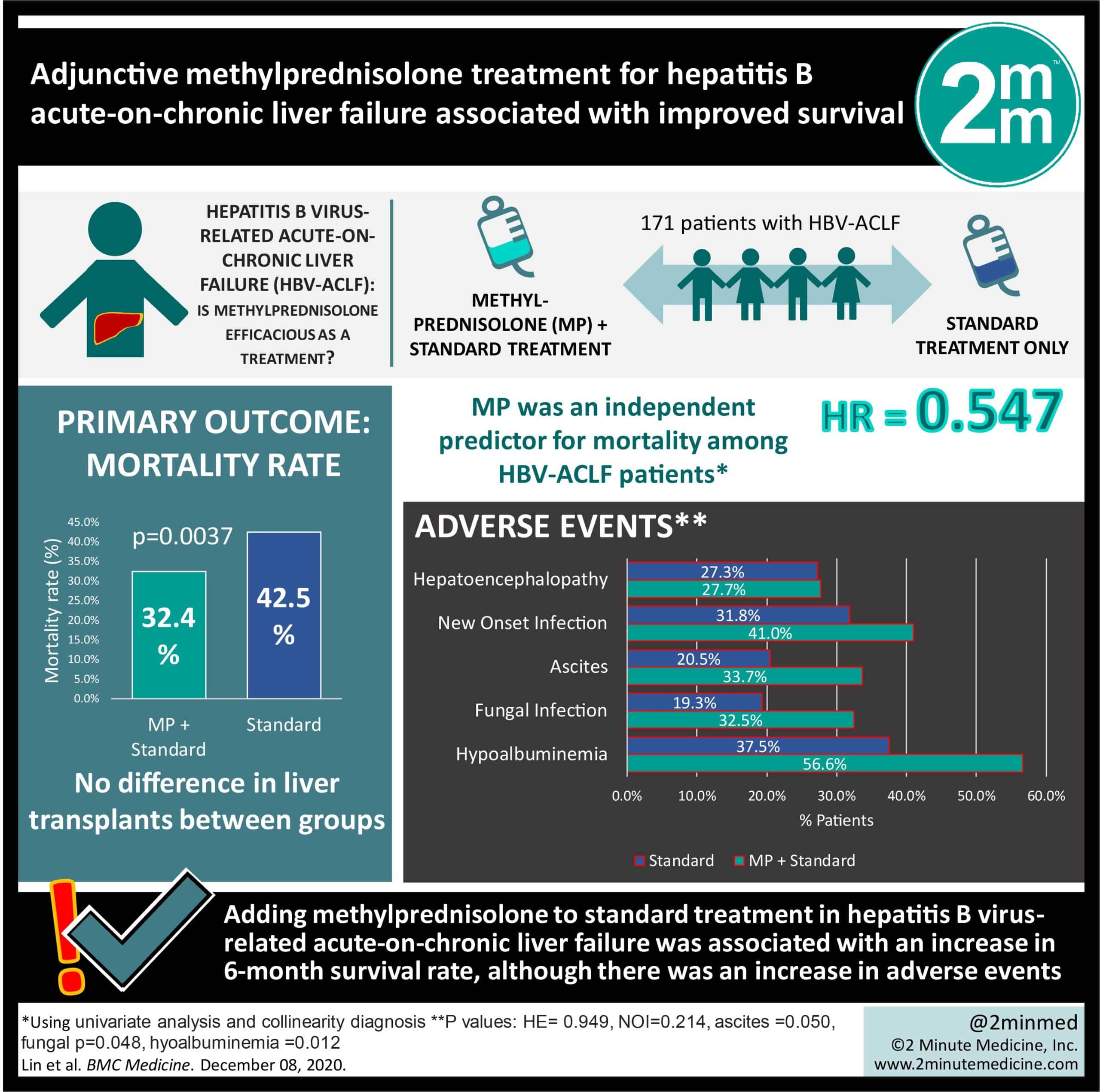
Prevention And Management Of Na Resistance
Treatment-naïve patients
Potent antivirals with minimal resistance, such as ETV, TDF, and TAF are recommended.
During treatment
HBV DNA levels should be quantified regularly to detect virological breakthroughs and initiate save therapy as soon as possible . For patients who develop resistance to NAs, IFN- is associated with low response rates.
Indications For Antiviral Therapy
Patients should be assessed for the risk of disease progression to determine whether to start antiviral therapy based on a comprehensive analysis of serum HBV DNA levels, ALT levels, the severity of liver disease, as well as their age, family history, and concomitant diseases.6,112,113 Dynamic assessment is more meaningful than a single test .
Flow chart of antiviral therapy for patients with chronic HBV infection.
Follow-up tests: virological test, liver biochemical test, AFP test, PIVKA-II test, abdominal ultrasound, and liver stiffness measurement. HBV-related extrahepatic manifestations: glomerulonephritis and vasculitis. Follow-up criteria for patients with HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis during NA treatment: perform a routine blood test, liver biochemical test, renal function test, virological test, and test for blood ammonia, AFP, and PIVKA-II, and abdominal ultrasound every 3 months. If necessary, perform enhanced CT or MRI. Other causes of ALT elevation: infection by other pathogens, history of drug or poison use, history of alcohol use, lipid metabolism disorders, autoimmune disorders, liver congestion or vascular diseases, inherited metabolic liver disease, systemic diseases. NAs-ETV, TDF, TAF. HbsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen HBV, hepatitis B virus ALT, alanine aminotransferase HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma NAs, nucleoside analogs peg-IFN-, pegylated interferon-.
Efficacy And Safety Of Nas
Entecavir
Numerous studies have shown that the use of ETV is safe and highly effective to suppress virus replication and reduce liver inflammation.117119 Long-term treatment with ETV can improve histological changes in patients with cirrhosis,120,121 significantly reduce the incidence of cirrhosis-related complications and HCC, and reduce liver-related and all-cause mortality.53,122 The 5-year cumulative probability of ETV resistance was 1.2% in treatment-naïve patients with CHB but increased to 51% in CHB patients who were resistant to lamivudine .123
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
Multicenter clinical studies of TDF treatment for CHB patients have shown that it can strongly inhibit virus replication and has low rates of resistance.124,125 A study of TDF usage for 8 years showed that there were 41 cases of virological breakthroughs, 29 cases of which were due to poor compliance. In total, 59% of patients with virological breakthroughs continued to receive TDF treatment and achieved virological responses. Further nucleic acid sequencing did not identify TDF-related resistance.126 Long-term treatment with TDF can significantly improve liver histology and reduce the incidence of HCC.127,128
Tenofovir alafenamide fumarate tablets
Other drugs
Telbivudine can improve eGFR but it is associated with high rates of resistance.113 LdT exhibits favorable efficacy and safety in blocking mother-to-child transmission .
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Spit
Preventive Strategies For Hbv
In the past few years, the incidence and mortality of HBV-related HCC has continuously increased. Thus, efforts in the development of prevention measures is urgently needed to decrease the global burden of HBV-related HCC. From the literature, the three levels of preventive strategies, including primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention will be effective for the prevention of HBV-related HCC .
Figure 2. Preventive strategies of HBV-related HCC. HBV: hepatitis B virus HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Get Hepatitis B
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education remains one of the most important components in preventative measures regarding HBV infection.
Education should be provided to expecting parents about the importance of vaccination and to clarify erroneous beliefs about vaccinations.Patient education should also include counseling about the avoidance of risky behaviors that predispose an individual to be infected, including promiscuous sexual activity or intravenous drug abuse. They should also be advised not to share items such as shaving razors, toothbrushes, or hair combs due to possible transmission via mucosal contact or through microtrauma to protective barriers.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
Management Of Adverse Events Of Peg
Influenza-like syndrome
If patients complain of fever, headache, myalgia, or fatigue, peg-IFN- could be injected before sleep or taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents along with the IFN-.
Myelosuppression
If neutrophil count 0.75×109/L and/or platelet count < 50×109/L develops, peg-IFN- dosage should be reduced and cell counts retested after 12 weeks. If cell counts return to normal, the initial dosage should be restored. If neutrophil count 0.5×109/L or platelet count < 25×109/L, or both, the peg-IFN- should be discontinued. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor could be used for those with significantly decreased neutrophil counts.
Mental disorders
If patients experience depression, delusions, severe anxiety, or other mental disorders, peg-IFN- should be immediately withdrawn, and patients could seek consultations with psychiatrists and psychologists if required.
Autoimmune diseases
Some patients might develop autoantibodies, and few patients develop thyroid disease, diabetes, decreased platelet count, psoriasis, vitiligo, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. In such cases, patients should have consultations with physicians with related expertise, and treatment should be discontinued for patients with severe symptoms.
Other rare adverse events
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Can Be Spread By
Uses Of Surveillance Data
Acute and chronic hepatitis B surveillance data can be used to inform and improve public health interventions in the following ways:
Detection Of New Hbv Markers
Anti-HBc quantification
A novel double-antigen sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay can quantitatively determine serum anti-HBc levels. In natural history studies, the quantitative anti-HBc levels in patients during the immune clearance and reactivation phases were significantly higher than those in the immune tolerance and low replication phases.60,61 The baseline qAnti-HBc levels of HBeAg-positive CHB patients could predict the efficacy of peg-IFN- and nucleoside analogues .62,63 In addition, qAnti-HBc levels are strongly correlated with ALT levels and are associated with the degree of necroinflammation in liver tissue in patients with normal ALT levels.64
HBV RNA quantification
HBV RNA levels are related to the transcriptional activity of cccDNA in liver cells, and further study is required to assess the risk of recurrence after withdrawal of NAs.65,66 Its use is limited, because the detection methods used by different research teams are different.
Hepatitis B core-related antigen
This is a composite marker that contains HBcAg, HBeAg, and p22. It is related to the transcriptional activity of cccDNA in liver cells. Studies have examined its usefulness to determine disease progression, predict the antiviral efficacy of peg-IFN- and NAs, and assess the risk of HBV recurrence and HCC development with the discontinuation of treatment.6770
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis B And Hiv The Same Thing
Asian Pacific Association For The Study Of The Liver
The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver hepatitis B guidance was generated by a panel of experts in this region, predominantly from the specialties of hepatology and gastroenterology. The most recent guidance was published in 2015. The 2015 APASL Hepatitis B Guidelines recommend initiating HBV treatment in the following situations for persons with chronic HBV.
- : Treatment is recommended with any detectable HBV DNA level, regardless of ALT levels or HBeAg status.
- Compensated Cirrhosis: Treatment is recommended with HBV DNA level greater than 2,000 IU/mL regardless of ALT level or HBeAg status, or any detectable HBV DNA level if ALT elevated, regardless of HBeAg status.
- Without Cirrhosis: Treatment may be started in noncirrhotic patients who have persistent elevation of ALT and elevated HBV DNA above 2,000 IU/mL if HBeAg negative or above 20,000 IU/mL if HBeAg positive. The ALT upper limit of normal used to guide management decisions is 40 U/L for both males and females.
Immune Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
From a conceptual standpoint, chronic hepatitis B virus infection has been characterized by four phases : immune tolerant, immune active, inactive carrier, and reactivation. The liver damage that can occur with chronic HBV infection is primarily related to the host immune response to hepatocytes infected with HBV the inflammation and liver cell death associated with this immune response is thought to occur predominantly in the immune-active phase of chronic HBV. The phases of chronic HBV infection are not considered staticindividuals can undergo transitions in and out of these different stages throughout their lifetime .
Immune-Tolerant Chronic HBV
Immune-Active Chronic HBV or Reactivation of Chronic HBV
Inactive Chronic Hepatitis B
Recommended Reading: How Would You Know If You Have Hepatitis
What Is Immune Tolerance
Generally, immune tolerance is defined as the specific non-response state of the immune system after receiving specific antigen. The liver has a unique immune regulation function, which can promote the tolerance to HBV, and this may be the main reason of HBV persistence and chronic infection. In 1972, Dudley et al. firstly proposed that HBV persistent infection was related to immune tolerance, and the liver injury was determined by T cell-mediated immune response . In 1983, Liaw et al. reported that HBeAg clearance was related to the enhancement of host immune response . Based on the above findings, Chu et al. firstly divided the natural history of HBV infection into three phases of immune tolerance, immune clearance, and residual integration , and then divided it into four phases of immune tolerance, immune clearance, inactive carrier status and reactivation . The latter four phases are the current widely used classification of hepatitis B natural history.
Candidates In The General Population
Antiviral treatment is an effective therapeutic strategy for CHB patients that efficiently suppresses HBV replication, decreases inflammatory necrosis in the liver, reduces the incidence of liver cirrhosis and related complications, and reduces the fatality rate associated with hepatocellular carcinoma and other liver diseases. In the 2019 China guidelines , HBV infection is divided into four phases: immune tolerance, immune clearance, immune control, and immune reactivity, and it is different from the 2015 version . Additionally, the 2019 China guidelines eased the restrictions on indications for antiviral therapy, and reducing the demand for HBV-DNA load. Conversely, the HBV-DNA load is considered for the performance of antiviral therapy in the 2018 guidelines updated by the 2018 AASLD guideline and the 2017 EASL guidelines . For the treatment of HBV infection with normal ALT , antiviral therapy is recommended in patients > 30-years-old with a family history of liver cirrhosis or cancer in the 2019 China guidelines. In another case > 30-years-old without a family history of liver cirrhosis or cancer, a hepatic biopsy was recommended. Although we can refer to many guidelines, there are many patients failed to fulfill the criteria for treatment at follow-up and eventually developed liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and cancer .
Table 1. Comparison between 2015 and 2019 guidelines.
Table 2. Indications for chronic hepatitis B treatment in 2017 and 2018 guidelines.
Also Check: How Can You Spread Hepatitis C
Bq 21 Are Biochemical Examination Of Blood And Imaging Findings Useful For The Diagnosis Of Liver Cirrhosis
- The determination of fibrosis scores based on several blood tests and evaluation of liver stiffness by elastography is useful for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis.
A diagnostic algorithm is shown in Fig. 1.
Diagnostic algorithm for liver cirrhosis. After obtaining basic information on the cause of liver cirrhosis, characteristics of the patients, and physical examinations, we should combine several diagnostic tools, such as serum biomarkers, imaging modalities, and endoscopy, as noninvasive alternatives to liver biopsy. This algorithm diagnoses cirrhotic F4 fibrosis. A special blood test or histological characteristics are often needed to determine the cause of cirrhosis. aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index, FIB-4 fibrosis-4 index, HCV hepatitis C virus, hx history, M2BPGi Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer
Patients With A Normal Level Of Alanine Aminotransferase
Hepatitis B virus infection is a dynamic process characterized by fluctuations in alanine ALT, which might hint toward immune-mediated virus clearance . Since the ALT level is not always indicative of inflammation in the liver, patients with normal ALT levels can present inflammation and fibrosis on liver biopsy. Thus, ALT is used as a substitute for liver inflammation when liver histology is a failure . But the challenge in defining the ULN of ALT is the difficulty of including totally healthy subjects without liver diseases, especially MAFLD , the leading cause of liver disease worldwide . An Italy study reveals that Male sex, body mass index, glucose, lipids, ferritin, hypertension, and younger age are independent predictors of ALT . Many hepatologists call for the adjustment of the ULN of ALT . In 2019 China guidelines, the ULN remains constant at 50 U/L in males and 40 U/L in females however, many studies have recommended rational values as 35 U/L in males and 23 U/L in females . In 2018 AASLD guidelines, the ALT ULN is modified as 35 U/L in males and 25 U/L in females, as described previously . In 2017 EASL guidelines and 2015 APASL guidelines, the ALT ULN is 40 U/L in both males and females . Therefore, whether patients have normal ALT levels partially depends on the ULN. The ULN values mentioned in this study are consistent with those in the literature.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis D Transmitted
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
Special Considerations During Immunosuppressive Therapy
With immunosuppressive therapy, both in the context of malignancy and rheumatologic/autoimmune diseases, reactivation of HBV infection can occur. HBV reactivation in HIV-negative people with HBsAg-positive/anti HBc-positive disease receiving immunomodulatory therapy is well described.147,148 Even among people with HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc-positive disease, HBV reactivation occurs in 8% to 18% of people receiving anti-cancer drugs149 and 1.7% of people receiving rheumatologic disease drugs.150
Don’t Miss: Screening Test For Hepatitis C
Patients With Poor Response
CHB patients
After treatment with ETV, TDF, or TAF for 48 weeks, if HBV DNA is > 2×103 IU/mL, and excluding compliance and detection errors, NA-based treatment regimens should be adjusted , or combination therapy could be used . Peg-IFN- therapy can also be used in combination.
Patients with HBV-related cirrhosis
After treatment with ETV, TDF, or TAF for 24 weeks, if HBV DNA is > 2×103 IU/mL, and excluding compliance and detection errors, NA-based treatment regimens could be adjusted , or combination therapy might be used .
Monitoring Of Na Treatment
Detection of the following relevant indicators at baseline before treatment
major biochemical markers, such as ALT, AST, bilirubin, and albumin major virological and serological markers, such as HBV DNA quantification, HBsAg, HBeAg, and anti-HBe blood routine serum creatinine levels, blood phosphorus levels, and renal tubular function should be tested if required noninvasive tests for liver fibrosis, such as liver stiffness measurement and when ETV and TDF are used in patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min, the doses of both drugs should be adjusted. There is no recommended dose for TAF when it is used in patients with creatinine clearance < 15 mL/min who are not receiving hemodialysis. In other cases, no dose adjustment is required.
Patient compliance
It should be closely monitored, which includes dosage, method of use, missed medication or self-discontinuation, to ensure that patients understand the risks that might result from unwarranted discontinuation and improve their compliance.
Prevention and management of rare adverse events
Monitoring and management of drug resistance
The use of potent antiviral drugs with minimal resistance has resulted in significantly reduced rates of resistance that could arise from long-term treatment of NAs. If HBV DNA levels increased > 2 lg IU/mL from nadir during treatment and the potential of poor compliance has been ruled out, salvage therapy should be initiated promptly, and drug resistance should be tested for.
Also Check: Glomerulonephritis Due To Infectious Hepatitis