Do I Need A Hepatitis Panel
Few reasons that have prompted your healthcare provider to order the hepatitis panel for you are: You have exhibited some acute symptoms of hepatitis and the type of virus A, B, or C is not known. You carry an elevated risk of hepatitis infection due to recent exposure and a hepatitis panel may be recommended to determine the type of virus behind the hepatitis infection. Your doctor may ask you to undergo the test even in the absence of symptoms. If you show signs of liver damage, then the hepatitis panel test is a must for you. Some of the overriding symptoms that prompt a hepatitis panel test are: Loss of appetite Illegal drugs
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
How Could I Have Gotten The Virus Without Knowing It
The virus is passed through contact with stool from an infected person, typically via contaminated food or water. If a person infected with HAV does not wash their hands after using the bathroom, that person can pass the virus by handling raw fruits and vegetables consumed by others, or directly through person to person contact. You can also contract the virus by eating raw or improperly cooked seafood that had fed in contaminated waters. You may also contract the virus through sexual contact with someone who is infected but asymptomatic.
Recommended Reading: How Long Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
Meaning Of Hcv Viral Load
The number of HCV RNA international units per milliliter of blood must be measured before treatment and during the course of treatment, to assess response. Before treatment, however, the HCV viral load is not related to the patient’s liver disease severity or HCV prognosis. This is important for patients and providers to understand.
Note: In hepatitis B, unlike hepatitis C, a higher HBV DNA viral load does correlate with increased disease severity and increased likelihood of outcomes such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sensitivity And Specificity Of Serological Assays
The overall sensitivity and specificity of second generation assays are both 95-98%. They may be increased somewhat by third generation tests which incorporate extra HCV antigens. The results obtained within each generation of tests are very similar, regardless of the commercial source of the test.
The results of screening tests can be divided into two sets based on the risk of infection:
- low-risk populations, including blood donors and individuals with no risk factors for HCV infection
- high-risk populations, including individuals with a risk factor for HCV infection or documented liver disease presumed to be due to hepatitis C.
Low-risk populations
The first generation tests suggested that between 0.3% and 1.5% of blood donors world-wide were positive for anti-HCV. In Australia, 0.45% of blood donors in New South Wales were found to be anti-HCV positive. At first, HCV was only identified in 95-98% of the units of blood responsible for post-transfusion hepatitis C infections. This suggested that some infected units of blood were being missed.
Second generation assays detected one additional anti-HCV positive donor per 1000 tested. However, the introduction of these two generations of tests led to successive reductions in the incidence of post-transfusion hepatitis. The third generation tests are thought to detect a single additional infectious unit of blood for every 10 000 units screened.
High-risk populations
The Australian situation
Recommended Reading: Can You Cure Hepatitis A
Test Frequency And Turnaround Time
Hepatitis C Serology testing is performed daily Monday to Friday.
Turnaround time is up to 3 days from receipt by PHO laboratory for Non-reactive antibody results. Reactive and Indeterminate HCV antibody results are available and reported within 6 days.
Repeat testing may be indicated in those with ongoing risk factors for the acquisition of HCV.
Once a patient tests positive for HCV antibodies, other than in cases of maternal antibody transfer, there is no value in repeating the test as they will remain antibody positive for life regardless of whether they have cleared the virus or are chronic carriers.
When Is It Ordered
The CDC, the Infectious Diseases Society of America , the American Association of the Study of Liver Diseases , and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend screening with an HCV antibody test at least once in your lifetime when you are 18 years old or older . The CDC also recommends HCV screening for women with each pregnancy or for anyone who requests it.
One-time screening is recommended regardless of age if you:
- Have ever injected illegal drugs
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992*
- Have received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- Were ever on long-term dialysis
- Are a child born to HCV-positive women
- Have been exposed to the blood of someone with hepatitis C
- Are a healthcare, emergency medicine, or public safety worker who had needlesticks, sharps, or mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood
- Have evidence of chronic liver disease
- Have HIVabout 21% of those with HIV are also infected with HCV .
*The blood supply has been monitored in the U.S. since 1992, and any units of blood that test positive for HCV are rejected for use in another person. The current risk of HCV infection from transfused blood is about one case per two million transfused units.
Screening at regular intervals is recommended if you have ongoing risk of HCV infection, such as current injection drug use and sharing needles or syringes.
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting
- Dark urine
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
An HCV RNA test is ordered when:
Also Check: Hepatitis C And Fatty Liver
Screening For Hcv Infection
HCV screening has several potential benefits. By detecting HCV infection early, antiviral treatment can be offered earlier in the course of the disease which is more effective than starting at a later stage. Further, early detection together with counseling and lifestyle modifications may reduce the risk of transmission of HCV infection to other people. The optimal approach to screen for HCV is to test the individuals having risk factors for exposure to the virus. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases recommends screening for HCV for the following individuals:
-
Recipient of blood or blood components .
-
Recipient of blood from a HCV-positive donor.
-
Injection drug user .
-
Persons with following associated conditions
-
persons with HIV infection,
-
persons who have ever been on hemodialysis, and
-
persons with unexplained abnormal aminotransferase levels.
-
Children born to HCV-infected mothers.
-
Healthcare workers after a needle stick injury or mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood.
-
Current sexual partners of HCV-infected persons.
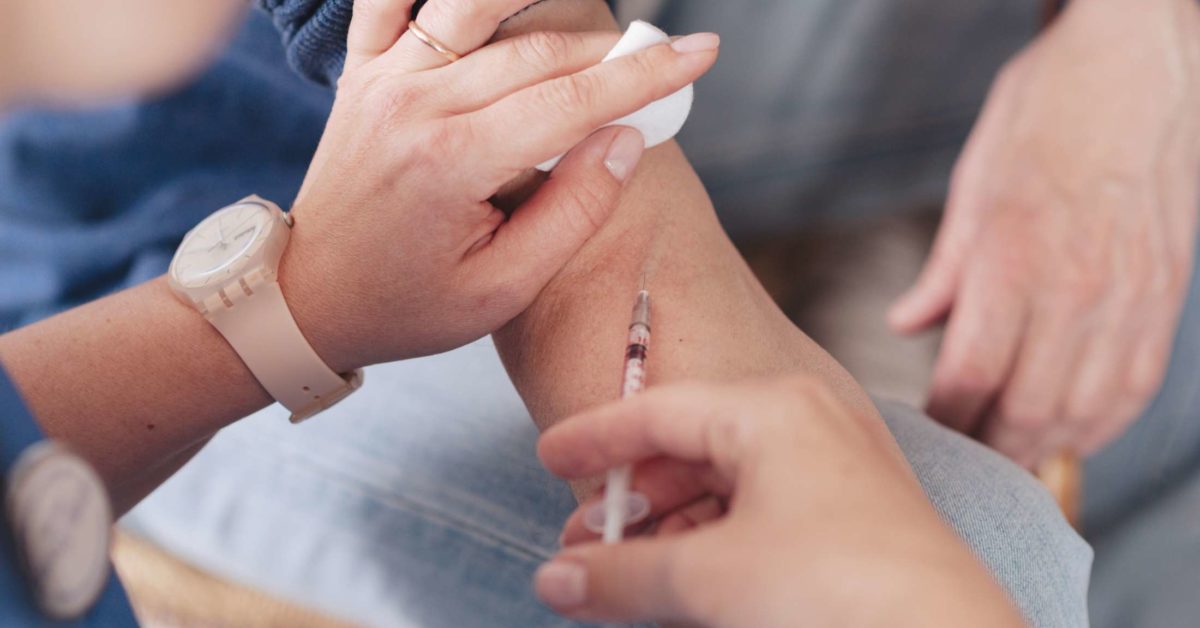
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
You may also be able to use an at-home kit to test for hepatitis. While instructions may vary between brands, your kit will include a device to prick your finger . Youll use this device to collect a drop of blood for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your health care provider.
You May Like: Where To Get A Hepatitis B Shot
How Hepatitis C Is Diagnosed
To determine a hepatitis C diagnosis, your doctor will:
- Get your medical history .
- Perform a physical exam, especially checking for changes in skin color, swelling in your lower extremities, and tenderness in your abdomen.
- Order certain diagnostic blood tests.
The first diagnostic tool in the screening process is a blood test that screens for HCV antibodies proteins the body produces in response to the virus. An enzyme immunoassay is used to perform this test.
A negative result for the antibody test means that you’ve never had HCV in your blood, while a positive result means you were exposed to the virus at some point in your life. Up to a quarter of people spontaneously clear the virus from their blood within six months of contracting it.
Because EIA sometimes produces false-positive results, a test called recombinant immunoblot assay may be used to confirm that you have the HCV antibody. This test is not necessary for most patients, and it is more commonly performed by blood banks to check for the virus in donated blood.
A negative EIA result may just mean that your body has not yet produced the HCV antibody , and you may need to be tested again in a few months.
If you have a positive antibody test, your doctor will then use another blood sample to conduct a qualitative polymerase chain reaction test or a process called transcription-mediated amplification , which looks for the presence or absence of RNA of HCV in your blood.
Specific Hcv Rna Assays And Range Of Detectable Virus
HCV RNA tests use target amplification techniques. Several assays exist for HCV RNA testing. Methods include polymerase chain reaction , transcription mediated amplification , and branched chain DNA tests. Results are expressed as international units/mL . The different methods and different commercial assays each have a lower limit of quantification and lower limit of detection , therefore a patient’s results could be reported differently depending on the assay used. HCV RNA tests must have an LLOQ of 25 IU/mL or lower when used to assess treatment response with DAAs.
LLOQ = the lowest HCV RNA level that is within the linear and analytically acceptable range of the assay.
LLOD = the lowest level of HCV RNA that is detected 95% of the time.
You May Like: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Hepatitis C
Appropriate Uses Of The Hcv Rna Test
There are 4 major reasons that HCV RNA tests are used:
More rarely, HCV RNA is used when either very acute HCV infection is suspected or a false HCV Ab is suspected.
It would not be appropriate to repeatedly order HCV RNA viral load screening for a patient who is not on or was recently on HCV treatment, or to use the HCV viral load to determine the severity of the patient’s infection or the patient’s risk of developing significant liver disease.
How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Several testing procedures are available to accurately diagnose hepatitis C infection.
Masterfile
Hepatitis C, an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus , often goes undiagnosed until serious liver problems develop decades after contracting the virus. This is because the illness is asymptomatic for most people, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
For these asymptomatic people, hepatitis C is generally detected when blood screenings show they are HCV-positive, or routine examinations show they have elevated levels of the liver enzyme alanine aminotransferase , an indication of liver cell damage.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Have A Cure
How Can I Tell If I Am Contagious And Can Spread The Infection To Others
If you have detectable HCV RNA in your blood, you have the potential to spread the disease to other people. Hepatitis C is spread by exposure to contaminated blood. The most common mechanism of exposure is the sharing of needles or other ‘works’ used in consuming drugs such as cocaine or heroin. Other routes of transmission include use of contaminated equipment for body piercing and tattooing, occupational exposure of healthcare workers to used needles or other sharp objects, and, less commonly, through sexual activity that results in tissue tears or from mother to baby during childbirth.
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: Early Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Hepatitis C Virus Is Diagnosed
Hepatitis C virus is usually diagnosed with blood tests. An antibody test can detect whether your body has had to fight off HCV infection. A blood test which measures the virus in your blood confirms the diagnosis, but results take longer. Sometimes, liver function tests, imaging studies, or a biopsy can support or confirm the diagnosis as well.
As of March 2020, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends HCV screening for all adults ages 18 to 79. The CDC also updated their guidelines in April 2020, recommending screening for all adults and pregnant women.
What Is The Treatment For Hcv
There are several drugs that can be used to treat HCV infection. Most commonly, a combination of drugs is used, and new drugs are under development. Before 2000, chronic HCV was curable in only 10% of cases. Now, treatments for HCV can cure over 90% of people with hepatitis C before late complications occur, but even those with advanced liver disease often respond to treatment. This increases the opportunity to intervene early and prevent HCV-associated deaths.
- According to the CDC, recent treatment guidelines recommend monitoring people with acute HCV but only considering treatment if the infection persists longer than 6 months.
- Chronic HCV is usually treated with a combination of drugs.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
Besides Hcv Testing What Other Tests Might Be Done
Healthcare practitioners may also order a liver panel, which is a group of tests that help assess the health of your liver. Liver tests such as ALT and AST may be used to detect ongoing liver injury. You will likely be checked to see if you are immune to hepatitis A and hepatitis B, and if not, you will be offered vaccination, since infection with these other viruses can further damage your liver. Other tests such as albumin, prothrombin time, and bilirubin can also be used. They are typically normal unless you have developed cirrhosis. Sometimes a liver biopsy may be performed to determine the severity of liver damage. If you are going to be treated, you will be checked for exposure or infection with hepatitis B virus, as HCV treatment can cause a flare-up of hepatitis B.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is swelling that happens when tissues of the body are injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
There are different types of hepatitis. One type, hepatitis C, is caused by the hepatitis C virus . Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness.
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis C is a short-term infection. The symptoms can last up to 6 months. Sometimes your body is able to fight off the infection and the virus goes away. But for most people, an acute infection leads to chronic infection.
- Chronic hepatitis C is a long-lasting infection. If it is not treated, it can last for a lifetime and cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis , liver cancer, and even death.
Recommended Reading: How Long Can Hepatitis C Live Outside The Body
What Are The Hepatitis C Testing Options For Infants
If you receive an HCV-positive result on an antibody test, it usually means youve been infected with HCV at some point. This also means your immune system has been triggered to fight the virus.
During the perinatal period and birth, a mothers antibodies and some viruses, including HCV, cross the placenta and are passed on to her child. Infants born to mothers infected by HCV often test positive for HCV antibodies for up to 18 months after birth. This doesnt necessarily mean that they have hepatitis C, though. HCV antibody tests are often inaccurate.
The antibodies present in the test may come from the infected mother and not the child. Because of this, its recommended that you hold off on getting an HCV antibody test for your child until after theyre at least 18 months old. By this point, any remaining antibodies from the mother should be out of the childs system. This means a more definitive result can be obtained.
HCV RNA-PCR tests are also used. Though HCV RNA-PCR tests are considered a more reliable way to detect the virus in the blood, a two-step approach is often recommended. To determine a diagnosis, your infant will be given two HCV RNA-PCR tests at least six months apart. This test can be done after 3 months of age, though it usually isnt done until later. If your infant tests positive on both, they will be diagnosed with HCV.