Complications Of Hepatitis B
A small proportion of people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus develop a long-term hepatitis B infection. They may have the virus in their bloodstream for most of their life without realising they are infected.
People with chronic hepatitis B infection may not notice any health problems until they develop liver problems such as liver disease or liver cancer later in life. Treatment for hepatitis B is essential because it is not possible to be a healthy carrier of the hepatitis B virus. Chronic hepatitis B infection occurs more commonly in some communities, including:
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities.
- In people from parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, such as:
- North-East Asia
- Sub-Saharan Africa.
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2018, 3,322 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 21,600 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 257 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Hepatitis B Treatment Guidance Recommendations
Several leading organizations have addressed guidance for treatment of chronic HBV, including when to initiate treatment. The following summary is intended to provide a succinct description of the indications for initiating HBV treatment in persons with chronic HBV, as outlined by the different organizational guidelines. The reader is encouraged to access these documents for additional details, descriptions, and discussion. The following summaries do not include guidance for the treatment of HBV in special situations or circumstances, such as reactivation of HBV, pre- or post-liver transplantation, treatment of HBV in persons who have coinfection , or treatment of HBV reactivation in persons undergoing immunosuppressive or cytotoxic therapy. These issues are addressed later in this topic review.
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis C Take To Show Up
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
What Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
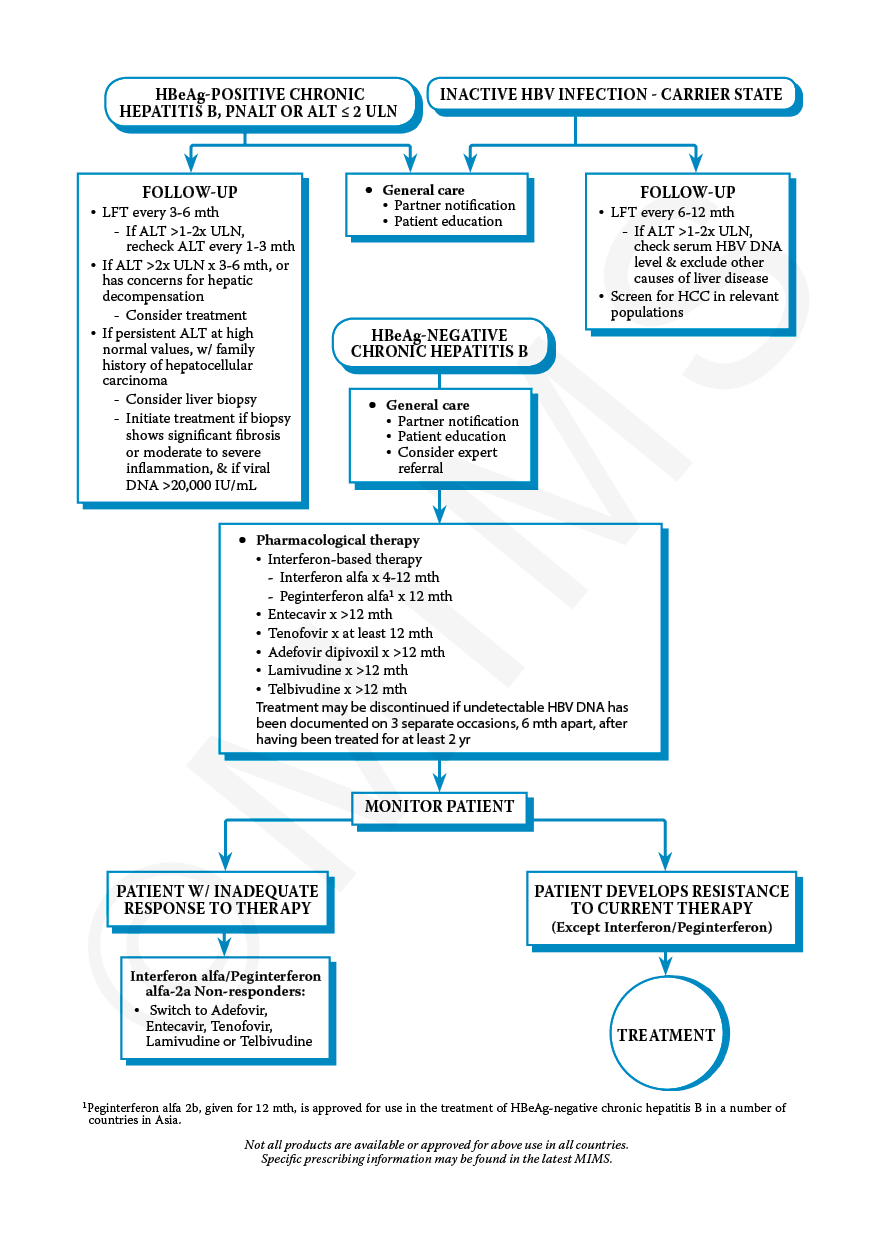
Hepatitis B is a serious infection. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer, which can cause severe illness and even death.
If a pregnant woman has the hepatitis B virus, her baby has a very high chance of having it unless the baby gets a special immune injection and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
Sometimes, HBV doesn’t cause symptoms until a person has had the infection for a while. At that stage, the person already might have more serious problems, such as liver damage.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Baby Vaccine Schedule
What Treatments Are Available For Chronic Hepatitis B If Medications Dont Work
If you have advanced hepatitis B, you might also become a candidate for a liver transplant. This path does not always result in a cure because the virus continues in your bloodstream after a transplant. To prevent being infected again after your transplant, you may be prescribed hepatitis B immunoglobulin with an antiviral agent.
Is There A Hepatitis B Vaccine
There is a vaccine against the hepatitis B virus . It is safe and works well to prevent the disease. A total of 3 doses of the vaccine are given over several months. Hepatitis B vaccine is also produced as a combination product which includes other common childhood vaccinations. This can reduce the number of shots that a child needs at a single visit.
The following groups should be vaccinated for hepatitis B:
- All children younger than 19 years, including all newborns – especially those born to mothers who are infected with HBV
- All health care and public safety workers who may be exposed to blood
- People who have hemophilia or other blood clotting disorders and receive transfusions of human clotting factors
You May Like: How Can A Person Get Hepatitis C
Factors Used To Determine Whether To Initiate Treatment
Because of inability to eradicate HBV and the potentially long if not indefinite duration of therapy , treatment is not universally indicated for everyone with chronic HBV, but rather reserved for those who are thought most likely to benefit from the standpoint of disease modification. Conceptually, the clearest indications for treatment are when extensive liver fibrosis has occurred and/or when there is active HBV DNA replication causing ongoing significant hepatic inflammation. The decision to treat persons with chronic HBV therefore typically incorporates the following three factors: cirrhosis status, evidence of hepatic inflammation, as measured by alanine aminotransferase levels or liver biopsy, and ongoing HBV replication as indicated by serum HBV DNA levels. Some guidelines incorporate the HBeAg status as another parameter to consider in deciding whether to initiate HBV treatment.
Asian Pacific Association For The Study Of The Liver
The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver hepatitis B guidance was generated by a panel of experts in this region, predominantly from the specialties of hepatology and gastroenterology. The most recent guidance was published in 2015. The 2015 APASL Hepatitis B Guidelines recommend initiating HBV treatment in the following situations for persons with chronic HBV.
- : Treatment is recommended with any detectable HBV DNA level, regardless of ALT levels or HBeAg status.
- Compensated Cirrhosis: Treatment is recommended with HBV DNA level greater than 2,000 IU/mL regardless of ALT level or HBeAg status, or any detectable HBV DNA level if ALT elevated, regardless of HBeAg status.
- Without Cirrhosis: Treatment may be started in noncirrhotic patients who have persistent elevation of ALT and elevated HBV DNA above 2,000 IU/mL if HBeAg negative or above 20,000 IU/mL if HBeAg positive. The ALT upper limit of normal used to guide management decisions is 40 U/L for both males and females.
Read Also: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse
Low Response Rates And Nonresponders
Low vaccination response rates have been associated with obesity, smoking, immunosuppression, and advanced age. Approximately 25-50% of persons who initially do not have a vaccine response will show a response to 1 additional vaccine dose, and 50-75% of individuals will have a response to a second 3-dose series.
It is recommended that testing for anti-HBs be obtained 4-12 weeks following vaccination. Revaccinate nonresponders, with another series of 3-dose hepatitis B vaccine. Consider delaying revaccination for several months after initiation of antiretroviral therapy in patients with CD4 counts below 200 cells/mm3 or those with symptomatic HIV disease. The delay in these individuals is an attempt to maximize the antibody response to the vaccine.
Do not defer vaccination in pregnant patients or patients who are unlikely to achieve an increased CD4 count. Individuals at increased risk of severe complications due to HBV infection include those unlikely to achieve CD4 counts of 200 cells/mm3 or above after antiretroviral therapy and HIV-infected pregnant women.
A combined hepatitis A virus /HBV vaccine is licensed in many countries and offers the advantage of protection against both of these viruses at the same time. The vaccine seems to be safe, although some questions exist regarding neurologic complications.
Doctors And Specialists Who Can Treat Hepatitis
Robert Burakoff, MD, MPH, is board-certified in gastroentrology. He is the vice chair for ambulatory services for the department of medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College in New York, where he is also a professor. He was the founding editor and co-editor in chief of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.
If you have hepatitis, you may be wondering who can treat your hepatitis. Well, a hepatitis specialist can help. But do you know the difference between the different kinds of clinicians who can treat your hepatitis? To help you understand who does what, here’s a short description of the different professionals who might work in your healthcare setting.
You May Like: What Is Hepatic Dog Food
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Living With Hepatitis B
If you have hepatitis, you should:
- avoid having unprotected sex, including anal and oral sex, unless you’re sure your partner has been vaccinated against hepatitis B
- avoid sharing needles used to inject drugs with other people
- take precautions to avoid the spread of infection, such as not sharing toothbrushes or razors with other people
- eat a generally healthy, balanced diet there’s no special diet for people with hepatitis B
- avoid drinking alcohol this can increase your risk of developing serious liver problems
- speak to your doctor if you’re thinking of having a baby
People with hepatitis B can usually have a healthy pregnancy, but it’s a good idea to discuss your plans with a doctor first as you may need extra care and your medications may need to be changed.
There’s a risk of pregnant women with hepatitis B passing the infection on to their child around the time of the birth, but this risk can be reduced by ensuring the baby is vaccinated shortly after they’re born.
Page last reviewed: 30 January 2019 Next review due: 30 January 2022
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Signal To Cut Off
What Will I Need To Do If I Am On Hepatitis B Medications
- Take oral medications every day to avoid developing resistance.
- See your provider on a regular basis
- If you have cirrhosis or high risk of liver cancer, get liver imaging on time as prescribed by your provider
- Have periodic laboratory tests to monitor HBV viral load and liver enzymes to monitor disease activity and response to medications
- You may need blood tests every 3-6 months initially and at least once a year thereafter if virus is undetected in blood.
How Do Doctors Treat Autoimmune Hepatitis
Doctors treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress, or decrease the activity of, your immune system, reducing your immune systems attack on your liver. The medicines doctors most often prescribe are corticosteroidsprednisone or prednisolonewith or without another medicine called azathioprine.
Doctors typically start with a relatively high dose of corticosteroids and then gradually lower the dose. Your doctor will try to find the lowest dose that works for you. Your doctor will use blood tests to find out how you are responding to the treatment. A decrease in levels of the liver enzymes alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase shows a response to treatment. ALT and AST falling to normal levels shows a full response. In some cases, a doctor may repeat a liver biopsy to confirm the response to treatment and find out whether the damage has resolved.
Treatment can relieve symptoms and prevent or reverse liver damage in many people with autoimmune hepatitis. Early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis can lower the chances of developing cirrhosis and other complications. A minority of people who have no symptoms or only a mild form of the disease may or may not need medicines.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Hurdles And Opportunities In Viral Hepatitis Treatment
In the last decade, rapid and significant advances in diagnosing and managing viral hepatitis were made and changed its treatment. These advances include the development of DAAs for the treatment of chronic hepatitis caused by HCV-with SVR rates greater than 95%, the improvement of HBV vaccination as well as enhancement of the immunogenicity of HBV vaccines, and the identification of antiviral therapies with low rates of viral resistance. Table summarises the current clinical management of viral hepatitis and areas of development for future treatments.
You May Like: Is Hepatitis Curable In Humans
Who Should Be Vaccinated For Hepatitis B
All newborns should be vaccinated. Also, people who are under 18 who were not vaccinated at birth should also get the vaccine. Other groups who should be sure to be vaccinated are those in certain high-risk categories, such as:
- People who have more than one sexual partner.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Adults with diabetes.
- Sexual partners of infected people and people who share households with infected individuals.
- People who are exposed to blood and other bodily fluids, including healthcare and public safety professionals, and people who work in jails and other places taking care of people who cant take care of themselves.
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted Sexually
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis B
Simple steps that everyone can take to protect themselves against hepatitis B include:
- Making sure you and your children are immunised this is the best protection.
- Using condoms every time you have anal or vaginal sex with new partners until you both get a check-up .
- Avoiding oral sex if you or your partner have herpes, ulcers or bleeding gums it is unlikely that you will contract hepatitis through oral sex unless blood is present.
- Choosing to have any body piercing or tattooing done by an experienced practitioner who follows good sterilisation and hygiene practices, and who works at premises registered by the local council.
- Wearing single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or need to clean up blood or body fluids.
- Never sharing needles and syringes or other equipment , if you inject drugs. Always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. Always wash your hands before and after injecting.
If you have hepatitis B:
If you think you have been exposed to hepatitis B, see a doctor immediately. Your doctor can give you treatment in some instances, which greatly reduces the risk of you becoming infected with hepatitis B.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Screening Guidelines Cdc