What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
Your Blood Sugar Is High
If you have hep C, youre also at risk for type 2 diabetes. Thats because HCV triggers an inflammatory response that interferes with your bodys ability to use insulin correctlywhat doctors call metabolic signaling. This results in insulin resistance, causing glucose to build up in the blood and leading to type 2 diabetes.The important thing to know, if you have any of these symptoms, is that there is a cure for hep C. Though best if treated early, late is better than never, so head to your doctor, stat!
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative Titer
How Are Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C Spread From Person To Person
Like HIV, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses spread:
- From mother to child: Pregnant women can pass these infections to their infants. HIV-HCV coinfection increases the risk of passing on hepatitis C to the baby.
- Sexually: Both viruses can also be transmitted sexually, but HBV is much more likely than HCV to be transmitted sexually. Sexual transmission of HCV is most likely to happen among gay and bisexual men who are living with HIV.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
Other Body Fluids And Tissues
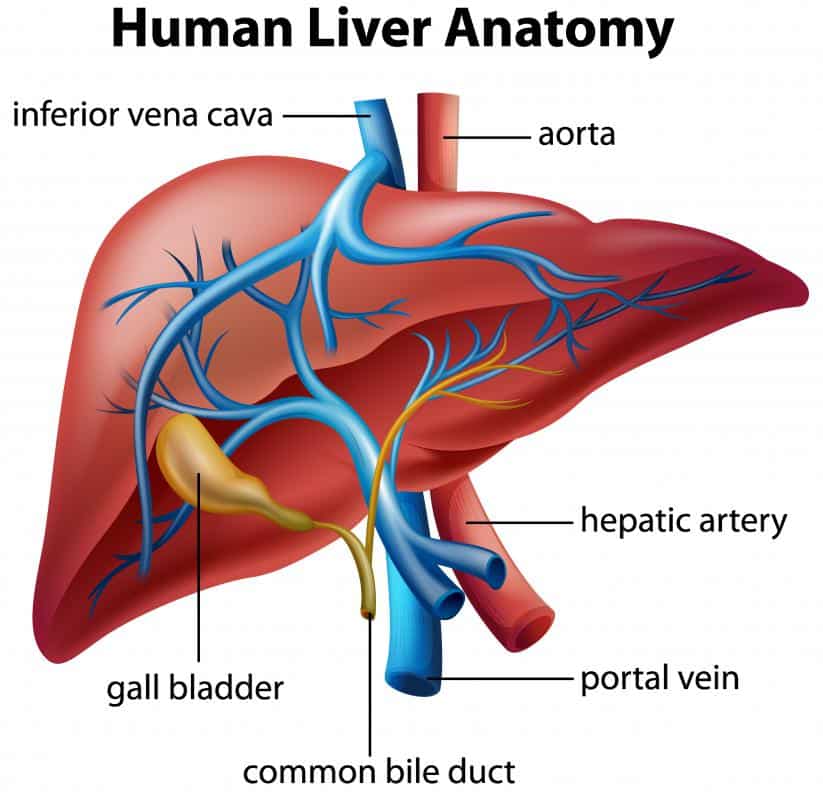
Synovial fluid , amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, and peritoneal fluid can contain the hepatitis B virus, but the risk of transmission to workers is not known.
Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomit have not been implicated in the spread of hepatitis B. Unless they are visibly contaminated with blood, the risk of contracting hepatitis B from these fluids in the workplace is very low.
Hepatitis B is not transmitted by casual contact. For example, hospital employees who have no contact with blood, blood products, or blood-contaminated fluids are at no greater risk than the general public. However, the virus can spread through intimate contact with carriers in a household setting, possibly because of frequent physical contact with small cuts or skin rashes. The virus can also spread through biting and possibly by the sharing of toothbrushes or razors. It is not spread through sneezing, coughing, hand holding, hugging, kissing, breastfeeding, sharing eating utensils, water or food.
You May Like: Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Antibody Negative Means
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success. Services include structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice.
Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
“Our team at Yale Medicine is uniquely equipped to serve patients with viral hepatitis from Connecticut and beyond and aims to offer outstanding, individualized, patient-centered care to help educate and guide patients through their treatment,” says Dr. Lim. We have specialists who have nationally recognized expertise in the management of viral hepatitis in special populations, including HCV-HIV coinfection, end-stage renal disease, cirrhosis/liver failure, post-liver transplant, and prior failure to respond to all-oral direct acting antivirals .
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C Through Sex
How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs and symptoms can vary, in particular by the age of the individual. Many individuals may not show symptoms . When symptoms develop, they include fever, joint pain, abdominal pain, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, dark urine, clay-coloured bowel movements, or jaundice.
Most infections are asymptomatic or mild. Occasionally, people with serious cases of hepatitis B require hospitalization. A very small proportion of these patients develop a critical form of the disease called âfulminantâ hepatitis B. This condition results from a sudden breakdown of liver function.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Pass Hepatitis C
How Is It Treated
If you have chronic hepatitis C infection, your healthcare provider will examine you for liver problems andmay prescribe drugs to help control the disease.Hepatitis C drugs can help to:
- Clear the virus from the body
- Slow down or prevent liver damage
- Lower the chance of getting cirrhosis and liver cancer
Before starting treatment it is important to discuss youroptions with your health care provider. Treatment forhepatitis C may not be for everyone. Some patientsmight not need treatment. Other patients might not beable to be treated due to other medical problems.
Also Check: How Does One Get Hepatitis B And C
Liver Definition And Facts
- The liver is an essential organ that has many functions in the body, including making proteins and blood clotting factors, manufacturing triglycerides and cholesterol, glycogen synthesis, and bile production.
- The liver is a large organ that sits on the right-hand side of the belly.
- The liver is the bodyâs largest internal organ.
- Many different disease processes can occur in the liver, including infections such as hepatitis, cirrhosis , cancers, and damage by medications or toxins.
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
What Does Hepatitis C Do To The Body
Hepatitis C is among the many diseases disproportionately affecting the African American community.
The disease, targeting the liver, can turn into a serious health problem over time resulting in liver damage and liver cancer. There is no vaccine for hepatitis C but there are treatments available.
After diagnosis, in the early stages, patients may not have any symptoms, according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . In fact, about 15 to 25 percent of people living with the hepatitis C virus will only develop an acute version of the disease. Meaning, the virus is cleared from the body without causing any liver damage.
You May Also Like
Others, though, could eventually experience severe symptoms one to three months after exposure. Joint pain is one early symptom, including inflammation and pain in the joints and muscles. This can be a sign that the immune system is working to fight off the virus.
Other early symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and other digestive issues. Some people may also experience jaundice a yellowing of the skin and eyes. This is a result of bilirubin, a greenish pigment found in the bile, not being removed properly from the body.
You May Also Like
7 Daily Habits That May Be Damaging Your Liver
5 Foods to Avoid at All Costs
You May Like: Hepatitis B Symptoms In Women
What Causes Hepatitis B
- being born to a mother with hepatitis B
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools that were used on an infected person and werent properly sterilized, or cleaned in a way that destroys all viruses and other microbes
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
You cant get hepatitis B from
- being coughed on or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking unclean water or untreated water that has not been boiled
- eating food that is unclean or has not been properly cooked
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
Mothers who have hepatitis B can safely breastfeed their babies. If a baby receives hepatitis B immune globulin and starts receiving the hepatitis B vaccine to prevent hepatitis B infection shortly after birth, hepatitis B is unlikely to spread from mother to child through breastfeeding.15
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Hcv Rna
If I Have Hepatitis How Can I Avoid Giving It To Someone Else
For hepatitis A, one of the best things you can do is wash your hands a lot. That will keep the virus out of food and drinks.
If you have hepatitis B and C, you need to find ways to keep others from making contact with your blood. Follow these tips:
- Cover your cuts or blisters.
- Carefully throw away used bandages, tissues, tampons, and sanitary napkins.
- Dont share your razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush.
- If your blood gets on objects, clean them with household bleach and water.
- Dont breastfeed if your nipples are cracked or bleeding.
- Dont donate blood, organs, or sperm.
- If you inject drugs, dont share needles or other equipment.
Show Sources
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C How You Get It
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Some people with hepatitis do not have symptoms and do not know they are infected. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Jaundice, yellowing of your skin and eyes
If you have an acute infection, your symptoms can start anywhere between 2 weeks to 6 months after you got infected. If you have a chronic infection, you may not have symptoms until many years later.
If You Have Hepatitis C
- See your health care provider regularly.
- Tell current and recent sex partners that you have hepatitis C.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Get plenty of rest.
If you have hepatitis C, you can prevent liver damage by not drinking alcohol and by getting vaccinated for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: Any Cure For Hepatitis B
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Also Check: What Drug Is Used To Treat Chronic Hepatitis B
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if youre worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
- Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
- The following groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991
- recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high risk areas include North Africa, the Middle East and Central and East Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Can It Be Cured
Curative Therapies For Hepatitis C
Current therapy to cure hepatitis C relies on oral antiviral medications taken for 8 to 16 weeks. Injection therapy is no longer used. The duration of therapy and the suitable regimen may depend on disease severity and viral genotype. Recent advancements in hepatitis C therapies have boosted cure rates to greater than 95% for nearly all individuals. Remarkably, tolerability has also improved dramatically, typically with only mild side effects if any at all. The following is an overview of most commonly used therapies in Canada.
Also Check: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Read Also: Treatment Of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.