Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
A blood test, called an HCV antibody test, is used to find out if someone has ever been infected with the hepatitis C virus. The HCV antibody test, sometimes called the anti-HCV test, looks for antibodies to the hepatitis C virus in blood. Antibodies are chemicals released into the bloodstream when someone gets infected.
Test results can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks to come back. Rapid anti-HCV tests are available in some health clinics and the results of these tests are available in 20 to 30 minutes.
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
What Do The Results Mean
There are two results from a hepatitis C antibody test.
- A non-reactive or negative test result means that the person does not have the virus. The exception is if someone has come into contact with the virus recently, such as through contaminated blood. If this is the case, they will need to have another test.
- A reactive or positive test result means that the person has had the virus at some point but does not mean that they still have it. Further tests will be needed to check whether the virus is still active in the body and if treatment will be required.
Once diagnosed with hepatitis C, a person will need to undergo a series of different tests to see how the virus has affected their body.
These tests will check for any liver damage, identify how well the liver is working, and help a healthcare professional to decide on treatment.
Hepatitis C is treated with medication known as an antiviral. It gets this name because it aims to clear the virus out of the body.
Another aim of the medication is to slow down damage to the liver. It may also reduce the chance of a person getting liver cancer or developing serious liver scarring, known as cirrhosis.
A person with hepatitis C will require regular testing during treatment to see how well the medication is working. Keeping healthy, getting enough sleep, and avoiding drugs and alcohol can help treatment to work.
Don’t Miss: How Do They Test For Hepatitis
Testing For Hepatitis C
Two tests need to be done to discover if you have hepatitis C:
- Antibody test: Which establishes whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus.
- PCR test: Which establishes whether the virus is still active and needs treating.
The two tests can often be done from one sample of blood which means you may only need to provide the sample once. Both tests can then be done on your sample at the laboratory. However, some services will perform one test and then call you back for a further blood sample to perform the second test.
Antibody test
A hepatitis C antibody test is the first test undertaken. This is to determine whether you have ever been exposed to the hepatitis C virus. It works by testing for the presence of antibodies to the virus generated by your immune system. If you receive a negative hepatitis C antibody test but have been experiencing symptoms or have been recently exposed to hepatitis C, then you are likely to be advised to have a second test.
It is important to remember that there is a ‘window period’. This is the short period of time when your immune system may not have had time to produce antibodies. It usually takes between six and twelve weeks for these antibodies to develop. However, in a few people it can take up to six months. So if you have the test within this window period and the result is negative, it does not necessarily mean that you don’t have the virus.
PCR test
Patient Discussion About Hepatitis C
Q. Is Hepatitis C contagious? My Girlfriend is a carrier for Hepatitis C. She got infected from a blood transfusion as a kid. Can I catch it from her?
A.
Q. What is the difference between hepatitis c and hepatitis b? and also can it be possible to have a false positive on a Hepatitis B test?
A.
Q. What is the difference between hepatitis c and hepatitis b? and also can it be possible to have a false positive on a Hepatitis B test?
A.
Recommended Reading: What Are The First Signs Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Antibody Blood Test With Reflex On Positives
Assess exposure to hepatitis C virus infection and tests blood safety.
Also Known As: HCV, Hep C.
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
If your results on the hepatitis C antibody test are positive or you have symptoms that suggest HCV, your healthcare provider may order a hepatitis C RNA test. This is a blood test that looks for genetic evidence of the virus itself. Another test, called “viral genotyping,” helps find out what kind of HCV infection you have and what type of treatment may be needed. In some cases, you may need a liver biopsy to look for liver damage related to HCV.
Other tests look for ballooning of the blood vessels in the esophagus or cancer in the liver . Chronic infection with HCV can cause inflammation and destruction to blood cells, blood vessels, and other tissues in the body. Your healthcare provider may test for these conditions, as well.
Also Check: Home Remedies For Hepatitis C In Urdu
What Do Antibodies Mean
Just remember that having antibodies does not always mean you have hep C – it only means you have had exposure to the virus as many as 25% or more people will clear the virus with their own immune response, and yes your antibodies do play a part in that. There is some research that looks at how immune response and treatment affect us over time, and I support more attention to discovering the connection between autoimmune disorders and chronic hep C and treatment, and how our bodys own immune response fits into these mechanisms. It is my hope that we can acquire more understanding, and through that process be able to prevent some of the issues that people are dealing with now and into the future. This has implications for other infectious disease and immunity research & understanding.
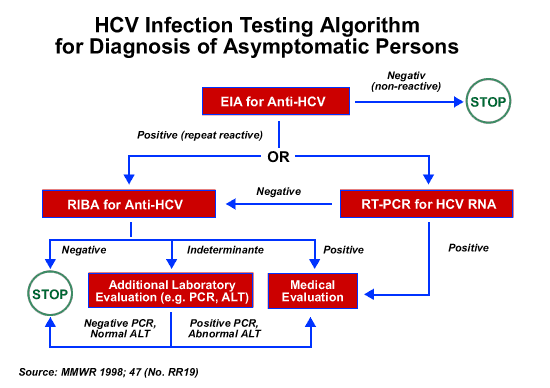
Evaluation Of Individuals With Positive Screening Test
Patients with a positive screening test for anti-HCV antibody should be tested for serum HCV RNA. Serum HCV RNA quantifies the amount of viral RNA in serum and indicates ongoing infection. If HCV RNA is detectable, tests should be performed to determine the extent of hepatic fibrosis. These tests typically include liver biopsy or noninvasive measures, such as biochemical markers of fibrosis or transient elastography., An ultrasound of the abdomen should also be performed to identify the possible presence of cirrhosis and focal lesions in the liver suspicious for hepatic malignancy.
Patients who have a positive anti-HCV on a screening test but have no detectable HCV RNA should have a confirmatory HCV RNA test a few months later. If HCV RNA remains undetectable, these individuals should be reassured that they do not have hepatitis C infection and that the anti-HCV may remain persistently positive. Such individuals have either cleared the virus or the true specificity of the test is lower than the reported 100%, and the test result was a false positive.
Read Also: How You Get Hepatitis B And C
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are: Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
Why Do You Need Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C virus primarily attacks the liver, which performs a number of crucial function in the body and the HCV kills of healthy cells in the liver causing damage and destruction of the liver, thereby, hampering many vital functions of the body. As such it is extremely important to get tested for Hepatitis C virus, as the sooner the HCV is detected, the sooner will the treatment start to eliminate and kill the virus.
Recommended Reading: Where To Get Hepatitis B Titer
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
Lab report for a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer . This is the blood test that checks for immunity to Hepatitis B. It is not a routine blood test, so it is not likely that you have done it in the past, unless needed for another academic health related program or job *Remember that the titer documentation is program specific …
Explanation Of Test Results:
If this test result is positive, it means your body was exposed to the hepatitis C virus and made antibodies . However, it does not tell you whether you are still infected with hepatitis C. If the antibody test result is positive, you should be tested for hepatitis C RNA , which determines whether you are chronically infected. The lab will perform this RNA test automatically if your hepatitis C antibody test is positive.
If the antibody test result is negative, it means you have not been infected with the hepatitis C virus, and further testing for hepatitis C usually is not needed.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Catch It
Hcv Core Antigen Detection
During the past decade, several assays for the detection of the core antigen of HCV by ELISA or CLIA have been developed. These assays were envisioned as alternatives to NAT to be used in resource-limited settings, where molecular laboratory services are either not available or not widely utilized owing to cost issues. Since these assays are either ELISA or CLIA based, they are user friendly, require less technical expertise and are less expensive compared to molecular techniques. Evaluations in transfusion settings have shown that the HCVcore Ag assay detects HCV infection as effective as NAT, about 40-50 days earlier than the current third generation anti-HCV screening assays. HCV core antigen levels closely follow HCV RNA dynamics, and allow clinical monitoring of a patient’s therapy, independently of HCV genotype. The major limitation of the HCV core Ag assay is its lower sensitivity limiting its utility. A new generation CLIA based quantitative test with sensitivity comparable to that of end point PCR but less than that of real time RT-PCR has been reported.
This Hepatitis C Screening Test Checks Whether You Test Positive For Hepatitis C
In the event that your test results are positive, an associate from our physician network will contact you directly to discuss your particular case as well as provide information on how to take the next steps to get treatment. We take customer privacy very seriously and will never share your information with a third-party with the exception of the lab we use to test your sample and our physician network.
As is the case with all STD testing – whether through EverlyWell or your doctor â we may be required by law to report positive test results to certain state health departments. This is only done to track infection prevalence. In rare cases you may not receive a definitive result because of early infection or inadequate sampling and repeat testing is suggested. Know where you stand with our at-home Hepatitis C test.
Don’t Miss: Where Can I Get Tested For Hepatitis
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs — even if it was just once or a long time ago.
- Youâre on kidney dialysis.
- You have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels .
- You had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992.
- Youâve ever gotten clotting factor concentrates made before 1987.
- You received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C virus.
- Youâre a health care worker, first responder, or have another job that exposes you to HCV-infected needles.
- You were born to a mother with HCV.
Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
- Hepatitis C Ab w/RFLX PCR
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis C Antibody w/Reflex PCR
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis C virus IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera by the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT Anti-HCV test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant HCV antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HCV present in the sample binds to the rHCV coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG/IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HCV. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of IgG/IgM anti-HCV in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an ARCHITECT Anti-HCV calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for IgG/IgM anti-HCV. Specimens with S/CO values < 0.79 are considered nonreactive and specimens with S/CO values between 0.80 and 0.99 are Indeterminate.
Reactive anti-HCV will reflex to Hepatitis C RNA, Quantitative for confirmation with an additional charge.
For anti-HCV testing without PCR reflex for REACTIVE results, see Hepatitis C Antibody without PCR reflex on reactive samples .
- Synonyms
Don’t Miss: How Do You Say Hepatitis C In Spanish
Other Hepatitis C Tests
After an individual has received a reactive or positive result from a hepatitis C antibody test, they will need to have two follow-up tests.
The first test checks to see whether a person still has the virus the other measures the amount of the virus in the blood.
The first test is the hep C RNA qualitative test, also known as the PCR test. A positive result means that a person has the hepatitis C virus. A negative result means that the body has cleared the virus without treatment.
The second test is the hep C RNA quantitative test. The result of this test is given as a number rather than a positive or negative. This is because the test compares the amount of the virus in the body before, during, and after treatment.
The number given as a result of this test is known as the viral load. The lower amount of the hepatitis C virus in the blood, the better the chances that a person can eliminate the virus from their body.
After hepatitis C virus is diagnosed, other tests may be needed:
Certain behaviors, experiences, and medical procedures increase the risk of getting the hepatitis C virus, which is transmitted by contact with blood.
The following are risk factors for contracting the virus:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advise all baby boomers get tested for hepatitis C. Baby boomers are people born between 1945 and 1965. They are five times more likely to have the virus than other adults.
Hepatitis C Reflex Testing
To ensure complete and timely diagnosis of HCV, HCV reflex testing is recommended following a reactive hepatitis C antibody screening test. Reflex testing means the laboratory will perform the hepatitis C antibody test, and if the result is positive, the laboratory will immediately perform an HCV RNA test on the same specimen. If the subsequent HCV RNA test is negative, HCV infection is effectively ruled out for most patients. If the reflex HCV RNA test is positive, a diagnosis of active HCV infection has been confirmed, and the individual should be referred directly for HCV care and treatment.
Reflex testing obviates the need for the patient to return for follow-up testing should the initially HCV antibody test be reactive. If the RNA test is negative, the work-up is done, and the patient may be reassured.
- Rationale for reflex testing:
Also Check: Best Medicine For Hepatitis C
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Natural History Following Infection With Hcv
Hepatitis C can present as acute or chronic hepatitis. Most of the cases of acute hepatitis C are asymptomatic. Symptomatic acute hepatitis with jaundice is seen in 10-15% of patients only and can be severe, but fulminant liver failure is rare. Spontaneous clearance is observed in 25-50% of those with symptomatic infection and in 10-15% of those with asymptomatic infection. The natural history following exposure to HCV is summarized in .
Natural history following infection with hepatitis C virus
Chronic hepatitis C is marked by the persistence of HCV RNA in the blood for at least 6 months after the onset of acute infection. The risk of progression to chronic infection by HCV is influenced by various factors including:
-
Age at the time of infection
-
Gender
-
Ethnicity
-
Coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus , HBV
-
Concomitant alcohol consumption
-
Comorbid conditions like cancer, immunosuppression, insulin resistance, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, etc.
Don’t Miss: Genotype 4 Hepatitis C Treatment