Laboratory Findings And Diagnostic Tests
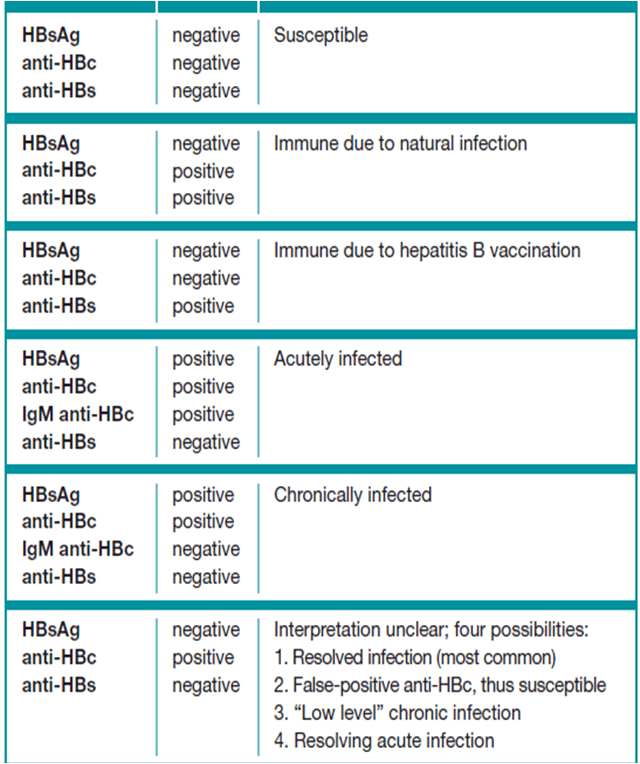
Serum HBsAg and anti-HBs are the most useful screening tests for chronic HBV infection or immunity to HBV. HBsAg is present in most chronically infected persons. Lack of anti-HBs in an unvaccinated HBsAg-negative person indicates susceptibility to HBV infection.3
Screening for HBsAg is recommended at the first prenatal visit for all pregnant women.3,109 Women in labor without HBsAg test information should have HBsAg serology on arrival. In addition, pretested women who have a history of certain risk factors should be retested at the time of admission to the hospital for delivery.3,110
Fabrizio Fabrizi MD, … Paul Martin MD, in, 2017
Scientific Tools And Resources
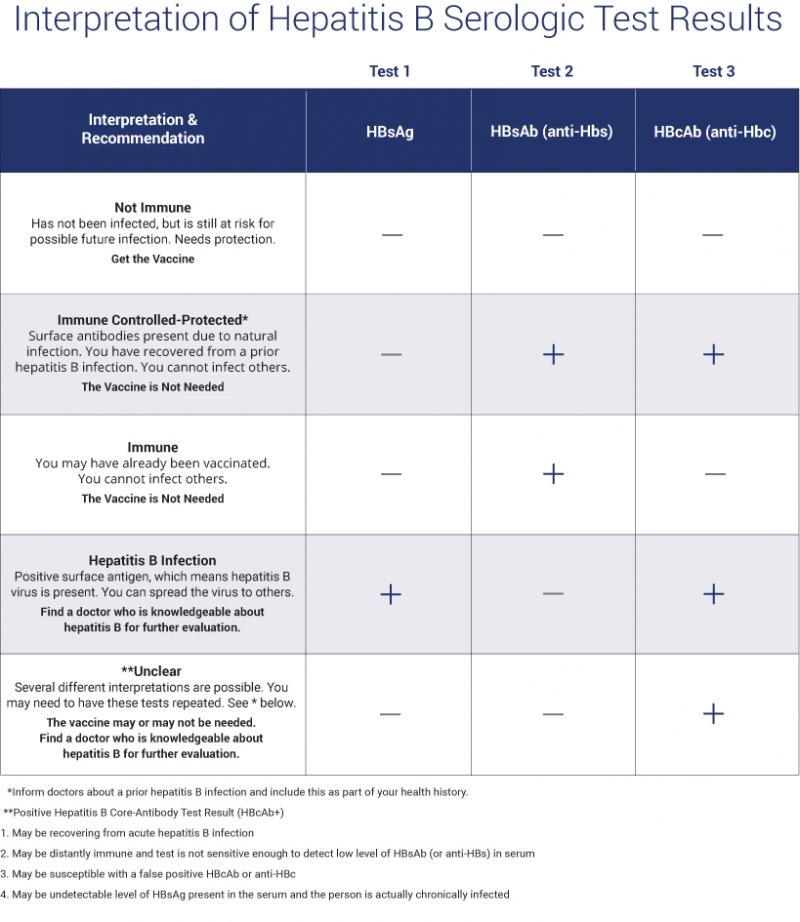
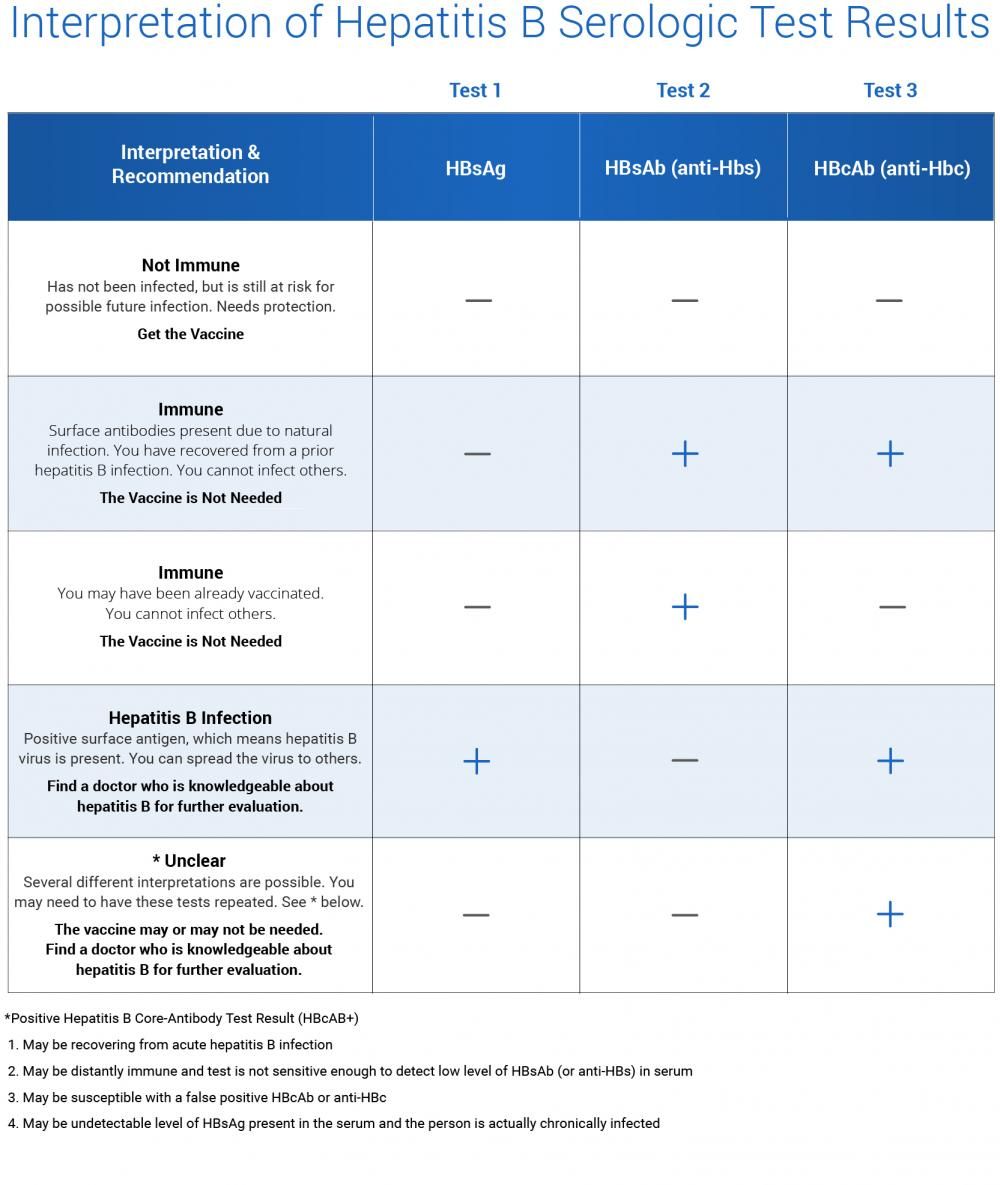
Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results
One page Summary Table describes the four most common tests used in hepatitis B serologic testing and provides guidance to interpret different patterns of test results.
Screening and Referral Algorithm for Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Pregnant Women
This is a clinical algorithm for screening and referral of pregnant women who are HBsAg-positive.
N/A=not available
*This CPT code corresponds only to the HBsAg screening component additional CPT codes might be associated with other component tests.
Notes: CDC recommends healthcare providers use prenatal HBsAg tests for pregnant women, which allows for reporting of positive results along with pregnancy status to public health jurisdictions. Refer all HBsAg positive pregnant women to Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program coordinators for case management of mother and infant: .
Laboratories reserve the right to add, modify, or stop performing tests at any time providers should review any test notifications from laboratories for changes.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
Notes From The Field: False
Weekly / March 16, 2018 / 67 311â312
Please note: An erratum has been published for this report. To view the erratum, please .
Blake Hendrickson, MPH1 Saleem Kamili, PhD2 Tim Timmons3 Peter C. Iwen, PhD4 Caitlin Pedati, MD1 Thomas Safranek, MD1
In March 2017, the Nebraska Department of Health and Human Services was contacted by a hemodialysis clinic regarding a patient who had tested negative for hepatitis B virus surface antigen after vaccination in 2010 and who later tested positive for HBsAg. A public health investigation subsequently determined that the false-negative results were caused by a surface antigen mutation. Notably, several commercial HBsAg testing kits cannot detect this mutant virus, making it a challenging pathogen for public health surveillance and intervention efforts .
Specific precautions for HBV-positive patients in a dialysis center include receiving dialysis in a separate room and being assigned separate staff members and equipment . These control measures were not implemented during 20102016 because the index patient had not had a positive HBsAg test result. After the positive HBsAg results were reported, an epidemiologic investigation was initiated by NDHHS and the Lincoln-Lancaster County Health Department to determine the cause of the false-negative test results and to identify any HBV transmission.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis Turn Into Aids
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Signs And Symptoms
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Sexually Transmitted Disease
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A, also called hep A, is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus. Some people have only a mild illness that lasts a few weeks. Others have more severe problems that can last months. You usually get the disease when you eat or drink something contaminated by poop from a person who has the virus.
The hepatitis A virus usually isnât dangerous. Almost everyone who has it gets better. But because it can take a while to go away, youâll need to take care of yourself in the meantime.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ab W/reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
You May Like: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C And B
Uses Of Surveillance Data
Acute and chronic hepatitis B surveillance data can be used to inform and improve public health interventions in the following ways:
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Don’t Miss: What Medication Is Used For Hepatitis B
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
06 February 2019
Chikako Yamamoto, Ko Ko, Junko Tanaka
17 December 2020
Desalegn Admassu Ayana, A. Mulu, R. Howe
11 July 2022
Guo Yonghao, Chen Yanping, Guo Wanshen
21 April 2021
Masami Miyakawa, Lay-Myint Yoshida, Hiroyuki Moriuchi
18 May 2021
Jaya Singh Kshatri, Debdutta Bhattacharya, ICMR-RMRC Serosurvey Team
30 April 2020
Piyawat Komolmit, Vinita Oranrap, Yong Poovorawan
volume 12, Article number: 7425
Surrogate Outcome For Nucleoside Analogs
Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion is much less durable for nucleoside analogs than peginterferon therapy, particularly among Asian patients for whom the infection has persisted since early childhood. Up to 50% of patients may experience hepatitis relapse after HBeAg seroconversion within 3 years posttreatment.92 Therefore HBeAg seroconversion is not an ideal surrogate marker of response for nucleoside analogs, particularly if the posttreatment follow-up is not long enough. As HBsAg clearance is rarely observed with nucleotide analogs, evaluation of predictors for HBsAg clearance may be difficult and less clinically useful.
Milan J. Sonneveld, Suzanne van Meer, in, 2021
You May Like: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis C
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis From Your Own Blood
Search Strategy And Identification Of Studies
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis on the diagnostic accuracy of HBsAg tests. The review was registered in PROSPERO and reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses check list. We utilised standardised methods for systematic reviews on diagnostics, including an a priori protocol .
Literature search strategies were developed by a medical librarian with expertise in systematic review searching, using a search algorithm consisting of terms for: hepatitis B, diagnostic tests, and diagnostic accuracy. We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Science Citation Index Expanded, SCOPUS, Literatura Latino-Americana e do Caribe em Ciências da Saúde , WHO Global Index Medicus, WHOs International Clinical Trials Registry and the Web of Science. We also contacted researchers, experts and authors of major trials, with no relevant manuscripts in preparation identified. Additional pertinent citations were identified through bibliographies of retrieved studies.
Abstracts were screened by reviewers AA and HK according to standard inclusion and exclusion criteria. All studies identified for full manuscript review were assessed independently by two reviewers against inclusion criteria. Papers were accepted or rejected, with reasons for exclusion specified. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion between review authors and, when required, a third independent reviewer .
Demographic Characteristics And Risk Factors For Infection With Hepatitis B Virus
As presented in Table , we had more female and married participants aged 30 years and above .
Table 1 Summary of the sociodemographic characteristics of the study participants.
A total of 1273 reported for screening for HBsAg as a prerequisite for immunization against HBV over a period of 9 months at Kibuku Health center IV, of which 624 were below the age of consent and 182 turned down subsequent recruitment in the study. Forty-three participants were HBsAg seropositive representing a prevalence of 9.2% and 424 were HBsAg seronegative. There was 100% concordance between the two screening tests .
The HBsAb, HBeAb, HBcAb seropositivity was detected among 48, 73 and 45 participants respectively. In contrast, 327 of the participants did not present with any marker of past exposure to HBV as an infcetion or as a vaccine. .
Figure 2
Representative results of the one step hepatitis B virus combo test cassette for the HBV serological markers among the HBsAg negative participants.
Interestingly, 3, 26 and 3 were simultaneously positive for the two markers of HBsAb/HBeAb, HbeAb/HBcAb and HBsAb/HBcAb respectively. In addition, 12 were concomitantly positive for the three markers of HBsAb/HBeAb/HBcAb .
Table 2 Outline of the HBV serological profile of HBsAg seronegative participants screened from Kibuku Health center IV.Table 3 Socio-demographic factors associated with HBsAb serostatus among HBsAg seronegative hospital attendees screened for HBV before immunization.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis A Caused
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Quantification And Liver Biopsy Assessment
Standard biochemical and virological assessments were previously performed according to the study protocols. Hepatitis B surface antigen levels were measured using the Abbott Architect or Roche Elecsys . Liver biopsy was a requisite for study enrollment, and biopsy samples were scored by experienced pathologists who either applied the Ishak or METAVIR systems. Liver fibrosis was defined as no significant fibrosis , significant fibrosis , or cirrhosis .
Study Selection And Characteristics
A total of 11,589 citations were identified, and 293 full-text articles examined which identified 40 studies meeting pre-defined criteria . Of the included studies, 33 compared RDTs and/or EIAs against an immunoassay reference standard, of which five focused on accuracy in HIV-positive individuals . Seven studies compared RDTs and/or EIAs against a NAT reference standard, of which 3 had data from HIV-positive patients . Studies were all either cross-sectional or case-control, predominantly in the laboratory setting, and performed in a broad range of populations, including healthy volunteers, blood donors, pregnant women, incarcerated adults, HIV and hepatitis patient cohorts with confirmed HBV infection. The prevalence of HBV ranged from 1.9 to 84% in populations tested. A mixture of serum, plasma and whole blood was used for RDTs, while studies of EIAs were performed on serum or plasma samples. Study characteristics are presented in Tables , and .
Fig. 1
Three studies had data from 442 HIV-positive patients in Uganda and South Africa, with pooled sensitivity and specificity of 57.9% and 95.8% , respectively. The corresponding pooled sensitivity and specificity for the 202 HIV-negative patients across two of these studies were 83.3% and 85.7% , respectively .
Read Also: Lactulose Dose For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Understanding Changes In Biomarkers During Disease Progression
Understanding the changes in HBV biomarkers over the course of a persons infection and recovery is key to interpreting the test results. Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 depict the typical biomarker changes over the course of hepatitis B disease.
Figure 3-1. Typical serologic course of acute hepatitis B to recovery
Acute, resolved, and chronic hepatitis BApproximately 90% of people > 5 years of age with acute hepatitis B will spontaneously clear their infection . People with resolved hepatitis B will remain positive for total anti-HBc and develop anti-HBs that protect against future HBV infection . Chronic hepatitis B is defined as an HBV infection lasting > 6 months. During the typical course of chronic infection, the total anti-HBc and HBsAg markers will always be present, whereas anti-HBc IgM will disappear . Hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B e antibody are variably present. HBV DNA levels vary during the course of chronic infection. Any detectable HBV DNA level is considered positive for surveillance purposes.
HBV-infected people with mutations in HBsAg that cannot be detected by current serologic assays may present with a negative HBsAg result despite high blood levels of HBV DNA. Some laboratories have the capacity to detect HBsAg mutants. Any HD interested in determining which laboratories can detect HBsAg mutants should follow-up with the major laboratories that perform HBsAg testing in their jurisdiction.
Data Presentation And Statistical Analysis
Categorical data are presented as frequencies and percentages. Univariate analysis was used to determine the crude odds ratio , whereas multinomial logistic regression analysis was used to determine the adjusted odds ratio . All analyses were performed at the 95% level of significance, and p< 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 26.
Read Also: Hepatitis A What Is It
Cases And Clusters Of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis B data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis B that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation based on the degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
- People of childbearing age who are or have the potential to become pregnant, indicating the potential for perinatal transmission
- Children 24 months of age to detect perinatal transmission
- People in age and demographic groups for whom infection may be acute due to recent transmission, including those
- 70 years of age
Ruling Out Cirrhosis Using Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels In Hepatitis B E Antigen
Because serum HBsAg levels were independently associated with presence of cirrhosis among HBeAg-positive patients, we attempted to identify a clinically relevant cutoff that could be used to rule out presence of cirrhosis in this population, applying our preset criteria . Because HBsAg levels varied significantly across the HBV genotypes, we performed HBV genotype-specific analyses.
As shown in , HBsAg levels could discriminate between presence or absence of cirrhosis in patients with genotypes B , C , or D , with AUROCs of 0.6620.712 . Genotype-specific cutoffs had excellent NPVs and low misclassification rates . Discrimination was suboptimal in patients with genotype A , and no clinically relevant cutoff could be identified for this subgroup because of a high rate of cirrhosis even among the patients with the highest HBsAg levels .
Also Check: If You Have Hepatitis B Do You Have Hiv
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. The symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same. So this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus and what stage of infection you may have.
Your healthcare provider may also order a series of blood tests called a hepatitis B monitoring panel to see if your infection is getting better.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Donât Miss: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive