Is There A Hepatitis C Vaccine
There is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C infection. Researchers at Canadaâs University of Alberta, the U.K.âs Oxford University, and the University of Ulsan in South Korea are looking into it, and clinical trials are underway in the U.S.
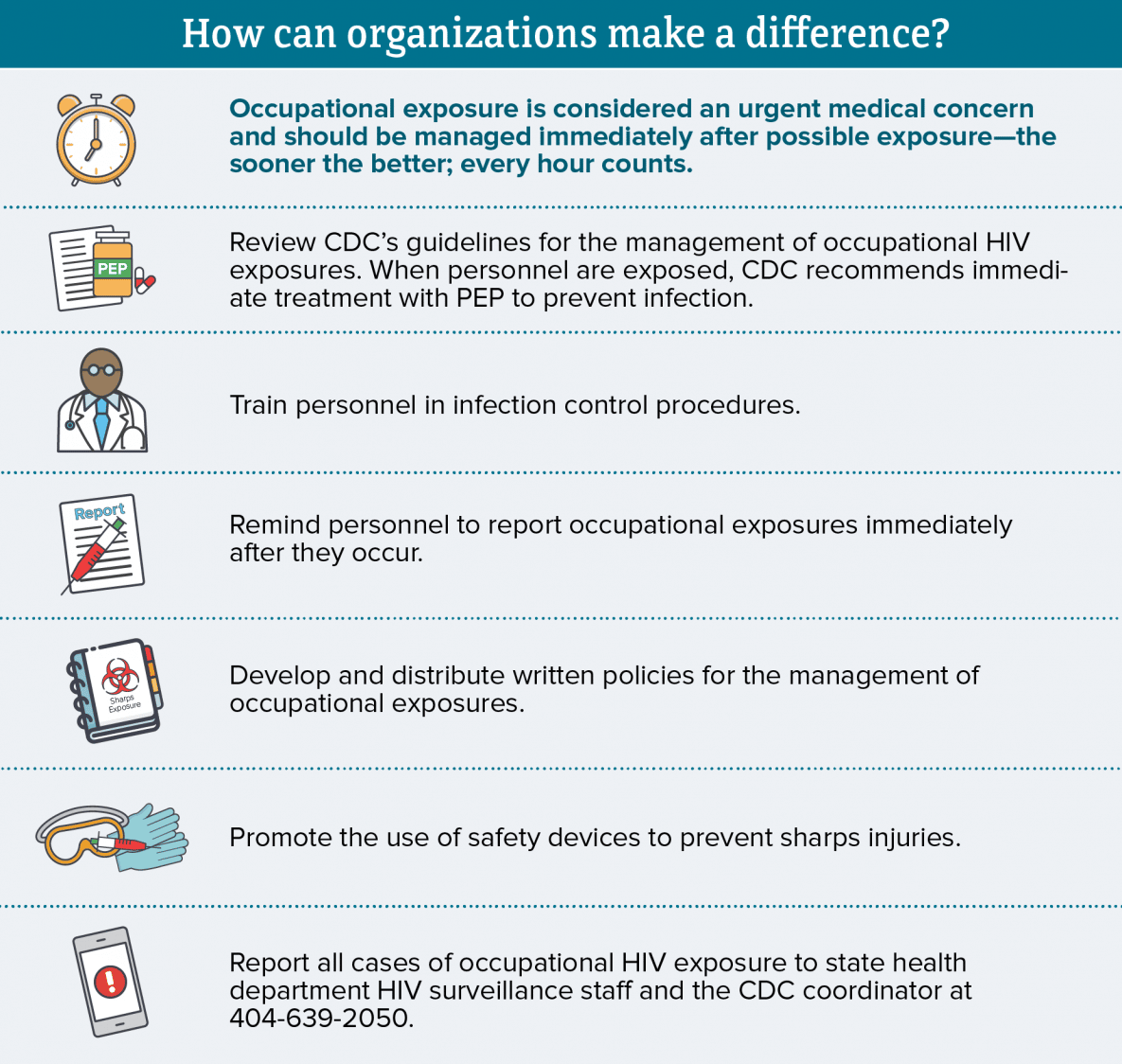
But if you have it, you should get vaccinated for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Show Sources
If You Have Hepatitis C Should You Get A Flu Shot
Yes. Having chronic hepatitis C is actually a good reason to get the flu shot. Chronic hepatitis C is a condition that can increase your risk of complications if you do get influenza. That’s why it is recommended for people with hepatitis C, and most chronic liver diseases, to be vaccinated against the flu.
To stay up to date with your influenza vaccinations, you need to be vaccinated every year–ideally, early in the flu season or as soon as the vaccine becomes available. Typically, flu season is considered to be October to March. It’s best to get vaccinated annually because the vaccine is designed differently each year to target the strains of influenza that are expected to circulate during that particular flu season.
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antibody
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Nurses Knowledge On Evidence

As expected, the degree of knowledge about the most common transmission routes of HCV was satisfactory in our sample, whereas less than half of nurses correctly recognized all modes of HCV transmission. As previously stated, our hypothesis was that several practice characteristics, such as years in practice, specific education programs provided at HDU and satisfaction with equipment at HDU, might be determinants of knowledge and that several aspects of knowledge might be associated to each other. Our findings have partly confirmed the hypothesis, since a lower number of years in practice is associated with higher knowledge and two out of three variables investigating knowledge were associated with our outcome variable on correct knowledge of all modes of transmission of HCV, whereas satisfaction with equipment at HDU and information about strategies to prevent HAI at the time of employment did not appear to be significant determinants of knowledge. This finding may be interpreted as a scarce effectiveness of information provided to HCWs in improving knowledge, or, since the mean years working in HDF was 11 years, information provided at the time of employment are no more relevant to discriminate knowledge of HCWs in our setting.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Worst Hepatitis
Standard Infection Control Precautions
A nurse who has contact with a hepatitis C patient needs only to maintain standard infection control precautions required for contact with any patient. Gowns and masks are generally not required gloves are required when drawing blood, starting IVs or handling any bodily fluids. Needles and other contaminated objects must be properly contained or disposed of. Nurses should wash their hands between patients, even if they wear gloves, and use a new pair of gloves for each patient. Blood spills should be cleaned with solutions of one part bleach to 10 parts water.
How Does Hepatitis C Progress
When someone is first infected with hepatitis C, most likely they have no symptoms and are unaware. Occasionally people experience fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness or sometimes having a yellow color in their skin or eyes. Although having any symptoms at all is rare, if they do occur, they usually go away within a few weeks.
Around 15-25% of people who are infected will spontaneously fight off the virus on their own and they will not have a chronic hepatitis C infection and no long term damage occurs.
But around 75-85% of people will develop chronic infection. Most of the time, people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms at the time of infection and no symptoms for years or even decades of chronic infection. The virus will be with them until they are successfully treated with hepatitis C medications.
Around 10-20% of people with chronic infection will slowly have gradual damage in the liver over years and will eventually develop cirrhosis . This can take 20 years or more from the time of the initial infection.
Cirrhosis is the replacement of liver cells with permanent scar tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to problems such as bleeding from veins in the esophagus, fluid buildup in the belly, and damaged brain function.Approximately 15% of people with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer during their lifetime. Drinking excessively can double the chance of liver cancer in people infected with HCV.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Are There Supplements That Are Good For My Liver
If a person eats a balanced diet, they will normally get enough vitamins and minerals. People with liver disease should avoid taking large amounts of supplements or “mega-vitamins.” This is because the liver has to do extra work to process them. Your provider may put you on a general multivitamin without iron.
Blood Donations Before September 1991
Since September 1991, all blood donated in the UK is checked for the hepatitis C virus.
There’s a small chance you may have been infected with hepatitis C if:
- you received a blood transfusion or blood products before September 1991
- you received an organ transplant before 1992
Before 1992 donated organs were not routinely screened for hepatitis C and there is a very small risk a donated organ from someone with hepatitis C could spread the infection.
There are blood tests to check for hepatitis C infection
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Hepatitis In Females
Spread Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is spread through blood-to-blood contact when blood from a person with hepatitis C enters another persons bloodstream.
The most common way people become infected with hepatitis C in Australia is by sharing injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, spoons and tourniquets. It is possible to be infected with hepatitis C after only one risk event.
Hepatitis C may also be spread through:
- tattooing and body piercing with equipment that has not been properly cleaned, disinfected or sterilised such as backyard tattoos’. Registered parlours with appropriate infection control procedures are not a risk
- needlestick injuries in a healthcare setting
- receiving blood transfusions in Australia prior to 1990 before hepatitis C virus testing of blood donations was introduced
- medical procedures, blood transfusions or blood products and mass immunisation programs provided in a country other than Australia
- pregnancy or childbirth there is a 5% chance of a mother with chronic hepatitis C infection passing on the virus to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Breastfeeding is safe, however if nipples are cracked or bleeding cease breastfeeding until they have healed.
Less likely possible routes of transmission of hepatitis C include:
Hepatitis C cannot be transmitted by:
- sharing food, cups or cutlery
- shaking hands or day-to-day physical contact.
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Hepatitis C Naturally
How Is Hepatitis C Spread Will My Loved Ones Catch It From Me
Household transmission of hepatitis C is extremely rare. Here are some ways the virus is transmitted:
The number one risk factor for infection and transmission is sharing needles for intravenous drug use. Most people who use IV drugs become infected with HCV within one year of sharing needles. Learn more.
Surgical And Anesthetic Concerns
Patients with liver disease are at particularly high risk for morbidity and mortality due to both the stress of surgery and the effects of general anesthesia. Decompensated liver disease increases the risk of postoperative complications . With cirrhosis, the reciprocal flow relation between the hepatic artery and the portal vein is not well maintained, and the liver architecture is disrupted by fibrosis and regenerative nodules. These pathologic alterations of the normal patterns of liver blood flow make the cirrhotic liver more prone to ischemia.12
Of all the inhaled anesthetics, halothane and enflurane appear to reduce hepatic artery blood flow the most because of systemic vasodilation and a mild negative inotropic effect.15 Halothane is also associated with the greatest risk of hepatotoxicity. Isoflurane is a safer choice than halothane in patients with liver disease because it may increase hepatic blood flow. Newer haloalkanes, such as sevoflurane and desflurane, also undergo less hepatic metabolism than halothane or enflurane. Atracurium has been recommended as the neuromuscular blocking agent of choice because it relies on neither the liver nor the kidneys for excretion. Likewise, drugs such as morphine, meperidine, benzodiazepines and barbiturates should be used with caution because of their dependence on the liver for metabolism.
Also Check: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
How Common Is Hepatitis C
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention think that 2.4 million Americans are infected with HCV. It is the most common infection carried by blood in the United States. Veterans have higher rates of hepatitis C than the rest of the country so it is especially important to discuss hepatitis C testing with your provider if you are a Veteran. But, Veterans are not the only ones with high rates of hepatitis C. Baby boomers have higher rates of hepatitis C than people in other age groups in the country as well. Often, people infected with hepatitis C are not aware of their infection because they have no symptoms and they do not feel ill so getting tested if you are at higher risk is important step.
What Are Genotypes And What Do They Mean
Viruses have genes, too. The genotype of virus you have can be one of six different groups, or genotypes. Most patients with hepatitis C in the United States have genotype 1a or 1b, but in other parts of the world, other genotypes are more common.
There isn’t a “better” or “worse” genotype to have. In the past , genotype 1 was the most difficult to successfully cure but this is no longer the case. All the new direct-acting antiviral medicines work extremely well in treating all genotypes. Sometimes genotype 3 is a little harder to cure, but in general, all genotypes now have extremely high likelihoods of being cured with hepatitis C treatment.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis B Antibody
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
During the acute phase most persons have no symptoms or might experience a mild illness. Symptoms of acute HCV infection, when present, may include:
- Dark-colored urine, light-colored stools
During the chronic phase hepatitis C usually progresses silently, with no symptoms at all during the first 10-20 years. Signs of severe liver scarring may include:
- Star-shaped vein pattern developing on the swollen belly
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Because symptoms of hepatitis C are usually absent, persons with risk for HCV infection should be tested. The blood test for hepatitis C infection is called the hepatitis C antibody test. People who have hepatitis C infection will show positive antibodies on this test. In many cases, it is necessary to confirm a positive hepatitis C antibody test with a more specific test, such as a test for HCV virus RNA.
If you think you have hepatitis C or have risk for hepatitis C, you should contact your doctor. The Communicable Disease Control Unit may be able to help answer your questions.
Assessment Of Infection Risk
The type of exposure should be reported , as should the body substance . The source person should be tested for the presence of HBsAg, HCV antibody and HIV antibody. If the source is unknown, the epidemiologic and clinical evidence should be assessed: namely, where and under what circumstances the exposure occurred and the prevalence of HBV, HCV or HIV in the population group.
Read Also: What To Do If You Have Hepatitis B
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatment
The direct acting antiviral regimens used to treat hepatitis C today are extremely well tolerated. You may experience mild side effects like headache or fatigue. For details on the side effects, review the handout specific to medication you take.
In rare instances, providers may recommend the addition of the medication ribavirin for more difficult cases of hepatitis C. Ribavirin may cause additional side effects such as fatigue, shortness of breath, cough, anemia, or rash. Patients who receive ribavirin may need more frequent monitoring for side effects as well as adjustment of the dose if side effects are experienced. For detailed information on ribavirin, patients should review the ribavirin handout.
Articles On Hepatitis C
If you’ve just been diagnosed with hepatitis C, you may wonder how you got it and worry about passing on the virus to a loved one. If you’ve had the disease for a long time without knowing it, you could dwell on every little incident in the past where you might have accidentally exposed a family member to the disease.
It’s important to remember that hepatitis C isn’t easy to catch. If you take a few precautions, it’s almost impossible to pass on the disease to someone else.
Read Also: Va Disability Rating For Hepatitis C
Prevention Of Hepatitis C
Exclusion from childcare, preschool, school and work is not necessary.
There is currently no vaccine for protection against hepatitis C virus infection. People with hepatitis C should ensure they are vaccinated against hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
There is no evidence that giving immunoglobulin after exposure to hepatitis C will prevent infection.
Infected health care workers must comply with the requirements of their professional boards.
Everyone has a responsibility to help prevent the spread of hepatitis C and to take care of themselves and others. This means:
For more information about Hepatitis C read the Get tested, get treated, eliminate Hepatitis C infographic.
It’s Different Than Hepatitis A And B
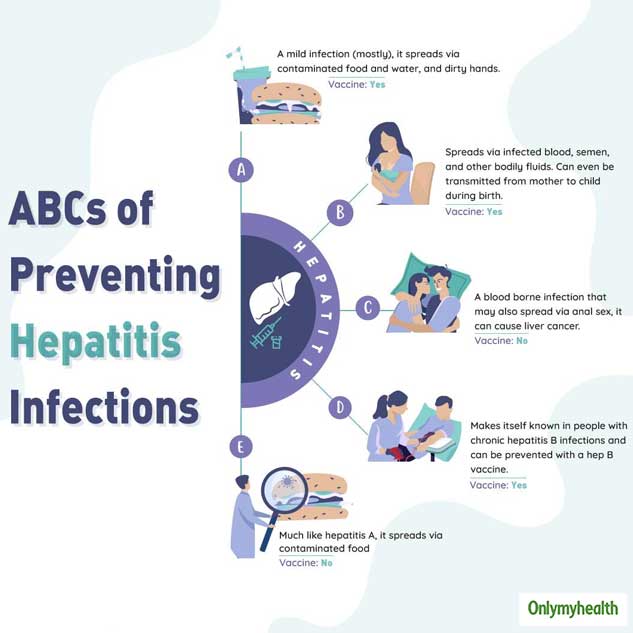
Each form of hepatitis has its own specific virus that spreads and is treated differently. “Hepatitis simply means inflammation of the liver, or that the virus has an affinity for hurting the liver,” Reau says.
- Hepatitis A is an acute, short-term infection that often does not require treatment.
- Hepatitis B hides deep in the body and, like hepatitis C, is treated in a variety of ways, from antiviral medications to liver transplants.
“The viruses are different, but all of them should be taken very seriously since they can lead to significant liver disease and even death,” she adds.
You May Like: Hepatitis A What Is It
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.