What Foods Should I Avoid
Everyone should avoid eating a lot of fat, cholesterol, salt and processed sugar, even if their liver is healthy. In addition, those with HCV should limit or avoid alcohol. Drinking alcohol will speed up liver damage.
Eating properly can help decrease some of the symptoms of Hepatitis C, like feeling tired and sick. Drink lots of water for general health benefits. HCV is not a digestive disease diet will not affect the disease. Your provider may put you on a special diet if you have advanced liver disease.
Read Also: Tenofovir Alafenamide Vs Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Hepatitis B
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
Can Hcv Cause Psychosis
At least 50% of patients infected with HCV suffer from a psychiatric illness, and the lifetime prevalences of psychotic, anxiety, affective, personality, and substance use disorders are all higher among patients with HCV,10,47 as compared to the general US population studied in the Epidemiologic Catchment Area study.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Is This Test
This test looks for antibodies called IgM in your blood. The test is used to find out whether you are actively infected with the hepatitis B virus .
HBV has a central core and a surrounding envelope. Your immune system makes IgM antibodies to the core of HBV during the active stage of infection. It can take 60 to 150 days to develop symptoms of hepatitis B after you become infected. Hepatitis B core IgM antibodies begin to appear in your blood several weeks after you are first infected with HBV. People who have had the hepatitis B vaccine will not have the core antibody in their blood.
HBV is one of 5 hepatitis viruses. The others are hepatitis A, C, D, and E. Most hepatitis infections are caused by these 5 viruses. HBV is spread through blood, seminal fluid, and vaginal secretions. The virus causes an infection in the liver. In most cases, this virus clears up on its own within 6 months. But in a small portion of adults and a larger portion of children, the virus does not go away. This is especially true for newborns. This is called having a chronic infection. It may lead to liver cell damage scarring, or cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Question 7 What Proportion Of Hcv Antibody

Among specimens with reactive HCV antibody results, approximately 52% have detectable HCV RNA at a level of > 15 IU/mL on reflex testing. However, the frequency varies markedly based on the strength of the signal of the antibody test, or signal-to-cutoff ratio. Specimens with an S/C ratio of at least 1.0 are considered reactive for HCV antibody7 and thus undergo reflex testing for HCV RNA. Analysis of approximately 200,000 specimens submitted to Quest Diagnostics for HCV antibody testing with reflex to HCV RNA testing demonstrate that the frequency of positive reflex results increases with increasing S/C ratio:
Recommended Reading: How Did I Get Hepatitis
Read Also: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule Adults
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
From an infected woman to her newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Do
How Do I Get Tested For Hep C
Finding out whether you have hep C starts with getting tested for HCV. This involves a blood test called an HCV antibody test.
You can ask to be tested at your primary care doctors office or a public health clinic, or you can test yourself using a home testing kit.
To find a clinic with HCV testing near you, visit the CDCs GetTested website and enter your zip code. This tool will help you find testing or free testing in nearby locations.
At-home test kits usually cost $50 to $100 for one test, which comes with all the materials and instructions you need. Youll collect a small amount of blood and send it off to a lab for testing.
Youll get your test result in 2 to 5 business days with most kits. Some at-home test options are Everlywell, LetsGetChecked, myLAB Box, and iDNA.
Test results may seem intimidating, especially if they can be a little more complicated than just positive or negative. With HCV testing, the antibody test determines whether you have ever contracted HCV.
Breaking down test results:
- A non-reactive HCV antibody test result means you do not currently have HCV.
- A reactive HCV antibody test result means you currently have HCV or had it at some point, and the antibodies are in your blood.
So, if you dont have any HCV antibodies, you are negative for HCV.
If you do have HCV antibodies, that means youve either had it before or currently have it. If youve had it once, youll always have antibodies for it, whether your treatment has cleared it or not.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Kissing
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Presence of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen is used to determine immune status to HBV or disease progression in individuals infected with HBV. Anti-HBs levels can be measured to determine if vaccination is needed, or following a vaccination regimen, to determine if protective immunity has been achieved.
â Anti-HBs usually can be detected several weeks to several months after HBsAg is no longer found, and it may persist for many years or for life after acute infection has been resolved.
â It may disappear in some patients, with only antibody to core remaining.
â People with this antibody are not overtly infectious.
â Presence of the antibody without the presence of the antigen is evidence for immunity from reinfection, with virus of the same subtype.
What is the Hepatitis B virus?
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days .
What are common symptoms?
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Read Also: Dna Test For Hepatitis B
Screening Tests For Hepatitis B
Your blood may be screened for HBV for many different reasons. The three tests generally include HBsAg, antibody to HBsAg, and antibody to hepatitis B core antigen. This allows the healthcare provider to know whether you could benefit from vaccination, or if you have active or chronic hepatitis B and need counseling, care, or treatment.
You may be routinely screened if you are pregnant, are donating blood or tissue, need immunosuppressive therapy, or have end-stage renal disease. You will also be screened if you are in groups that are at higher risk for HBV.
Please Explain What Does Hepatitis B Antibody Surface Ql Reactive Mean
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â itâs anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: How Does Hepatitis Affect The Body
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B Surface Ab Reactive
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â its anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: What Is Hepatic Function Panel
Diagnosis Of Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
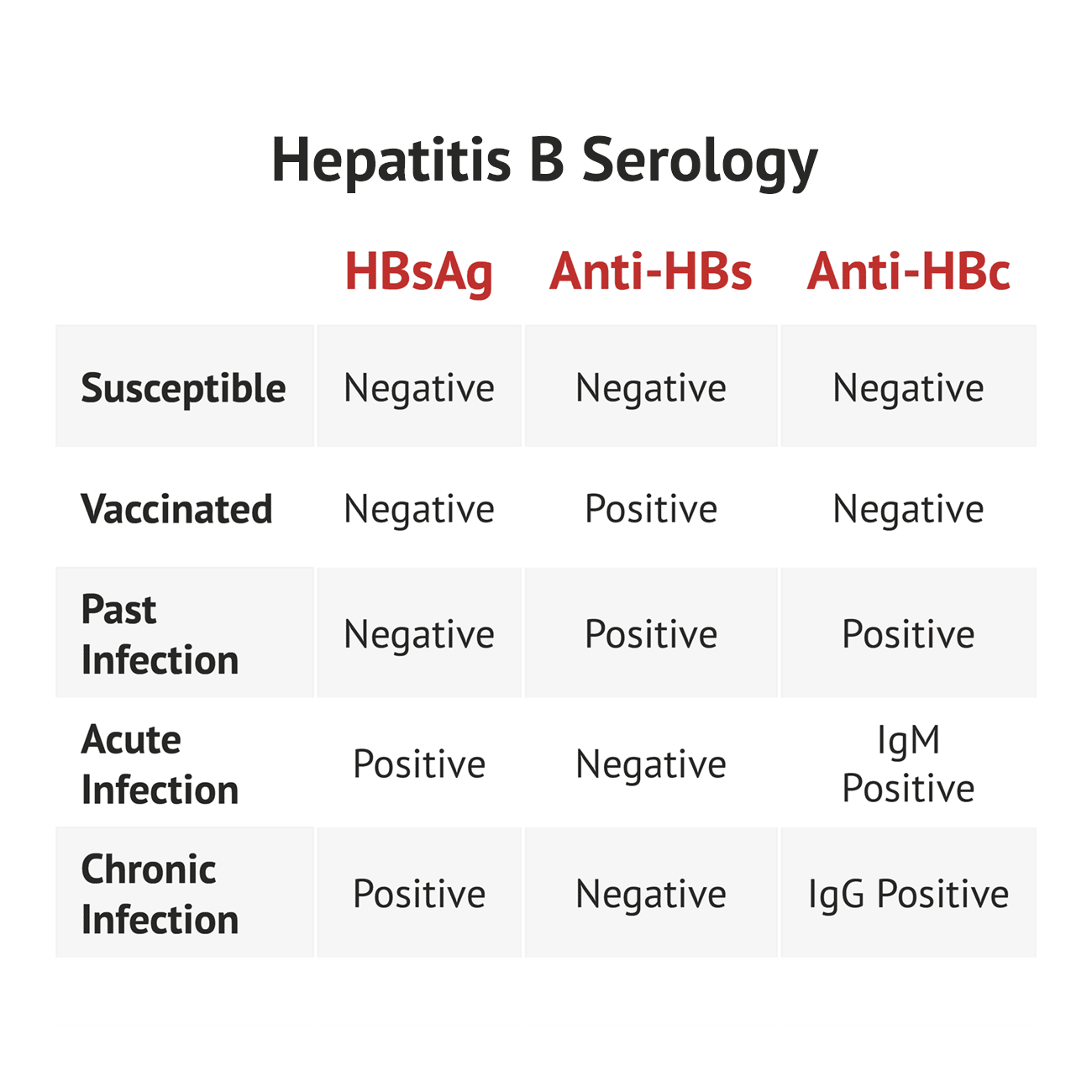
HBsAg is the first serologic marker to appear and may be detected within 1 to 2 weeks after exposure. It precedes the development of symptoms by an average of 4 weeks.104 The presence of HBsAg indicates ongoing infection. Qualitative but not quantitative methods are used by most clinical laboratories because the amount of antigen does not correlate with disease activity or with the presence of an acute or chronic infection.26 Some symptomatic patients may have self-limited, acute HBV infection without detectable HBsAg. These patients, up to 9% in some studies, have other detectable markers of infection.104 HBeAg appears virtually simultaneously, peaks, and then declines in parallel with HBsAg. It usually disappears before HBsAg. Adult patients who remain persistently positive for HBeAg for more than 10 weeks are likely to become chronically infected. HBeAg indicates a high level of viral replication and infectivity. Most patients with nondetectable HBeAg have resolving, minimal, or no active liver disease.26 Pre-core mutants of HBV do not express HBeAg they may be responsible for a more severe course and, in some cases, fulminant disease. Serum aminotransferase levels become raised but are nonspecific. They begin to increase just before the development of symptoms and then peak , with the development of jaundice.
Howard C. Thomas, Jennifer A. Waters, in, 1998
Recommended Reading: Can You Have Hepatitis C And Not Know It
Also Check: How Can I Catch Hepatitis
False Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Due To Recent
Hepatitis B is the most common viral hepatitis, potentially life threatening, with long term complications. Currently, vaccine is the most effective tool against hepatitis B infection. It is worthwhile mentioning that due to rampant use of hepatitis B vaccine , there have been concerns about hepatitis B surface antigen reactivity.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
Also Check: Can Hepatitis A Be Transmitted Sexually
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Question 2 What Is The Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
The hepatitis B surface antibody is the antibody that is produced in response to hepatitis B surface antigen , a protein present on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. Anti-HBs appears after convalescence from acute infection and lasts for many years. It can also be produced in response to hepatitis B vaccination.
Other hepatitis B antibodies are not produced in response to vaccination. This is because these antigens are not in the vaccine.
Read Also: What Does Hepatitis B Do To You
Read Also: What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatitis C
What Do My Test Results Mean
Test results may vary depending on your age, gender, health history, the method used for the test, and other things. Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you.
Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found.
If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV. In most cases this means that you will recover within 6 months. If you recover, you will have immunity from the virus and will not be able to pass the virus to others. A positive test may also mean you have chronic hepatitis B infection. If you dont recover in 6 months, the virus may stay in your blood and cause liver problems. You can also infect others. Your healthcare provider may give you medicines if you dont recover after 6 months.
What Does Hepatitis B Core Igm Mean
IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen : Positivity indicates recent infection with hepatitis B virus . Its presence indicates acute infection. Tests.
What does it mean to be non immune to Hep B?
Answer. This means that you are susceptible hepatitis B. Often these words are used when the blood tests for hepatitis B do not show reactive, or levels of, hepatitis B surface antibody .
What does non reactive hepatitis B test results mean?
If your test results for hepatitis B came back as Non-reactive that is actually very good news. It means that you have never been exposed to the Hepatitis B virus, so you do not have the virus.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Treat Hepatitis C
Did You Know Only 21% Of People Know They Have Hcv How Testing Plays A Role In Ending Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection in the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. It is spread through contact with blood from an infected person. Today, most people become infected with the virus by sharing needles or through equipment used to prepare or inject drugs. However, it can also be spread through birth from an infected mother to child, through sexual contact, sharing personal items contaminated with blood such as razors and toothbrushes, unregulated tattooing, and some health care procedures such as injections, infected blood transfusions , and needlestick injuries in healthcare settings.
The immediate period following infection is called the acute phase and lasts approximately six months. Many people do not experience symptoms during this phase, or if they do, they show non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, and depression.
After six months, approximately 70%-85% of those infected with HCV will fail to clear the virus on their own, or spontaneously, and this is when hepatitis C becomes a chronic or long-term infection. This high rate showcases the importance of regular testing so that treatment, which is highly effective, can start right away.
Reactivation Risk In Anti
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis B Caused By
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine Used For