The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate Plasma If You Had Hepatitis B
What To Think About
If you are exposed to HBV before you have received all three shots in the vaccination series, a dose of hepatitis B immune globulin usually will prevent infection until the vaccine takes effect.
If you have already had hepatitis B and have developed protective antibodies to the virus, you do not need the vaccine because you have lifetime protection against the infection. If you are not sure whether you have had hepatitis B, you can be tested, or you can be vaccinated without testing. The vaccine is not harmful for you if you are already immune.
If you have chronic HBV infection, the vaccine will be ineffective, although it is not harmful.
The vaccine is safe for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Who Is Allowed To Have The Vaccine
The vaccination is routinely available to children as part of the NHS 6-in-1 vaccine schedule from birth at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age.
Although the risk of infection is low in the UK, the virus persists for longer in children than it does adults so to avoid complications such as scarring and even liver cancer theyve given the vaccine.
Other high risk groups of people offered the vaccine include:
close family or sexual partners of someone with hepatitis B male and female sex workers people with any form of chronic liver disease people who inject drugs or have a partner who injects drugs babies born to infected mothers people who change their sexual partners frequently men who have sex with men anyone who receives regular blood transfusions or blood products, and their carers people with chronic kidney disease people who work somewhere that places them at risk of contact with blood or body fluids, such as nurses, prison staff, doctors, dentists and laboratory staff people travelling to high-risk countries prisoners families adopting or fostering children from high-risk countries
Also Check: How Long Is The Hepatitis A Vaccine Good For
What Hepatitis B Immunisation Involves
Full protection involves having 3 injections of the hepatitis B vaccine at the recommended intervals.
Babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection will be given 6 doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine to ensure long-lasting protection.
If you’re a healthcare worker or you have kidney failure, you’ll have a follow-up appointment to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
If you have been vaccinated by your employer’s occupational health service, you can request a blood test to see if you have responded to the vaccine.
Rare Side Effects After Immunisation
There is a very rare risk of a serious allergic reaction to any vaccine. This is why you are advised to stay at the clinic or medical surgery for at least 15 minutes following immunisation, in case further treatment is required.
If you think your child may be having a serious allergic reaction and you are no longer at the clinic where they were immunised, take them immediately to your doctor or to the nearest hospital, or call 000 for an ambulance.
Another rare side effect is the hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode . If they are experiencing HHE, a baby may be:
This may occur from one to 48 hours following vaccination. The whole episode may last from a few minutes to 36 hours.
If you think your child may be having an HHE episode, take them immediately to your doctor or to the nearest hospital.
Follow-up of children with HHE shows no long-term neurological or other side effects.
Read Also: Life Insurance For Hepatitis B Carrier
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Genotype 1a Treatment
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a highly infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus. It affects the liver and exists in two forms acute and chronic. The virus can be transmitted through direct contact with infected blood and other bodily fluids, as well as via sexual intercourse. It can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth.
Other ways to contract the virus include intravenous drug use, working in healthcare , tattooing, acupuncture, unprotected sex , and living with an infected individual. People with compromised immune systems and other chronic diseases are also at a higher risk of contracting the virus.
It is important to note that Hepatitis B cant be transmitted via holding hands, kissing, breastfeeding, or eating with the same utensils.
Commonly, the chronic variation of the disease shows no obvious symptoms, though people suffering from it may eventually develop liver cancer and cirrhosis. On the other hand, acute Hepatitis B takes between 30 and 180 days to show the first signs. The most common symptoms include a loss of appetite, fever, weakness, the yellowing of eye whites and skin, dark urine, fatigue, pain in muscles and joints, and abdominal discomfort.
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
Also Check: Can Liver Disease Cause Hepatitis C
Response To Booster Dose
Because study participants in group 3 received a booster vaccine dose 8 years earlier , they did not receive a booster dose at 30 years. Study participants in groups 1 and 2 with anti-HBs levels < 10 mIU/mL received booster doses however, because group 2 participants had anti-HBs levels 10 mIU/mL at 22 years, we chose to focus on group 1 for booster dose response. In group 1, among 118 eligible participants, 96 who had anti-HBs levels < 10 mIU/mL received a booster dose of hepatitis B vaccine. The median age of the 85 persons from whom serum was obtained after the booster dose was 40 years 47 were male. Among these 85 persons tested 30 days after the booster dose, 75 responded with anti-HBs levels 10 mIU/mL the GMC was 150.4 mIU/mL .
Level of Anti-HBs After Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster Dose in Persons Who Responded to the Primary Series, Had Not Received Subsequent Doses, and Had a 30-Year Anti-HBs Level < 10 mIU/mLAlaska, 20112012
| Characteristic . |
|---|
Immunisation Against Hepatitis B For Children
Vaccination is the best protection against hepatitis B infection and is recommended for all infants and young children, adolescents and those in high-risk groups. Vaccination can be with a vaccine against hepatitis B alone or with a combination vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis B is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule.
In Victoria, vaccination against hepatitis B is free for all babies and children including:
- Babies at birth vaccinate with hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth.
- Babies at 2, 4 and 6 months immunisation in the form of a diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, hepatitis B, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine .
- Premature babies at 12 months premature babies born under 32 weeks gestation or under 2,000g birth weight receive a single booster dose.
- Children up to and including 20 years of age.
Don’t Miss: Treatment To Cure Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable viral disease that involves inflammation of the liver.
The hepatitis B virus usually leads to a short-term infection known as acute hepatitis B. If their infection is left untreated, some people develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious, permanent condition that can cause organ damage, cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and even death.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , all people should be vaccinated against hepatitis B starting at birth. Adults who are at risk of developing hepatitis B should also receive the vaccine, which is highly effective in preventing infection.
Read on to learn more about the hepatitis B vaccine for adults, including who should receive it, the details of the dosage schedule, side effects, and more.
Prasit photo / Getty Images
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected dont know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
You May Like: Foods To Avoid With Hepatitis
Managing Fever After Immunisation
Common side effects following immunisation are usually mild and temporary . Specific treatment is not usually required.
There are a number of treatment options that can reduce the side effects of the vaccine such as giving extra fluids to drink and not overdressing if there is a fever.
Although routine use of paracetamol after vaccination is not recommended, if fever is present, paracetamol can be given check the label for the correct dose or speak with your pharmacist, especially when giving paracetamol to children.
How Is It Spread
- Sexual contact with an infected person
- Direct contact with infected blood, including sharing needles to inject drugs or other drug injection equipment that has blood on it
- Sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, syringes, or glucose monitors that may have blood on them
- Direct contact with open sores of an infected person
- Pregnant women infected with the virus passing it to their babies at birth.
The hepatitis B virus is NOT spread by casual contact such as hugging, or by sneezing, coughing, or sharing food and drinks. Hepatitis B is also not spread by breast feeding.
Read Also: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B And C
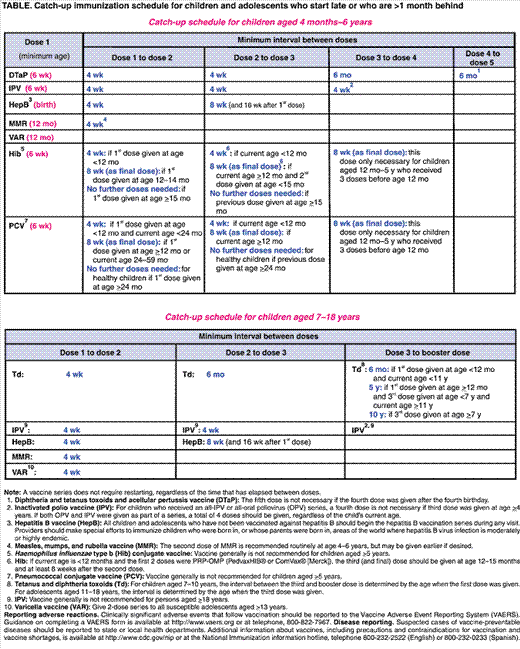
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Where Can You Get More Information
- Your doctor, nurse or health care clinic
- Your local board of health
- The Massachusetts Department of Public Health , Division of Epidemiology and Immunization at 983-6800
Chinese, Haitian Creole, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, and Vietnamese translations of this fact sheet are available under additional resources.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Take To Show Up
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Read Also: How Much Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Why It Is Used
Hepatitis B virus causes a liver infection that can lead to serious complications, including liver cancer. It is common in people throughout the world, particularly in Asia and sub-Saharan Africa.
The Canadian National Advisory Committee on Immunization recommends hepatitis B immunization for all children. Pregnant women and other adults who do not have immunity and who have a high chance of exposure should be vaccinated.