Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
Who Should Not Receive The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Talk to your healthcare provider before getting the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- You have had a severe allergic reaction to the hepatitis B vaccine or any of its ingredients in the past.
- You have had an allergic reaction to yeast in the past.
- You are moderately or severely ill.
- You are currently taking immunosuppressive medications.
In addition, pregnant people should not receive the Heplisav-B or PreHevbrio vaccines until more safety information is available.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Non Reactive Mean
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Don’t Miss: Can You Recover From Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis B
One U.S. study following trends in hepatitis B infection over a three-year periodfound that 4.3% of the population had a past or present HBV infection.
Estimates suggest that about 240 million people around the world have chronic hepatitis B. Up to 1.89 million people in the United States have a chronic HBV infection.
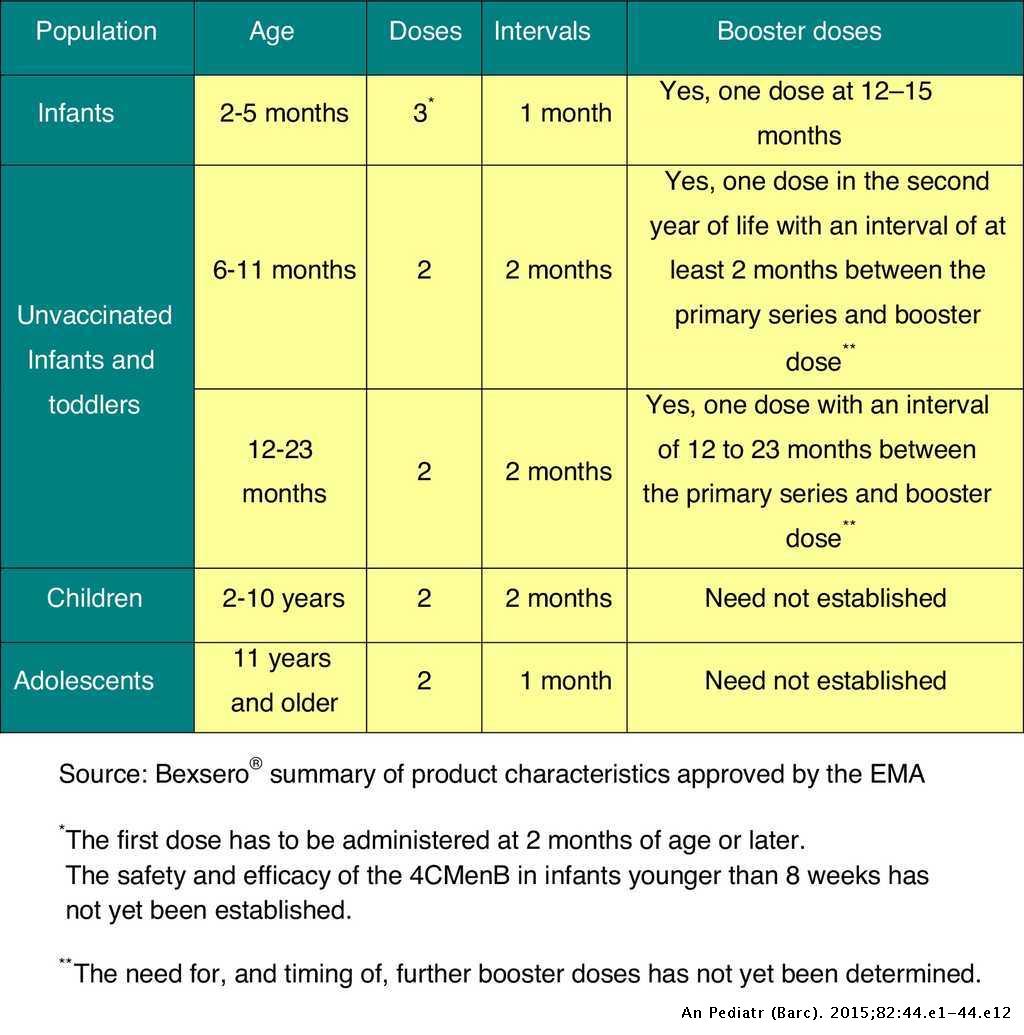
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule Adults
Concerns About Immunisation Side Effects
If the side effect following immunisation is unexpected, persistent or severe, or if you are worried about yourself or your child’s condition after a vaccination, see your doctor or immunisation nurse as soon as possible or go directly to a hospital.
It is important to seek medical advice if you are unwell, as this may be due to other illness, rather than because of the vaccination.
Immunisation side effects may be reported to SAEFVIC, the Victorian vaccine safety and reporting service. Discuss with your immunisation provider how to report adverse events in other states or territories.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Don’t Miss: How Many Shots For Hepatitis B
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. Hepatitis B virus infections are known as the “silent epidemic” because many infected people don’t experience symptoms until decades later when they develop hepatitis , cirrhosis , or cancer of the liver . Every year in the United States about 22,000 new hepatitis B infections occur and about 2,000 people die from their infections.
Testing Your Baby For Infection
Each year, a very small number of babies may develop infection so your baby will be offered a blood test when they are 1 years old. This is to check that the course of vaccines have prevented them from developing hepatitis B.
There are 2 ways that this may be done and your GP, health visitor or practice nurse will advise you which test your baby will have:
If they do have the infection, they will be referred to a specialist for treatment to reduce their risk of developingserious liver disease.
If a young infant is infected, they are more likely to develop long lasting infection without any signs or symptoms of infection. Even if your baby has no signs or symptoms of infection they should still have the blood test.
Infection can be prevented in 90% of cases if the first dose of vaccine is given at birth and the full course of vaccines is completed on time.
You May Like: Is Hiv The Cause Of Hepatitis B
What About Simply Testing For Immunity With A Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Blood Test After One Or Two Doses
CDC does not recommend routine testing of children and teens who are vaccinated against hepatitis B.
If a child/teen who has had only one or two documented doses of hepatitis B vaccine is tested and found to be immune by anti-HBs serology, CDC still recommends that the child/teen receive three doses in order to assure long-term protection.
Infants Born To Mothers Who Have Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
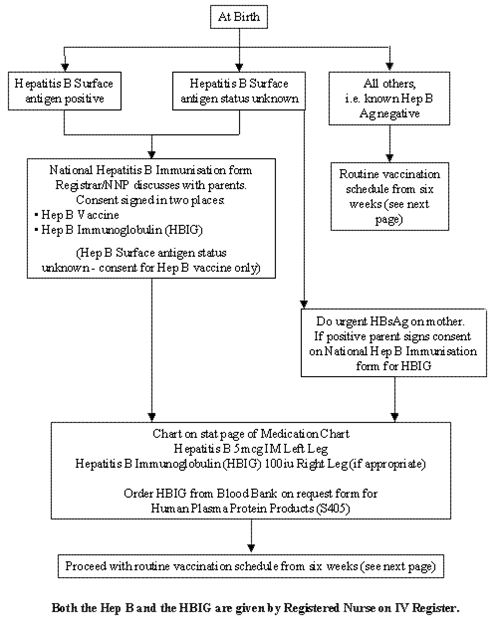
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
Protecting Your Baby
Infants born to women with hepatitis B must receive accurate doses of hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin to ensure complete protection. In order to protect these infants, medications should be given immediately after birth in the delivery room or within the first 12-24 hours of life*.
* See Testing and Treatment During Pregnancy section for details. Please note that testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B is a global recommendation.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends that infants born to hepatitis B positive mothers receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, and ideally a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin . These shots must be followed by the additional vaccine doses given on the recommended schedule. In the U.S., infants should follow a 1 month and 6-month schedule for the additional two doses.
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Don’t Miss: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
What Are The Side Effects
The most common of the hepatitis B vaccine are mild and include:
- Sore arm from the shot.
Prepare for your child’s vaccine visit and learn about how you can:
- Research vaccines and ready your child before the visit
- Comfort your child during the appointment
- Care for your child after the shot
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms To Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine Can Protect Your Baby
A complete course of 6 doses of vaccines is needed to fully protect your baby against long lasting hepatitis B infection. The vaccine is given as a small injection into the thigh.
Your midwife will know that your baby should have the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
Your baby may also need hepatitis B immunoglobulin at the same time as their birth dose of vaccine, if there is a higher risk of infection. Your midwife will tell you if it is needed. HBIG is also given as a single injection in the thigh.
The second dose of single hepatitis B vaccine needs to be given at 4 weeks of age.
The next 3 doses of hepatitis B containing vaccine are routinely given to all babies at 8, 12 and 16 weeks old. These also protect against other serious infections including diphtheria, tetanus, polio, whooping cough and haemophilus influenzae type B.
Your babys final dose of single hepatitis B vaccine should be given when they reach 1 year of age. This dose can be given at the same time as their other routine vaccines.
If you are not able to attend any of the appointments, please let your GP know as soon as possible so that anotherappointment can be arranged.
Common And Local Adverse Events
HB vaccine
HB vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and include: irritability, headache, fatigue and injection site reactions in 10% or more of recipients.
HAHB vaccine
There is no increase in adverse events when HAHB vaccine is compared with HA vaccine given alone or concomitantly with HB vaccine at a different injection site. When the adult formulation of HAHB vaccine is given to children in the 2 dose schedule, there is no increase in adverse events compared with those occurring after administration of the pediatric formulation of HAHB vaccine.
DTaP-HB-IPV-Hib vaccine
Reactions are usually mild and transient, and include fever, irritability, restlessness and injection site reactions .
HBIg
Headache, diarrhea, fever, urticaria, angioedema and injection site reactions may occur.
Don’t Miss: Does Planned Parenthood Test For Hepatitis
Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease
- Men who have sex with men
- Persons who inject drugs
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Persons with chronic liver disease
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes
- Persons with HIV infection
- All other persons seeking protection from hepatitis B infection.
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
Recommended Reading: How Can I Catch Hepatitis