What Does It Mean When Hepatitis Is Reactive
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time. Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
What does it mean if hepatitis B surface antibody is non reactive?
Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV. In most cases this means that you will recover within 6 months.
What is the difference between Hep B surface antigen and antibody?
The basic blood test for hepatitis B consists of three screening tests: a hepatitis B surface antigen test, which determines whether a person currently has the infection a hepatitis B core antibody test, which determines whether a person has ever been infected and a hepatitis B surface antibody test, which determines
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If Have Hepatitis C
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
Did You Know Only 21% Of People Know They Have Hcv How Testing Plays A Role In Ending Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection in the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. It is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. Today, most people become infected with the virus by sharing needles or through equipment used to prepare or inject drugs. However, it can also be spread through birth from an infected mother to child, through sexual contact, sharing personal items contaminated with blood such as razors and toothbrushes, unregulated tattooing, and some health care procedures such as injections, infected blood transfusions , and needlestick injuries in healthcare settings.
The immediate period following infection is called the acute phase and lasts approximately six months. Many people do not experience symptoms during this phase, or if they do, they show non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, and depression.
After six months, approximately 70%-85% of those infected with HCV will fail to clear the virus on their own, or spontaneously, and this is when hepatitis C becomes a chronic or long-term infection. This high rate showcases the importance of regular testing so that treatment, which is highly effective, can start right away.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is A Hepatitis C Test
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Antibody To Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Harvest Order Choice: 90640
Synonyms: Anti-HBs HBs Ab Hepatitis B Post-vaccine screen
Program: Virology
Unit: Viral Serology
Useful For: Qualitative and quantitative enzyme immunoassay for the detection of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen in human serum and EDTA, heparin, or citrated plasma. The assay results may be used as an aid in the determination of susceptibility to hepatitis B virus infection in individuals prior to or following HBV vaccination or where vaccination status is unknown. Assay results may be used with other HBV serological markers for the laboratory diagnosis of HBV disease associated with HBV infection.
Method: Enzyme Immunoassay
Request Form: SRD-1
Container/ Tube: The following tube types and anticoagulants, including those in both glass and plastic tubes, have all been evaluated and found to be acceptable: SST, EDTA, sodium citrate, lithium heparin, and sodium heparin.
Type: Human serum or plasma
Volume: Fill tubes as labeling indicates to avoid improper dilution
Collection Instructions: venipuncture
Storage: Serum/ plasma should remain at room temperature for no longer than eight hours. If assays are not completed within eight hours, serum/plasma should be refrigerated at 2-8C. Specimens may be stored at 2-8C for 7 days. For long-term storage, the specimens should be frozen . Specimen should not be used if they have incurred more than 5 freeze-thaw cycles. Mix specimens thoroughly after thawing.
Reference Interval: Negative, non-reactive
Read Also: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Risk Factors Include:
- Being born to mothers infected with hep B
- Being born or traveling in countries where hep B is common
- Exposure to blood on the job, such as health care workers
- Having sexual partners with hep B
- Coming into contact with infected bodily fluids
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment
- Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
- Being born in the US, not vaccinated as an infant, and having parents born in high-risk countries
- Living or lived with a partner who has chronic hep B
- Having had a tattoo or body piercing with unsterilized tools
Please Explain What Does Hepatitis B Antibody Surface Ql Reactive Mean
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Contract Hepatitis
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
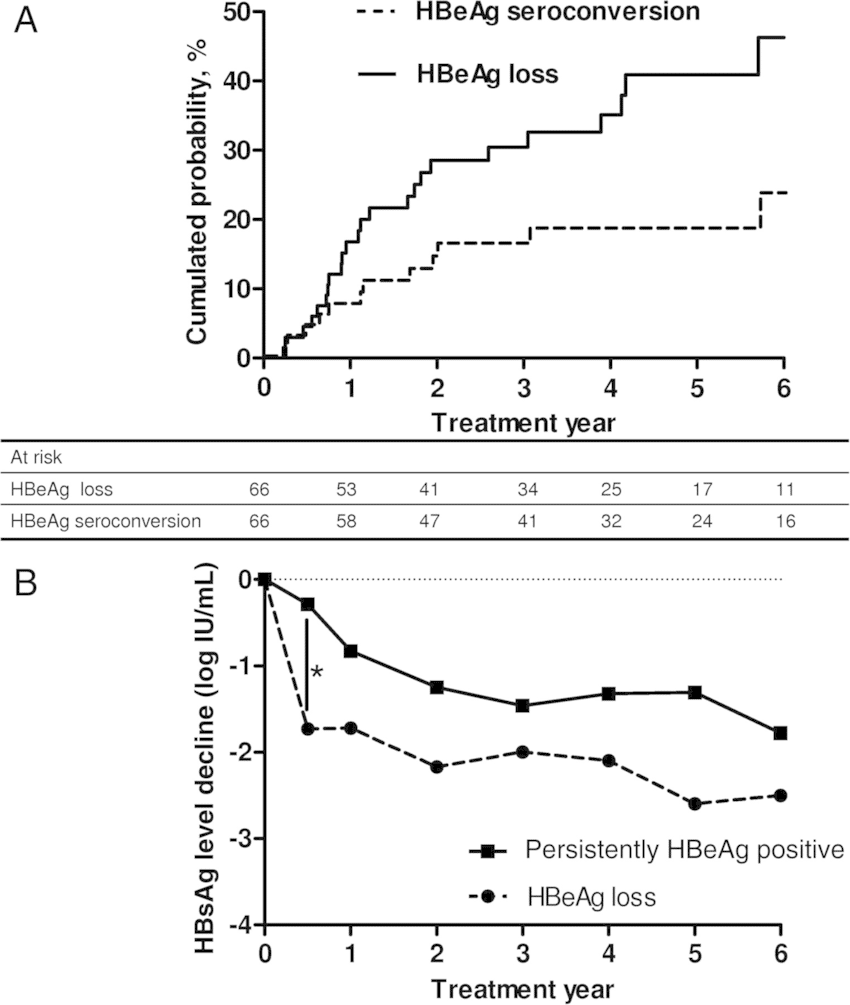
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
â Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
â It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
â People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
â Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B In Blood Test
What Do Hepatitis B Test Results Mean
Hepatitis B test results help determine if HBV infection is negative or positive, and if positive, whether the infection is acute or chronic, or if recovery is complete. A combination of results are considered to identify and classify HBV infection status.
The following are some interpretations of hepatitis B test results:
Table: Hepatitis B test results and interpretations
| Test |
|---|
Also Check: What Does Immunity To Hepatitis B Mean
How Do I Get Tested For Hep C
Finding out whether you have hep C starts with getting tested for HCV. This involves a blood test called an HCV antibody test.
You can ask to be tested at your primary care doctors office or a public health clinic, or you can test yourself using a home testing kit.
To find a clinic with HCV testing near you, visit the CDCs GetTested website and enter your zip code. This tool will help you find testing or free testing in nearby locations.
At-home test kits usually cost $50 to $100 for one test, which comes with all the materials and instructions you need. Youll collect a small amount of blood and send it off to a lab for testing.
Youll get your test result in 2 to 5 business days with most kits. Some at-home test options are Everlywell, LetsGetChecked, myLAB Box, and iDNA.
Test results may seem intimidating, especially if they can be a little more complicated than just positive or negative. With HCV testing, the antibody test determines whether you have ever contracted HCV.
Breaking down test results:
- A non-reactive HCV antibody test result means you do not currently have HCV.
- A reactive HCV antibody test result means you currently have HCV or had it at some point, and the antibodies are in your blood.
So, if you dont have any HCV antibodies, you are negative for HCV.
If you do have HCV antibodies, that means youve either had it before or currently have it. If youve had it once, youll always have antibodies for it, whether your treatment has cleared it or not.
Recommended Reading: Where Was Hepatitis C Discovered
How The Test Is Performed
Blood is most often drawn from a vein from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. The site is cleaned with germ-killing medicine . The health care provider wraps an elastic band around the upper arm to apply pressure to the area and make the vein swell with blood.
Next, the provider gently inserts a needle into the vein. The blood collects into an airtight tube attached to the needle. The elastic band is removed from your arm. Once the blood has been collected, the needle is removed. The puncture site is covered to stop any bleeding.
In infants or young children, a sharp tool called a lancet may be used to puncture the skin and make it bleed. The blood collects into a small glass tube, or onto a slide or test strip. A bandage may be placed over the area if there is any bleeding.
The blood sample is sent to a lab to be examined. Blood tests are used to check for antibodies to each of the hepatitis viruses.
What Does Reactive Result Mean In Hepatitis B
I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
liver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.
Don’t Miss: Hepato Liver Support For Dogs
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.104 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.26 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.104 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.26 Pre-core mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become raised but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak , with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Also Check: How Can I Catch Hepatitis
What Type Of Disease Is Cystic Fibrosis
It means that the test result was positive for the antibody thatwas being tested.
If it is the Hepatitis B surface antibody then it means you havebeen exposed to either the infection of gotten the immunizations.
If it is other antibodies, such as the core or envelope, then itmeans you have been exposed to the infection at some point.
About 90% of adults who catch Hepatitis B get better on theirown so if you are antibody positive in order to know if you stillhave the infection you need to check a surface antigen or do a DNAtest.
Also Check: How Many Hepatitis C Genotypes Are There
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis C Ab Non Reactive Mean