What Is Hepatitis C Infection How Many People Are Infected
Hepatitis C virus infection is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus . It is difficult for the human immune system to eliminate hepatitis C from the body, and infection with hepatitis C usually becomes chronic. Over decades, chronic infection with hepatitis C damages the liver and can cause liver failure. In the U.S., the CDC has estimated that approximately 41,200 new cases of hepatitis C occurred in 2016. When the virus first enters the body there usually are no symptoms, so this number is an estimate. About 75%-85% of newly infected people become chronically infected. In the U.S., more than 2 million people are estimated to be chronically infected with hepatitis C. Infection is most commonly detected among people who are 40 to 60 years of age, reflecting the high rates of infection in the 1970s and 1980s. There are 8,000 to 10,000 deaths each year in the U.S. related to hepatitis C infection. HCV infection is the leading cause of liver transplantation in the U.S. and is a risk factor for liver cancer. In 2016, 18,153 death certificates listed HCV as a contributing cause of death this is believed to be an underestimate.
Those who have cirrhosis from HCV also have a yearly risk of liver cancer of about 1%-5%.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Other Causes Of Liver Cirrhosis
A number of other medical conditions that result in liver damage can cause cirrhosis, including:
- some autoimmune diseases certain types of cells of the immune system attack and damage the liver. These uncommon conditions that can cause liver cirrhosis include autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis .
- exposure to poisons can damage the liver because one of the livers main roles is to remove toxins from the blood. Prolonged exposure to environmental toxins such as arsenic can damage the liver and lead to cirrhosis.
- schistosomiasis a tropical disease caused by a parasitic worm called Schistosoma. The worm is passed to humans from snails, and the disease is also known as bilharziasis. Chronic schistosomiasis causes damage to internal organs including the liver
- certain medications in rare cases, may cause cirrhosis in susceptible people
- unknown conditions can cause cirrhosis in about one third of cases .
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
When the physician makes a diagnosis of hepatitis C, it is important that the patient sees a gastroenterologist who specializes in the treatment of hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C therapy consists of the use of direct-acting antivirals . This cures 99% of hepatitis C cases within 6 months. In the past interferon therapy was given, but this had a lot of side effects and lower cure rates.
Chronic hepatitis
Chronic hepatitis develops in about 80% of hepatitis C patients. About 20% of patients with chronic hepatitis develop cirrhosis of the liver from the chronic inflammation, but it often takes several decades to develop to this stage. Here is a picture of a cirrhotic liver. A patient with this type of liver often has jaundice, has ascites in the abdomen and portal hypertension with periumbilical varicose veins as well as gynecomastia. Once cirrhosis has developed, the patients are at a higher risk to develop cancer of the liver later in life. In the past corticosteroids were thought to be useful, but now we know that they are not advisable for the treatment of chronic viral hepatitis. Corticosteroids enhance viral multiplication. Physicians used interferon treatment three times per week. This has led to remissions in about 1/3 of hepatitis B patients.
Higher cure rates with ribavirin and direct-acting antivirals
1) The response rate improved with the addition of ribavirin, an antiviral drug that the doctor ordered twice per day.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Through Intercourse
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
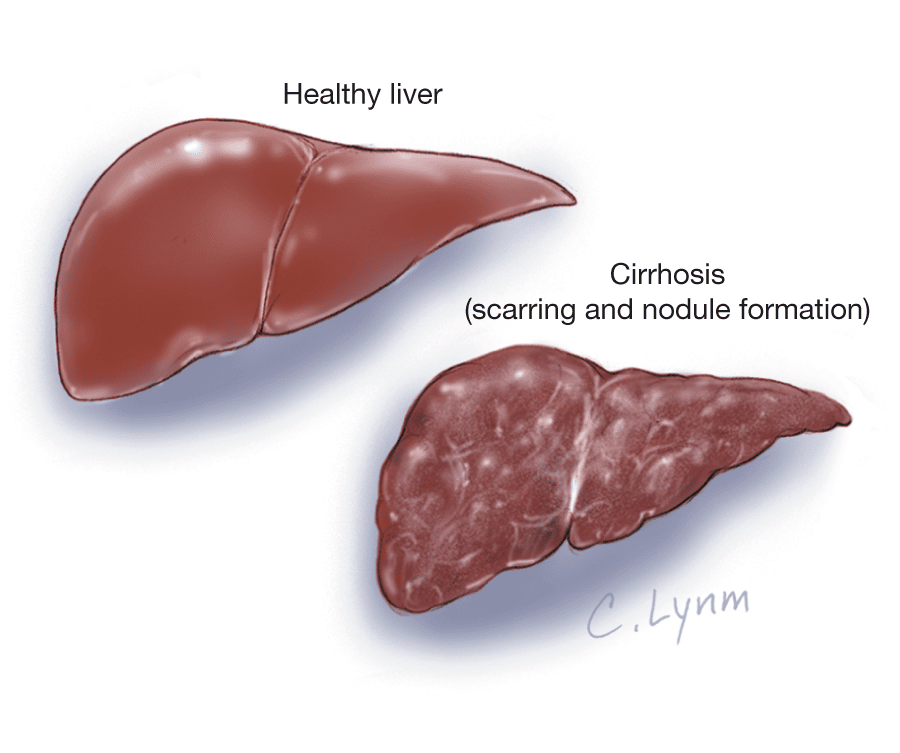
Facts at-a-Glance
Read Also: Hepatitis B Homeopathy Treatment In Hindi
Also Check: Help With Hepatitis C Treatment
What Are The Treatment Options For Hcv
Currently, the standard of care for the treatment of HCV is pegylated interferon in combination with ribavirin. This combination therapy is typically a 24-week or 48-week course. Research has shown that combination therapy with pegylated interferon and ribavirin can result in undetectable levels of HCV in 40-50 percent of people with genotype 1 and 70-80 percent of people with genotypes 2 and 3.11,12,13,14
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis C Do
Hepatitis C Information Center
Hepatitis C is a disease caused by a virus that infects the liver. The virus, called the Hepatitis C virus or HCV for short, is just one of the hepatitis viruses. The other common hepatitis viruses are A and B, which differ somewhat from HCV in the way they are spread and treated. According to the Centers for Disease Control , an estimated 2.7 million people in the United States have chronic Hepatitis C infection. The CDC now recommends one-time hepatitis C testing of all adults and all pregnant women during every pregnancy. CDC continues to recommend people with risk factors, including people who inject drugs, be tested regularly.
Explore this Hepatitis C Information Center by clicking through to the Diagnosis, Treatment and Support landing pages where youll find more information to help you manage Hepatitis C.
What Are The Complications Of Cirrhosis
There are many complications of cirrhosis of the liver. Because cirrhosis develops over many years, some of these complications may be your first noticeable signs and symptoms of the disease.
Portal hypertension: This is the most common serious complication. Portal hypertension is an increase in the pressure in your portal vein . This increase in pressure is caused by a blockage of blood flow through your liver as a result of cirrhosis. When blood flow through veins is partially blocked, veins in your esophagus, stomach or intestines can become enlarged . As the pressure in these veins builds, the veins can bleed or even burst, causing severe internal bleeding.
Additional complications of portal hypertension include:
- Swelling in your legs, ankles or feet.
- Buildup of fluids in your abdomen .
- Swelling/enlargement of your spleen .
- Formation and dilation of blood vessels in the lungs , leading to low levels of oxygen in the blood and body and shortness of breath.
- Failure of kidney function as a result of having portal hypertension as a complication of cirrhosis . This is a type of kidney failure.
- Confusion, difficulty thinking, changes in your behavior, even coma. This occur when toxins from your intestines arent removed by your damaged liver and circulate in the bloodstream and buildup in your brain .
Hypersplenism: Hypersplenism is an overactive spleen. This condition causes quick and premature destruction of blood cells.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Home Test Kit
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not been sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
Treatment Options For Hep C And Nhl
HCV treatment involves antiviral medication and focuses on reducing liver inflammation and preventing complications. The length of treatment varies depending on the extent of liver damage.
The goal is to clear the virus from the body before liver damage occurs. HCV becomes chronic if left untreated for more than about 6 months.
Chronic hep C can be a lifelong infection, if left untreated. In the case of severe chronic hepatitis C, which has led to liver damage, known as cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be required.
You May Like: What Is Included In A Hepatitis Panel
Also Check: How Does Someone Catch Hepatitis C
How Hepatitis C Damages The Liver
Hepatitis C causes damage to the liver mainly in the form of inflammation, which then leads to scarring or fibrosis.
Hepatitis C results in the death of liver cells. It is uncertain whether the virus kills the cells or if it is the immune systems response to invasion by the virus. At present it is thought that it is probably a combination of the two, but that the immune systems response is what causes the most damage. The death of liver cells triggers the dispatching of inflammatory cells to the affected area. Inflammation leads to the enlargement of the liver in over 60% of people infected with hepatitis C and can cause the fibroelastic sheath surrounding the liver to stretch, which may be the cause of pain in the liver area.
Inflammation begins the processes that lead to fibrosis. Fibrosis is not a disease but is a condition caused by the bodys response to liver damage. Inflammation triggers a reaction by a group of cells in the liver called stellate or fat cells. When the liver is functioning normally stellate cells store fat and vitamin A in the liver. They also help regulate the flow of blood through the liver. But when the liver is inflamed by the presence of hepatitis C, a reaction occurs amongst different liver cells. This leads stellate cells to dispense with vitamin A, altering their function.
Free Radicals and Fibrosis
Free radicals are of concern for people with hepatitis C for a number of reasons:
Why Hasn’t New England Made More Gains In Hepatitis C Treatment
Tracking by the Center for Health Law and Policy Innovation at Harvard Law School and National Viral Hepatitis Roundtable shows that Medicaid restrictions for hepatitis C treatment remain across much of the country today.
Seventy-three percent of states currently require prior authorization before Medicaid beneficiaries can access treatment, and 36% still put restrictions in place for those actively using drugs, despite drug users being at disproportionate risk for contracting the virus, according to the 2022 State of Hep C Report.
More:States make secret deals with drugmakers to fight hepatitis C and taxpayers pick up the tab
The federal Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services has previously told states that some of those restrictions violate federal law, and yet they persist. CMS has not released any updated guidance for states since 2015.
Dr. Arthur Kim, director of the Viral Hepatitis Clinic in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, said populations that acquire and live with hepatitis C are more likely to be on Medicaid than private insurance, making Medicaid a good barometer of how the country as a whole is making progress, or not, against the virus.
Treatment roadblocks in state Medicaid programs pose extremely large barriers to eliminating hepatitis C completely, experts say, because the lion’s share of those infected have insurance through them.
All of New England has since eliminated Medicaid restrictions for substance users.
Recommended Reading: How You Contract Hepatitis B
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Liver Cirrhosis From Inherited Conditions
Some inherited conditions damage the liver and this leads to the scarring that can contribute to cirrhosis. These conditions include:
- haemochromatosis the body accumulates iron, which can damage many organs, including the liver
- Wilson disease the tissues of the body accumulate copper
- galactosaemia the body is unable to process galactose so it accumulates in the blood and can result in liver damage
- cystic fibrosis mainly affects the lungs, but can also cause scarring of the liver
- alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can cause lung damage but can also affect liver function and lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Common Genotype Of Hepatitis C
Are Hepatitis B And C Preventable
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable disease.
There is a three-shot vaccination series that is very effective in protecting people against the virus if theyre exposed. In the United States, all newborns are vaccinated for hepatitis B and all pregnant women are screened for hepatitis B during pregnancy. This way, mothers infected with hepatitis B can take protective steps to decrease the risk of transmission of the virus to the child.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
Causes Of Liver Cirrhosis
The main causes of cirrhosis are viral infections, alcohol consumption and obesity .
The viruses known to cause chronic liver damage are hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus and Delta virus. All of these viruses are transmitted parenterally, i.e. by contagion with infected blood or more rarely with bodily fluids from infected persons.
The Delta virus is not capable of causing infection on its own, but requires the presence of the hepatitis B virus.
The incidence of B virus infection, and consequently of Delta virus, has been drastically reduced in recent years following the introduction of the hepatitis B vaccination, which is compulsory in pre-school children.
As a consequence of vaccination against the hepatitis B virus, at present, the virus mainly responsible for chronic liver damage has become the hepatitis C virus.
This infection is more frequent in persons over 40 years of age and its prevalence increases progressively with increasing age.
This is due to the use in the past of non-returnable glass syringes, inadequately sterilised surgical instruments, haemotransfusions and plasma derivatives not tested for hepatitis C virus infection, and in drug-using individuals, the habit of exchanging syringes often infected by a sick person.
These risks are now considered to be steadily decreasing, due to the use of disposable syringes and the introduction of the hepatitis C virus antibody test since 1989.
A vaccine to prevent hepatitis C virus infection is not yet available.
Recommended Reading: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Hepatitis A
What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease that can be mild or very serious as it causes inflammation of the liver. Type 1 autoimmune hepatitis is the most common type found in North America, affecting approximately one in every 235,294 people, and it is more common in women. It often occurs in adolescence or adulthood but may occur at any age.
Approximately one-half of the people that have this disease also have another autoimmune disease. Type II is rare and usually affects females between two and fourteen.
What Is Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Cirrhosis of the liver is a chronic, degenerative disease of the liver, characterised by the presence of regenerative nodules and fibrosis as part of a more or less aggressive inflammatory process.
Depending on the size of the nodules, one can classify cirrhosis into micronodular , macronodular , or mixed.
The replacement of normal liver tissue with regenerative nodules and fibrotic scars causes a profound alteration of the livers microcirculation, making contact and thus exchanges between the blood, rich in nutrients from the intestine, and the liver cells difficult .
This process leads to the creation of a vicious circle that causes self-perpetuation and aggravation of cellular damage, with a reduction in the function and consistency of the liver and a progressive increase in pressure in the portal vein .
The increase in pressure in the portal vein , due to the difficulties in the transit of blood through the cirrhotic liver, favours the opening of alternative venous outlets and thus the appearance of venous dilatations , which occur mainly in the oesophagus and stomach.
Portal hypertension also leads to congestion of the splenic vein and the spleen, which is expressed by an increase in its volume , which in turn causes a sequestration of circulating blood .
Read Also: Side Effects Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
You May Like: Hepatitis B How Long Does It Last