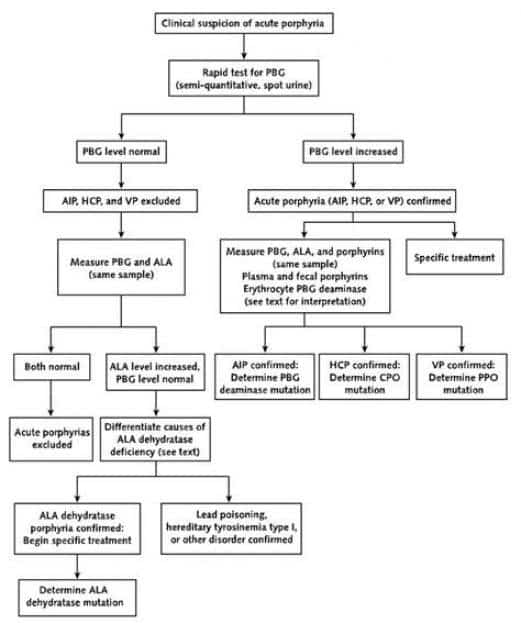
Question 7 Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Antibody Always Acquired After A Completed Vaccination Protocol
No. After 3 intramuscular doses of vaccine, > 90% of healthy adults and > 95% of those < 19 years of age develop immunity .1 However, there is an age-specific decline in development of immunity. After age 40 years, about 90% of people become immune, but by age 60 years, only 75% of people become immune.1 Larger vaccine doses or an increased number of doses are required to induce immunity in many hemodialysis patients and in other immunocompromised people.1
References
This FAQ is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A clinicians test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on his/her education, clinical expertise, and assessment of the patient.Document FAQS.105 Revision: 0
Discusses Conditions That May Cause Diagnostic Confusion Including Improper Specimen Collection And Handling Inappropriate Test Selection And Interfering Substances
Individuals who have received blood component therapies , plasma, or intravenous immunoglobulin infusion) in the previous 3 to 6 months may have false-positive hepatitis B surface antibody results due to passive transfer of anti-HBs present in these products.
Individuals possessing IgM anti-rubella virus may have falsely high results with the VITROS Anti-HBs quantitative test.
Anti-HBs levels from past hepatitis B or hepatitis B virus vaccination may fall below detectable levels over time.
A positive anti-HBs result does not exclude infection by another hepatitis virus.
Performance characteristics have not been established for the following specimen characteristics:
-Grossly icteric
Also Check: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Reactive
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Also Check: Hepatitis A Is A Virus
What Do The Results Mean
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Potent Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies To Hepatitis B Virus From Natural Controllers
Disclosures: V. Hehle reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Beretta reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Bourgine reported a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. M. Ait-Goughoulte reported a patent planned on the antibodies pending, Roche. S. Pol reported personal fees from Gilead, Abbvie, BMS, Janssen, and Roche outside the submitted work. H. Strick-Marchand reported a patent to human neutralizing HBV antibodies and their use thereof, pending. N. Pelletier reported personal fees from Hoffmann-La Roche outside the submitted work in addition, N. Pelletier had a patent planned to be submitted, pending Roche Innovation Center Basel. H. Mouquet reported grants from Institut Roche during the conduct of the study in addition, H. Mouquet had a patent to anti-HBV antibodies and methods of use, pending. No other disclosures were reported.
V. Hehle and M. Beretta contributed equally to this paper.
H. Strick-Marchand and N. Pelletier contributed equally to this paper.
J Exp Med
Don’t Miss: How Much Does Hepatitis C Medicine Cost
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Study Cohort And Study Design
Universal HepB immunization in newborns began in 1986 in the community. From then on, a database about the assessment of the immunity efficacy of HepB was established in which data about primary immunization were recorded. Between 1997 and 2001, a CHO-derived HepB with a dosage of 10g/mL was used for the newborns according to the 0, 1, and 6month schedule. In total, 92.9% of individuals maintained positive for anti-HBs in the cross-sectional survey in May 1999. By screening the historical database, participants born between 1997 and 1999 living in seven townships in Zhengding County who completed the full course primary vaccination were enrolled in this study. In the present study, a questionnaire, including name, sex, date of birth, and history of HepB booster vaccination, was completed, and those who underwent a booster dose before this study were excluded from the final analysis. A blood sample was collected from each participant who provided written informed consent, and the serum was isolated aseptically and stored at 20°C until testing.
Participants who were hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core antibody -negative and anti-HBs< 10 mIU/mL were randomly assigned to two groups using the random numbers 1 and 2, receiving a booster dose of HepB derived from either Saccharomyces cerevisiae or CHO . Blood samples were collected 30days after boosting to determine the potential immunological response.
Also Check: Country That Accept Hepatitis B
Ethical Approval And Informed Consent
This study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital . The requirement for informed consent from subjects was waived because the researchers accessed only deidentified database entries for analytical purposes.
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: How Common Is Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Can You Transmit Hepatitis C
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
You May Like: Purina Pro Plan Hepatic Cat
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Why Is This Analysis Important
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus that can lead to an acute or chronic liver infection that can severely damage the liver. It is transmitted by contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Vaccination against hepatitis B is recommended for adults and children that are at high risk of infection which may be due to occupational exposure, or travel to certain areas of the world.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis Be Antibody
Understanding Of Lab Tests Results
Please visit the site associated with The American Association for Clinical Chemistry for better understanding of tests. There you will find the most detailed and full information regarding lab tests. In common questions tab you will find answers on the most common questions.
In addition, you can use a special form to ask the question. It is useful, if there is no answer on your question on the web site. A laboratory scientist will answer your question. It is a part of voluntary service provided by the American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science.
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Also Check: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Hepatitis C Treatment
Assessment Of Hbsag And Anti
During the study, two techniques were employed. The Electrochemiluminescence technique was used as the primary method for detecting HBsAg and Anti-HBcAb, and the enzyme immunoassay technique was used as a backup if the ECL technique is not available.
Blood samples were aseptically collected by trained lab technicians using a disposable syringe. The blood sample was allowed to clot in a sterile tube before centrifugation. A total of 11,121 serum samples were separated and analyzed for HBsAg and Anti-HBcAb by the ECL technique using the Immunoassay Cobas e 411 analyzers . The remaining 3178 serum samples were analyzed for HBsAg and total anti-HBcAb by the enzyme immunoassay technique according to manufacturer instructions.
The HBsAg is the first line of screening for HBV infections in blood donors prior to donation. Samples that have initially reactive results are tested repeatedly in duplicate. If one or both tests are positive, the blood donor is deferred indefinitely for donation. Confirmatory testing using HBV NAT is not routinely done but is available in the Blood Center and special private laboratories at the blood donors expense.
Predictors Of Protective Levels Of Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Findings from our multivariable analyses revealed several significant results and confirmed a number of our bivariate findings. Younger adults aged 1829 and 3039 years were more likely to have protective levels of anti-HBs compared with adults aged 4049 years. Females had higher odds than males of being protected. Compared with non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic blacks were less likely to have protective levels of anti-HBs. Adults with greater than a high school education had increased odds of being protected from hepatitis B compared with those with a high school education or less. Finally, adults with health insurance compared with those without health insurance and those who reported having received hepatitis A vaccine compared with those who did not were more likely to be protected from hepatitis B.
Multivariate Logistic Regression Estimates of Characteristics Predicting the Likelihood of Having Protective Levels of Hepatitis B Virus Antibody Among Adults Aged 1849 Years at High Risk of HBV Infection, United States, 20032014
| Characteristic . |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Who Should Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Read Also: How Can You Transmit Hepatitis C