with newer immunoassays. In a recent study, 19 out of 417 KT recipients were HCV RNA-positive and 3 of those patients were anti-HCV-negative by using chemiluminescence immunoassays. This inability to mount an antibody response against HCV is probably related to the immunosuppressive therapy. Another consequence of immunosuppression is the significant increase in HCV viral load, with no reports of intermittent viremia so far. Interestingly, similarly to hemodialysis subjects, there is a very low prevalence of occult HCV infection in KT recipients.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis A Spread
When Do Symptoms Develop
Many patients experience no symptoms and, for those who do, symptoms may not show up for years or even decades. Chronic liver disease in HCV-infected people usually progresses slowly without detection. Many times, HCV infection is not recognized until it is identified when people are screened for blood donations or through routine examinations.6 HCV is not routinely screened for in regular examination, so its important that someone who may have been exposed talk to a doctor. When left undiagnosed, HCV can lead to serious liver problems, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, and is the most common reason for liver transplantation in the United States.1
Hepatitis C And Kidney Disease
Ashik HayatAhmad Mitwalli
1Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine , King Khalid University Hospital, Riyadh 11461, Saudi Arabia
Academic Editor:
Abstract
Multiple extrahepatic manifestations have been associated with chronic hepatitis C, the most important among them being cryoglobulinemia, glomerulonephritis, porphyria cutanea tarda, lichen planus, seronegative arthritis, and lymphoproliferative disorders as in the sudies of Bonkovsky and Mehta and El-Serag et al. . We will discuss in this paper chronic hepatitis C- related kidney disease and course and management of patients with chronic hepatitis C in special circumstances like hemodialysis and kidney transplantation.
1. Cryoglobulinemia
2. HCV-Related Glomerular Disease
3. Treatment of HCV-Related Cryoglobulinemia and Glomerular Disease
4. Hepatitis C in Dialysis
References
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Chronic Hepatitis B
Treatment Choices For Hepatitis C In Patients With Kidney Disease
Hepatitis C virus infection has an estimated prevalence of 3% in the world population and is still frequent among patients undergoing long-term dialysis all over the world. The Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study found that the frequency of patients with HCV in developed countries was 7.5% .
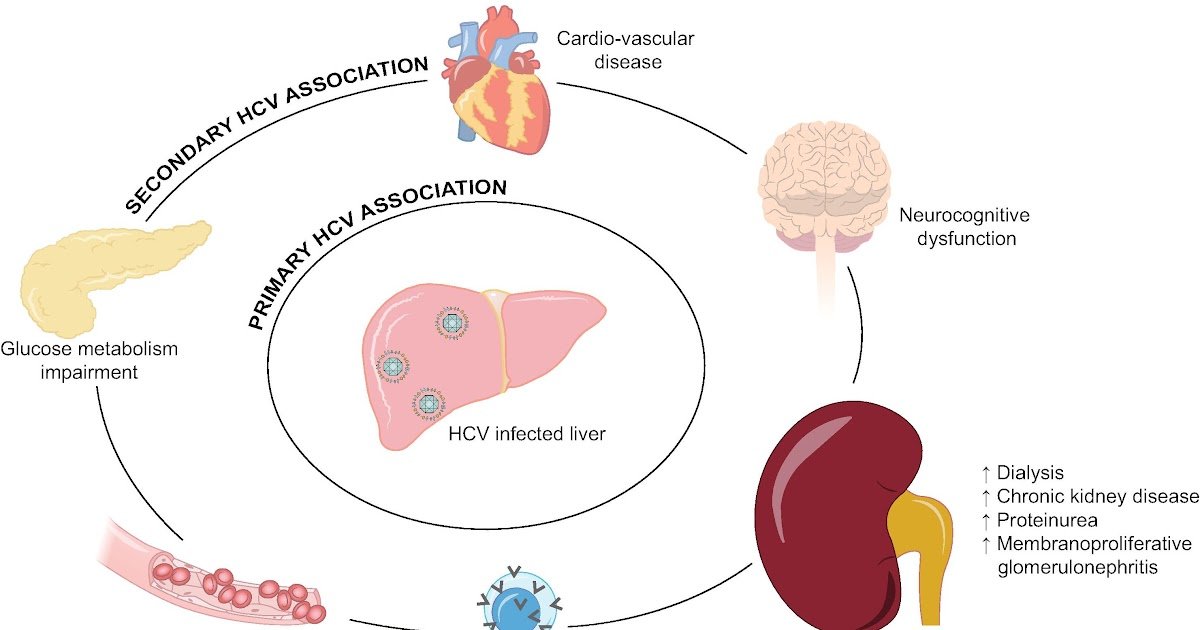
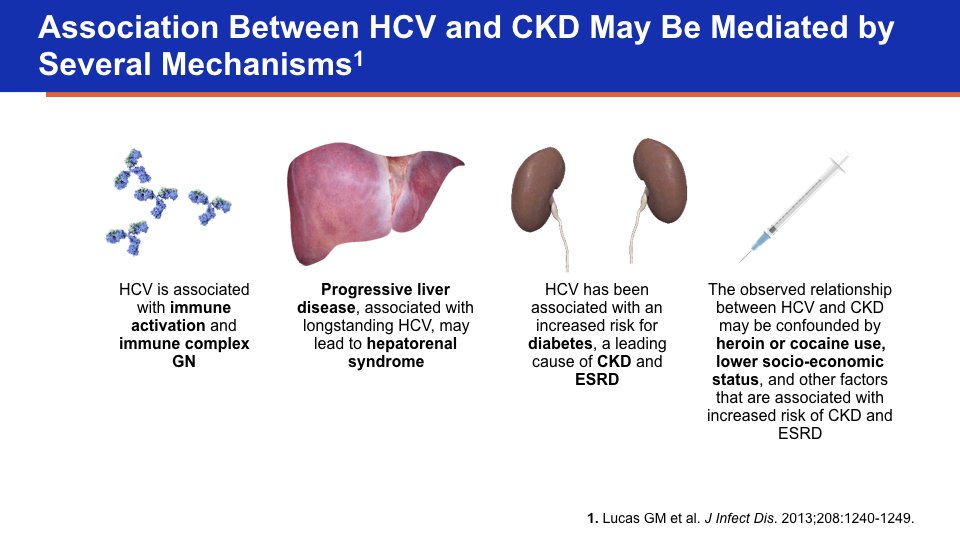
Patients with long-standing HCV infection are at risk for progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent evidence has been accumulated showing that chronic HCV infection can have serious consequences for several organs and systems other than the liver. The extrahepatic activity of chronic HCV could explain the relationship between HCV infection and the decline in kidney function in patients with CKD. A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies demonstrated a relationship between anti-HCV positive serologic status and higher incidence of CKD in the general population the summary estimate for adjusted hazard ratio with HCV was 1.43 , according to a random-effect model . In addition, interferon -based regimens were able to reduce progression or incidence of CKD in diabetic and nondiabetic populations. Various hypotheses have been given to explain the kidney damage caused by HCV, such as subclinical immune complex deposition or accelerated atherosclerosis at kidney level induced by HCV . Also, chronic HCV could promote atherosclerosis through several direct or indirect biologic mechanisms .
The relationship between chronic HCV and cardiovascular or kidney risk.