Who Should Get The Hepatitis A Vaccine
The hepatitis A vaccine is given in two doses, six to 18 months apart. Two doses are needed for lasting protection.
The vaccine is recommended for:27
- All children, starting at 1 year
- Men who have sex with men
- People who travel or work in a part of the world where hepatitis A is common, such as certain parts of Central or South America, Asia, Africa, and eastern Europe. See the CDCs Travelers Health Information.
- People who use illegal drugs
- People who are treated with clotting factor concentrates, such as people with hemophilia
- People with chronic liver disease
- People who work with hepatitis A in a laboratory or with hepatitis Ainfected primates
- Members of households planning to adopt a child, or care for a newly arriving adopted child, from a country where hepatitis A is common. See the CDCs Travelers Health information page for international adoptions.
How Is The Diagnosis Of Viral Hepatitis Made
In acute hepatitis patients, diagnosis is promptly made based on their presenting symptoms, as mentioned earlier. In the case of chronic hepatitis patients, diagnosis becomes tricky due to the absence of symptoms or the presence of mild non-specific symptoms. The following investigations are suggested for establishing a diagnosis.
Blood Tests –
-
Liver Enzymes: Increased levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase can be found in the blood sample in patients with viral hepatitis. Apart from hepatic virus-induced liver disease, there are other causes like alcohol, medications, bacterial infection, etc., which can also cause a spike.
-
Viral Antibodies: To confirm that hepatitis is caused due to a virus, viral antibodies test is beneficial. Antibodies to hepatic viruses are identified in the blood of the infected individual.
-
Viral Proteins Test: This test is beneficial to identify the presence of the virus in chronic viral hepatitis patients wherein the virus genetic material and protein are detected in the blood.
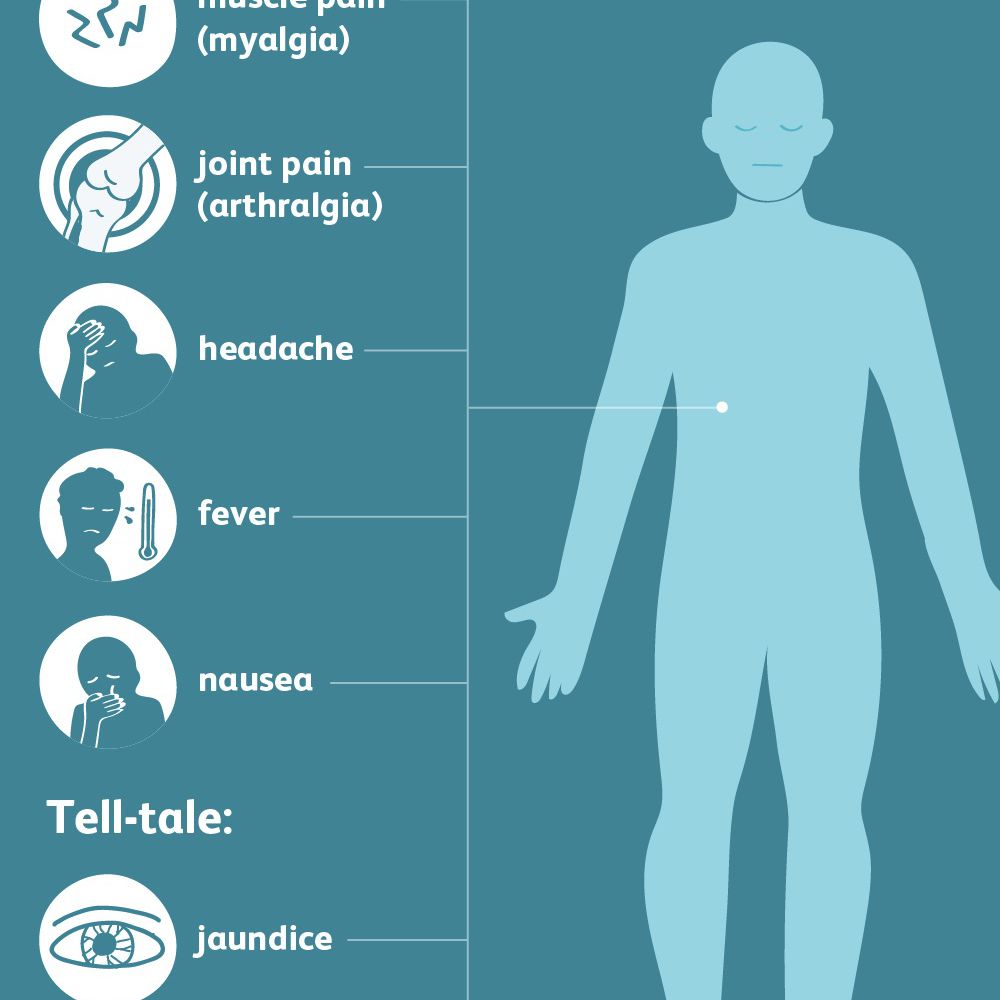
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Not all people newly infected with Hepatitis B have symptoms, but for those that do, symptoms can include:
For many people, hepatitis B is a short-term illness. For others, it can become a long-term, chronic infection that can lead to serious, even life-threatening health issues like cirrhosis or liver cancer. Your risk for developing chronic infection depends on how old you were when you first contracted the infection. About 90% of infants with hepatitis B will develop chronic infection, whereas only 2%6% of people diagnosed with hepatitis B as adults develop chronic infection.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Lead To Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
If you think you may have hepatitis B or you might have been exposed to the virus through sex or drug use, see your doctor or gynecologist to get tested. The blood test also can tell whether someone has an acute infection or a chronic infection. Let the doctor know the best way to reach you confidentially with test results.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
Start Treatment For Viral Hepatitis Today
If you have been diagnosed with viral hepatitis, or suspect that you may have viral hepatitis, contact our team at Washington Health Institute in Washington, D.C. Our experienced providers can review your medical history, discuss your symptoms, address any questions or concerns you may have and develop a personalized treatment plan to meet your needs. Fill out our online appointment request form or call us at to get started.
Don’t Miss: Cirrhosis Caused By Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is usually spread through:12
- Birth to a mother who has hepatitis B
- Sharing or reusing needles, syringes, and drug preparation equipment such as cookers and cotton when injecting drugs. Hands or drug preparation equipment that have even tiny amounts of blood on them can spread hepatitis B.
- Accidental needle stick or other sharp instrument injury
A less common way to spread hepatitis B is through pre-chewed food to a baby from a mother who has hepatitis B.12 However, hepatitis B cannot be spread through breastfeeding.
When To See Your Doctor
Always check with your doctor if you have any of the signs of hepatitis. If you don’t get treatment it can lead to cirrhosis, a serious scarring of your liver.
Also make an appointment if a friend or member of your family comes down with the disease. There’s a risk you could get infected, too.
Be on the lookout for symptoms of hepatitis if you travel to a country where the disease is common. Call your doctor if you think you’re showing any signs.
Show Sources
You May Like: Can Hepatitis Be Sexually Transmitted
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Recent Increases In Hepatitis C Infections
Between 2013 and 2020, the reported number of acute HCV infections more than doubled. High rates of new infections were predominantly among young adults aged 20-29 years and aged 30-39 years. The number of cases continues to increase, in 2020 an estimated 66,700 new HCV infections occurred in the United States. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
You May Like: What Form Of Hepatitis Is Sexually Transmitted
Abnormalities In Heme Metabolism And Excretion
One way to understand jaundice pathophysiology is to organize it into disorders that cause increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin excretion .
Prehepatic pathophysiology
Prehepatic jaundice results from a pathological increase in bilirubin production: an increased rate of erythrocyte hemolysis causes increased bilirubin production, leading to increased deposition of bilirubin in mucosal tissues and the appearance of a yellow hue.
Hepatic pathophysiology
Hepatic jaundice is due to significant disruption of liver function, leading to hepatic cell death and necrosis and impaired bilirubin transport across . Bilirubin transport across hepatocytes may be impaired at any point between hepatocellular uptake of unconjugated bilirubin and hepatocellular transport of conjugated bilirubin into the gallbladder. In addition, subsequent cellular due to inflammation causes mechanical obstruction of the intrahepatic biliary tract. Most commonly, interferences in all three major steps of bilirubin metabolism â uptake, conjugation, and excretion â usually occur in hepatocellular jaundice. Thus, an abnormal rise in both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin will be present. Because excretion is usually impaired to the greatest extent, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia predominates.
Posthepatic pathophysiology
| Present | Present |
Laboratory findings depend on the cause of jaundice:
Role In Human Disease
Examples of common human diseases caused by viruses include the , , , and . Many serious diseases such as , , , , and are caused by viruses. The relative ability of viruses to cause disease is described in terms of . Other diseases are under investigation to discover if they have a virus as the causative agent, such as the possible connection between and neurological diseases such as and . There is controversy over whether the , previously thought to cause diseases in horses, could be responsible for illnesses in humans.
Viruses have different mechanisms by which they produce disease in an organism, which depends largely on the viral species. Mechanisms at the cellular level primarily include cell lysis, the breaking open and subsequent death of the cell. In , if enough cells die, the whole organism will start to suffer the effects. Although viruses cause disruption of healthy , resulting in disease, they may exist relatively harmlessly within an organism. An example would include the ability of the , which causes cold sores, to remain in a dormant state within the human body. This is called latency and is a characteristic of the herpes viruses, including EpsteinâBarr virus, which causes glandular fever, and , which causes chickenpox and . Most people have been infected with at least one of these types of herpes virus. These latent viruses might sometimes be beneficial, as the presence of the virus can increase immunity against bacterial pathogens, such as .
Also Check: How Much Is A Hepatitis A Shot
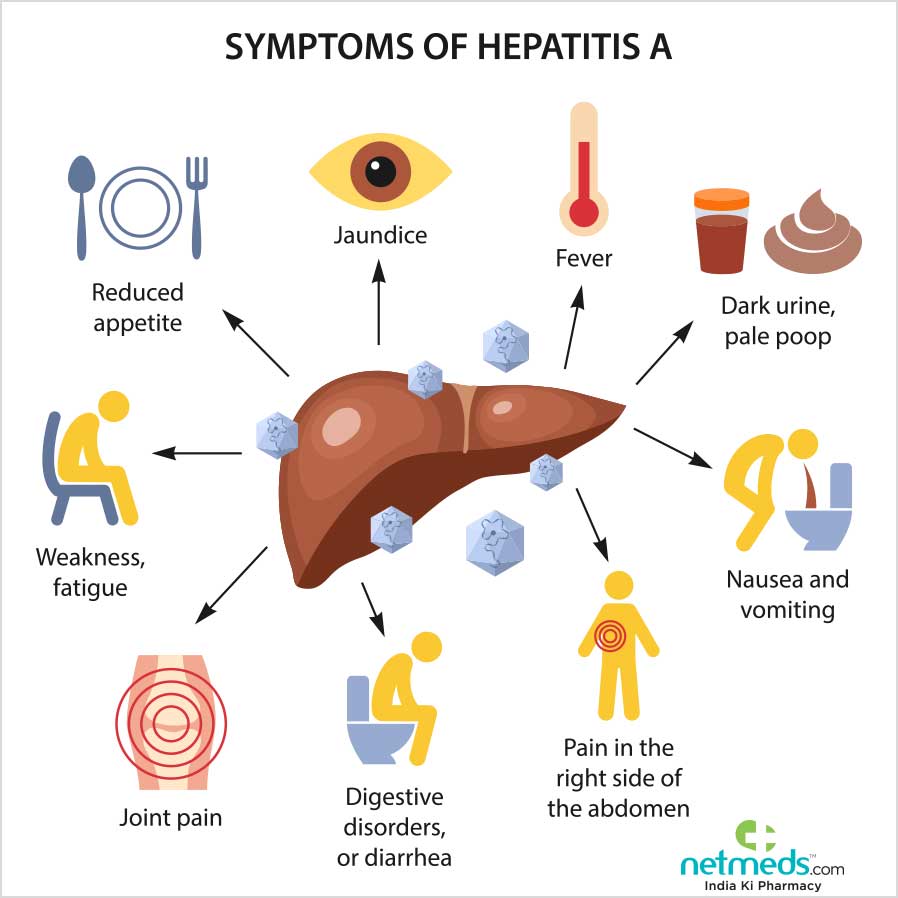
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is contagious. The virus lives in poop from people who have the infection. That’s why it’s so important to wash your hands before eating and after going to the bathroom. If you don’t, and then go make yourself a sandwich, hep A virus might end up on your food, and then in you! People who recover from hepatitis A have immunity to the virus and won’t get it again.
The hepatitis A vaccine has made the infection less common in the United States and other developed countries. Getting vaccinated helps a person’s body make antibodies that protect against hepatitis infection. The hepatitis A vaccine is given to all kids when they’re between 1 and 2 years old, and to people who travel to countries where the virus could get into the food and water supply.
These steps also help keep people safe from hepatitis A:
- regular hand washing, especially after going to the bathroom or diapering a baby, and before eating
- washing fruits and vegetables before eating them
- not eating raw shellfish, such as raw oysters
Testing For And Preventing Hepatitis
Lok says a simple blood enzyme test can confirm a liver injury. The most common tests include the aspartate aminotransferase test and the alanine aminotransferase test. A blood sample also can help identify the cause of the hepatitis.
People who have risk factors for hepatitis should have blood tests to determine whether they are infected, even if they do not have symptoms or their AST and ALT tests are normal, because liver injury may wax and wane.
If you dont have hepatitis, get vaccinated. Being more health conscious, like eating healthy foods and exercising regularly, can also help prevent hepatitis.
Prevention is always better than the cure, Lok says. There are safe, effective vaccines that can prevent hepatitis A, B and D. However, there isnt a vaccine for hepatitis C, and the vaccine for hepatitis E is not FDA-approved or available in the U.S.
Raise awareness of this virus. Screen those at risk, vaccinate those susceptible and treat chronic infection is indicated, says Lok, who has been involved in developing the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases guidelines since 2001.
To make an appointment to discuss hepatitis concerns or treatment, call Michigan Medicines Hepatology Program at 844-233-0433.
You May Like: Ways To Catch Hepatitis C
Viral Hepatitis And Hepatitis A Outbreak
Southeast Michigan is experiencing an outbreak of hepatitis A. Information about this outbreak is at the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services website. Vaccination is recommended to prevent hepatitis A.
if you are concerned about symptoms or risk for viral hepatitis, and you are a U-M student or other UHS patient, you may call for Nurse Advice by Phone.
Do I Need To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Maybe. Most people with hepatitis C dont have any symptoms. This means you might have the infection without knowing it. The CDC recommends hepatitis C testing for some women without symptoms.
Ask your doctor about getting tested for hepatitis C if:
- You were born between 1945 and 19659
- You have ever injected drugs, even once17
- You had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- You received clotting factors made before 1987
- You have sex with or share needles with someone who has hepatitis C
- You have been on dialysis
- Your liver test results were not normal
Recommended Reading: What Are Treatments For Hepatitis C
The Symptoms Are General
Since the liver has a part in so many essential functions, many symptoms are constitutional, meaning they affect the entire body. For example, a sore leg will usually just hurt in and around the leg. With hepatitis, you may feel pain around the liver, but you will also probably have chills and aches in your joints and muscles.
Life Sciences And Medicine
Viruses are important to the study of and as they provide simple systems that can be used to manipulate and investigate the functions of cells. The study and use of viruses have provided valuable information about aspects of cell biology. For example, viruses have been useful in the study of and helped our understanding of the basic mechanisms of , such as , , , , transport, and .
Geneticists often use viruses as to introduce genes into cells that they are studying. This is useful for making the cell produce a foreign substance, or to study the effect of introducing a new gene into the genome. Similarly, uses viruses as vectors to treat various diseases, as they can specifically target cells and DNA. It shows promising use in the treatment of cancer and in . Eastern European scientists have used as an alternative to antibiotics for some time, and interest in this approach is increasing, because of the high level of now found in some pathogenic bacteria.The expression of heterologous proteins by viruses is the basis of several manufacturing processes that are currently being used for the production of various proteins such as vaccine and antibodies. Industrial processes have been recently developed using viral vectors and several pharmaceutical proteins are currently in pre-clinical and clinical trials.
Virotherapy
Also Check: How Much Are Hepatitis B Shots
How Long Do The Hepatitis A And B Vaccines Protect You
During your lifetime, you need:
- One series of the hepatitis A vaccine
- One series of the hepatitis B vaccine
Most people dont need a booster dose of either vaccine. But if you have had dialysis, a medical procedure to clean your blood, or have a weakened immune system, your doctor might recommend additional doses of the hepatitis B vaccine.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is found in an infected persons blood and other body fluids.
Hepatitis C is usually spread through:
- Sharing or reusing needles, syringes, and drug preparation equipment such as cookers and cotton when injecting drugs. This is the most common way hepatitis C is spread in the United States. Hands or drug preparation equipment that have even tiny amounts of blood on them can also spread hepatitis C.
- Accidental needle stick or other sharp instrument injury
Less common ways to spread hepatitis C:13
- Birth to a mother who has hepatitis, though this is rare
- Sharing personal items like razors and toothbrushes
- Tattoos or body piercings
- Blood transfusions done in the United States before the 1990s or in other parts of the world where hepatitis C testing is less common
Read Also: Hepatitis C Treatment Side Effects
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
Does Hepatitis A Always Cause Symptoms
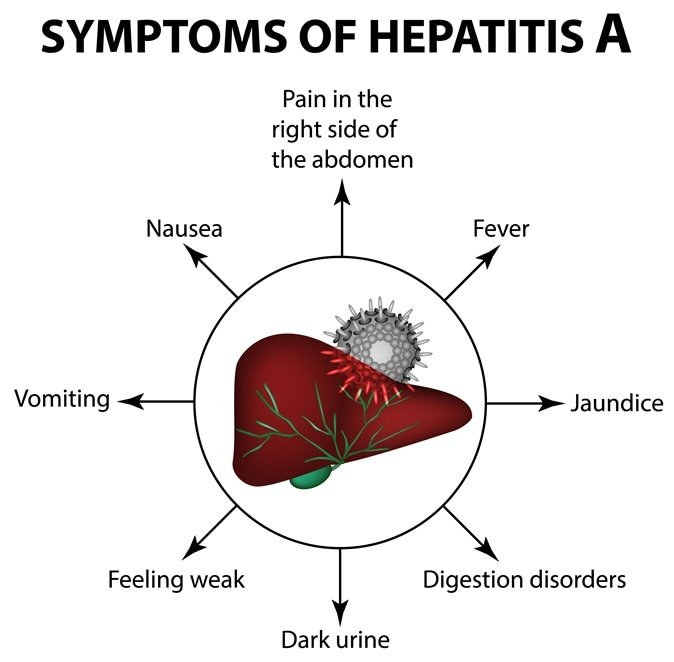
There’s a lot of variety in how people feel when they have the disease. It’s possible you might not have any symptoms. But people often feel and look sick. You might even need to go to the hospital.
Symptoms and complications are more common as you get older. Most children under age 6 with hep A don’t have any.
Also Check: Autoimmune Hepatitis Flare Up Symptoms
Acute Versus Chronic Viral Hepatitis
The term viral hepatitis can describe either a clinical illness or the histologic findings associated with the disease. Acute infection with a hepatitis virus may result in conditions ranging from subclinical disease to self-limited symptomatic disease to fulminant hepatic failure. Adults with acute hepatitis A or B are usually symptomatic. Persons with acute hepatitis C may be either symptomatic or asymptomatic .
Typical symptoms of acute hepatitis are fatigue, anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Very high aminotransferase values and hyperbilirubinemia are often observed. Severe cases of acute hepatitis may progress rapidly to acute liver failure, marked by poor hepatic synthetic function. This is often defined as a prothrombin time of 16 seconds or an international normalized ratio of 1.5 in the absence of previous liver disease.
Fulminant hepatic failure is defined as acute liver failure that is complicated by hepatic encephalopathy. In contrast to the encephalopathy associated with cirrhosis, the encephalopathy of FHF is attributed to increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier and to impaired osmoregulation in the brain, which leads to brain-cell swelling. The resulting brain edema is a potentially fatal complication of fulminant hepatic failure.
Although some patients with cirrhosis are asymptomatic, others develop life-threatening complications. The clinical illnesses of chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis may take months, years, or decades to evolve.
References