What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education remains one of the most important components in preventative measures regarding HBV infection.
Education should be provided to expecting parents about the importance of vaccination and to clarify erroneous beliefs about vaccinations.Patient education should also include counseling about the avoidance of risky behaviors that predispose an individual to be infected, including promiscuous sexual activity or intravenous drug abuse. They should also be advised not to share items such as shaving razors, toothbrushes, or hair combs due to possible transmission via mucosal contact or through microtrauma to protective barriers.
Information To Collect For Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
The following information is epidemiologically important to collect in a case investigation for chronic hepatitis B infection. Additional information may also be collected at the direction/jurisdiction of the state health department.
- Demographic information
- Laboratory results
- Risk behaviors/exposures
- Pregnancy status. All HBsAg-positive pregnant women should be reported to the Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program manager so that they can be tracked and their infants can receive appropriate case management
The recommended elements of case investigation and follow-up of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection are detailed elsewhere. The following should be included:
- Contact investigation and prophylaxis: Provision of hepatitis B vaccination for sexual, household, and other contacts of persons with hepatitis B, and counseling to prevent transmission to others
- Counseling and referral for medical management, including
- assessing for biochemical evidence of chronic liver disease, and
- evaluating eligibility for antiviral treatment
Also Check: Hepatitis A Vaccine Side Effects
Screening And Risk Factors
Screening of all pregnant women for HBsAg to identify infants requiring postexposure prophylaxis has been recommended since 1988. Universal infant hepatitis B immunization has been recommended since 1991, and universal adolescent hepatitis B immunization since 1995. In the United States, approximately 21,000 HBsAg-positive women give birth annually. Without postexposure prophylaxis to prevent perinatal HBV infection, it is estimated that HBV transmission would occur in 36% of infants born to HBsAg-positive women. Furthermore, before the implementation of universal infant hepatitis B immunization, an additional 16,000 children younger than 10 years old were infected annually in the United States through exposure to HBsAg-positive household members or community contacts. Populations with the highest rates of these early childhood infections included Alaska Natives, children of Pacific Islander parents, and children of first-generation immigrants from countries where HBV is of intermediate or high endemicity.
Among persons who reported risk behaviors/exposures in 2016, the most frequently reported risk behavior/exposure for acute, symptomatic hepatitis B was injection drug use , followed by sex with multiple partners . More than half of persons with newly acquired hepatitis B were previously seen in medical settings where hepatitis B vaccine is routinely recommended, such as sexually transmitted disease treatment clinics or drug treatment centers.
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
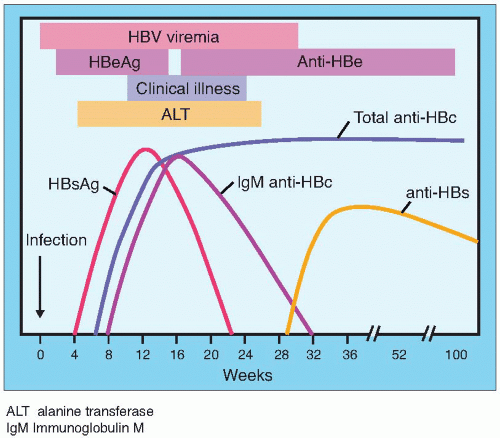
An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months and infected persons are able to pass the virus to others during this time. A simple blood test can let a person know if the hepatitis B virus is in their blood or if they have successfully gotten rid of the virus. The doctor should periodically test your blood over the six-month period to monitor the health of your liver and check progress towards recovery. In a person who has recovered from an acute hepatitis B infection, a taken six-months after initial diagnosis will show that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood.
Being diagnosed with acute hepatitis B can be difficult. As you move through the initial six-month period, there are tips and strategies to help.
Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection.
It is also important to have your sexual partner and family members get tested for hepatitis B. If they have not been infected and have not received the hepatitis B vaccine then they should also start the hepatitis B vaccine series.
Be sure to follow-up with your health care provider for any additional blood tests that are needed to confirm your recovery from an acute infection.
Also Check: How Did Naomi Judd Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Prevention Strategies
HepB vaccination is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention efforts. A comprehensive strategy to eliminate HBV transmission includes universal vaccination of infants beginning at birth, routine vaccination of previously unvaccinated children less than age 19 years, and vaccination of adults at risk for HBV infection, including those requesting protection from HBV without acknowledgement of a specific risk factor. It also includes universal testing of pregnant women for HBsAg to identify newborns who require immunoprophylaxis for prevention of perinatal infection and to pregnant women who can benefit from antiviral therapy to reduce perinatal transmission.
What Is The Incubation Period For Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is a liver disease caused by a viral infection. If left untreated, the virus can lead to serious liver damage.
HCV is a bloodborne disease, meaning its transmitted from person to person through contact with blood. The most common way people contract the virus is from sharing needles used to prepare or inject drugs.
Before 1992, blood transfusions were a common cause of HCV transmission. Since then, stricter screenings of the blood supply have greatly reduced this risk of transmission.
The majority of HCV cases are chronic . This means theyll persist until treatment knocks out the virus completely. However, cure rates for chronic HCV are improving.
Acute HCV appears much sooner with obvious symptoms. Unlike chronic HCV, the acute version of the illness is more responsive to traditional treatments. However, because new treatments are so effective and well tolerated, traditional treatments are not recommended.
The new preferred treatment method for HCV involves watchful waiting to see if acute HCV resolves without treatment. This occurs in
You should get tested for HCV if:
- you think theres any chance you may have been exposed to the virus
- you were born between 1945 and 1965
- you have used injected drugs, even if it was a long time ago
- youre HIV-positive
- you received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
Last medically reviewed on August 10, 2017
Read Also: How Hepatitis C Is Transmitted Sexually
What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis B
About 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments almost always work if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Perinatal Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Clinical description
Perinatal hepatitis B in a child 24 months of age may range from asymptomatic to fulminant hepatitis.
Laboratory criteria for diagnosis consists of one or more of the following
- Positive HBsAg test OR
- Positive HBeAg OR
- Positive HBV DNA
Case classification
Confirmed: Child born in the United States or a United States territory to a HBV-infected mother and positive for HBsAg at 1 month of age and 24 months of age OR positive for HBeAg or HBV DNA at 9 months of age and 24 months of age.
Probable: Child born in the United States or a United States territory and positive for HBsAg at 1 month of age and 24 months of age OR positive for HBeAg or HBV DNA at 9 months of age and 24 months of age, but whose mothers hepatitis B status is unknown.
Infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth, followed by the second and third doses of vaccine at 1 and 6 months of age, respectively, if receiving the single-antigen vaccine. Scheduling will be different if the infant received a combination vaccine or if the infant weighed < 2,000 grams at birth. Postvaccination serologic testing for HBsAg and anti-HBs is recommended at age 912 months . If the initial dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG are delayed for more than 1 month after birth, testing for HBsAg may determine if the infant is already infected.
Read Also: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
Hepatitis B can be transmitted from a birthing parent to a newborn infant. This is because the newborn is exposed to blood and bodily fluids during delivery.
In fact, 90% of mothers with an acute hepatitis B infection and 10% to 20% of mothers with chronic hepatitis B will transmit the virus to their newborn, estimates the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
For this reason, birthing parents are routinely screened for hepatitis B during each pregnancy.
Additionally, the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin are both administered to infants with an HBV-positive birthing parent within of birth to prevent infection.
According to the
- people with hepatitis C infection
- men who have sex with men
- people with multiple sexual partners
- people who are seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infections
- people with current or recent injection drug use
- family members or sexual partners of those with hepatitis B
- people with chronic liver disease
- people traveling to areas with high rates of hepatitis B
- people on maintenance dialysis
- people who are incarcerated
The hepatitis B vaccine is usually administered in three shots, given 1 month and 6 months after the first dose. Another recently approved vaccine is completed in two doses spaced 1 month apart.
You May Like: Confirmatory Test For Hepatitis C
Case Reporting Within A Jurisdiction
In the United States, case reports of viral hepatitis are classified as hepatitis A, acute hepatitis B, acute hepatitis C, perinatal HBV infection, chronic hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, past or present, and perinatal HCV infection. Serologic testing is necessary to determine the etiology of viral hepatitis, and case reports should be based on laboratory confirmation . Each state and territory has a list of reportable diseases and conditions of public health importance. This list also includes persons or groups who are responsible for reporting, such as healthcare providers, hospitals, laboratories, and other institutions. Persons reporting these conditions should contact their state/jurisdiction health department for jurisdiction-specific reporting requirements. The CDC Viral Hepatitis Case Report worksheet is included as Appendix 6, to serve as a guide for data collection during investigation of reported cases.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules For Infants By Maternal Hbsag Status
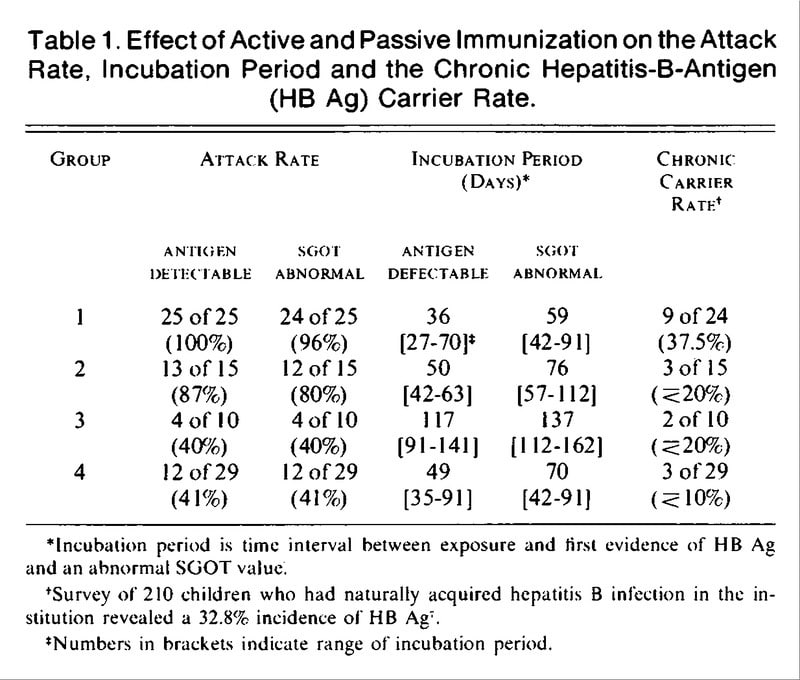
| Maternal HBsAg Status | |
|---|---|
| 4 | 6 mos¶ |
* Mothers should have blood drawn and tested for HBsAg as soon as possible after admission for delivery if the mother is found to be HBsAg positive, the infant should receive HBIG as soon as possible but no later than age 7 days. Pediarix and Vaxelis should not be administered before age 6 weeks.§ HBIG should be administered at a separate anatomical site from vaccine.¶ The final dose in the vaccine series should not be administered before age 24 weeks .
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Catch It
Important Questions And Needs For Future Research
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Antiviral Drugs Cost
What Should You Know About Hepatitis B Before You Travel
Hepatitis B is quite common in China and other Asian countries, where as many as 1 in 12 people have the virus, though many dont know it. Before traveling to those places, you should make sure youve been vaccinated against the virus.
In addition to getting the vaccine, you can take these additional precautions to reduce your risk of contracting the virus:
- Refrain from taking illegal drugs.
- Always use latex or polyurethane condoms during sex.
- Make sure new, sterile needles are used during all piercings, tattoos and acupuncture sessions.
- Avoid direct contact with blood and bodily fluids.
- Know the HBV status of all your sexual partners.
- Ask your doctor about possible vaccination before you travel to a place where hepatitis B is common.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/09/2020.
References
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus . The natural course of hepatitis B disease is different from one person to another.
Treatment with anti-viral drugs works for some people with HBV who are starting to develop liver damage. Whether treatment will be successful depends on many factors, and these are best discussed with a physician who specializes in liver diseases. When treatment is successful, liver scarring and the potential for liver cancer are reduced.
You May Like: How To Tell If You Have Hepatitis B
Signs And Symptoms Of Chronic Hbv
People with CHB often do not have symptoms, so those with the disease may have no way of knowing that they are infected. However, some complain of fatigue, aches and pains, fever, loss of appetite, nausea and abdominal pain.
The majority of acute HBV infections are also asymptomatic but around 30% of adults will present with jaundice, fatigue, poor appetite, weight loss, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, dark urine and light stools .
Diagnosis
HBV is diagnosed with a blood test to detect hepatitis B surface antigen . The different HBV serological markers may be used collectively to determine a persons HBV status. These are shown in Table 4.
HBV testing
Since 2000, all pregnant women have been tested for HBV. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence has published a new guideline to promote HBV and hepatitis C virus testing. The guideline recommends that the at-risk groups listed in Box 1 are tested for HBV, and given counselling before and afterwards.
Box 1. Who to screen
The following at-risk groups should be tested for HBV:
All those who test positive for HBV surface antigen should be referred to a specialist centre within six weeks. Pregnant women should be assessed by a specialist within six weeks of receiving the screening test result so treatment can be offered in the third trimester if necessary .
Read Also: How Do You Contact Hepatitis
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Read Also: Best Food For Hepatitis B